Carioca
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
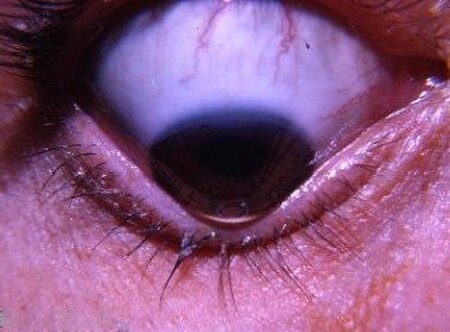
Medical condition involving the eye Not to be confused with Ketyconus. Medical conditionKeratoconusOther namesKC, KCN, conical cornea[1]The cone shaped cornea that is characteristic of keratoconusPronunciationKEHR-uh- toh-KOH-nus[2] SpecialtyOphthalmology, optometrySymptomsBlurry vision, nearsightedness, light sensitivity[3]Usual onsetEarly adulthood[3]CausesUnknown[3]Diagnostic methodSlit lamp exam[3]TreatmentGlasses, contacts, surgery[3&…

2011 film by Steven Spielberg War HorseTheatrical release posterDirected bySteven SpielbergScreenplay by Lee Hall Richard Curtis Based on War Horse (novel)by Michael Morpurgo War Horse (play)by Nick Stafford Produced by Steven Spielberg Kathleen Kennedy Starring Emily Watson David Thewlis Peter Mullan Niels Arestrup Jeremy Irvine CinematographyJanusz KamińskiEdited byMichael KahnMusic byJohn WilliamsProductioncompanies DreamWorks Pictures[1] Reliance Entertainment[1] Amblin Ente…

Ban asimetris Ban Asimetris adalah ban yang memiliki desain telapak yang tidak sama jarak antar kembangnya, jadi jarak antar kembangnya bisa saja berbeda-beda. Ban ini dibuat agar dapat mencengkram lebih baik pada kondisi jalan yang basah maupun kondisi jalan yang kering.[1] Referensi ^ http://www.tempointeraktif.com/hg/prototype/2009/08/05/brk,20090805-190917,id.html[pranala nonaktif permanen] Lihat pula Ban radial Ban tanpa tube Ban simetris Ban bias Artikel bertopik otomotif i…

Administrative entry restrictions A Montenegrin passport Visa requirements for Montenegrin citizens are administrative entry restrictions imposed by the authorities of foreign states on citizens of Montenegro. As of 2024, Montenegrin citizens had visa-free or visa on arrival access to 127 countries and territories, ranking the Montenegrin passport 46th in the world according to the Henley Passport Index.[1] Visa requirements map Visa requirements for Montenegrin citizens holding ordinary…

Institut national universitaire Jean-François-ChampollionHistoireFondation 2002StatutType Établissement d'enseignement supérieur (en)Forme juridique Établissement public national à caractère scientifique culturel et professionnel (d)Directrice Christelle FarencMembre de Toulouse Tech, université de Toulouse, Consortium universitaire de publications numériques CouperinSite web www.univ-jfc.frChiffres-clésÉtudiants 3 835 (2016)LocalisationPays FranceLocalisation Albimodifier - modif…
Penyuntingan Artikel oleh pengguna baru atau anonim untuk saat ini tidak diizinkan.Lihat kebijakan pelindungan dan log pelindungan untuk informasi selengkapnya. Jika Anda tidak dapat menyunting Artikel ini dan Anda ingin melakukannya, Anda dapat memohon permintaan penyuntingan, diskusikan perubahan yang ingin dilakukan di halaman pembicaraan, memohon untuk melepaskan pelindungan, masuk, atau buatlah sebuah akun. Kylian Mbappé [1] Mbappé dengan Paris Saint Germain pada 2019Informasi pri…

Ana y los lobosSutradaraCarlos SauraProduserElías QuerejetaDitulis olehCarlos SauraRafael AzconaPemeranGeraldine ChaplinFernando Fernán GómezRafaela AparicioPenata musikLuis de PabloSinematograferLuis CuadradoPenyuntingPablo González del AmoPerusahaanproduksiElías Querejeta Producciones Cinematográficas S.L.Tanggal rilis16 Juli 1973 (1973-07-16)Durasi102 menitNegara SpanyolBahasaSpanyol Ana y los lobos (Indonesia: Ana dan Serigalacode: id is deprecated ), juga dikenal sebagai An…

Frans Jeppsson WallJeppsson Wall pada tahun 2016Informasi latar belakangNama lahirFrans Jeppsson WallLahir19 Desember 1998 (umur 25)Ystad, Scania, SwediaGenrePopfolktronicaPekerjaanSingersongwriterInstrumenVokalTahun aktif2006–sekarangArtis terkaitElias Frans Jeppsson Wall (lahir 19 Desember 1998), yang lebih dikenal sebagai Frans, adalah seorang penyanyi dan penulis lagu Swedia. Ia memenangkan Melodifestivalen 2016 dan mewakili negara tuan rumah, Swedia, dalam Kontes Lagu Eurovision 2016…

Fast Fourier Transform algorithm The Cooley–Tukey algorithm, named after J. W. Cooley and John Tukey, is the most common fast Fourier transform (FFT) algorithm. It re-expresses the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of an arbitrary composite size N = N 1 N 2 {\displaystyle N=N_{1}N_{2}} in terms of N1 smaller DFTs of sizes N2, recursively, to reduce the computation time to O(N log N) for highly composite N (smooth numbers). Because of the algorithm's importance, specific variants and implementat…

Ir. H.Irfan Suryanagara Wakil Ketua DPRD Jawa BaratMasa jabatan22 Oktober 2014 – 1 September 2019Menjabat bersama Periode 2014–19 Irianto MS Syafiuddin Haris Yuliana Abdul Haris Bobihoe PresidenJoko WidodoGubernurAhmad HeryawanIwa Karniwa (Plt.)Mochammad Iriawan (Plt.)Ridwan Kamil PenggantiAchmad Ru'yatIneu Purwadewi SundariAde BarkahOleh SolehKetua DPRD Jawa BaratMasa jabatan16 Oktober 2009 – 31 Agustus 2014PresidenSusilo Bambang YudhoyonoGubernurAhmad Heryawan …

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Michaelmas (disambiguasi). Perayaan Santo Mikael, Gabriel, RafaelSanto Mikael Malaikat AgungDirayakan oleh Gereja Katolik Persekutuan Anglikan[1] Komunitas Steiner/Waldorf Lutheranisme Tanggal29 September (Gereja Barat)[2] 8 November (Gereja Timur)[3]Frekuensitahunan Michaelmas (/ˈmɪkəlməs/ mik-ƏL-məs; juga dikenal sebagai Perayaan Santo Mikael, Gabriel, dan Rafael, Perayaan Malaikat Agung, atau Perayaan Santo Mikael dan Seluruh Malaikat, …

Piala Raja Spanyol 1918Negara SpanyolJumlah peserta6Juara bertahanMadrid FCJuaraReal Unión(gelar ke-2)Tempat keduaMadrid FCJumlah pertandingan8Jumlah gol25 (3.13 per pertandingan)← 1917 1919 → Piala Raja Spanyol 1918 adalah edisi ke-16 dari penyelenggaraan Piala Raja Spanyol, turnamen sepak bola di Spanyol dengan sistem piala. Edisi ini dimenangkan oleh Real Unión setelah mengalahkan Madrid FC pada pertandingan final dengan skor 2–0. Final Artikel utama: Final Piala Raja Spanyol 191…

Heavy Rotation(ヘビーローテーション)Sampul Album Tipe A (berlatar kuning, tersedia dalam bentuk CD dan DVD) yang ditampilkan oleh (dari kiri ke kanan, atas ke bawah) Shania, Melody, Akicha, Haruka, Beby, Nabilah, Rena, Stella, Kinal, Veranda, Ayana, dan CigulAlbum studio karya JKT48Dirilis 16 Februari 2013 12 Juni 2013GenreJ-popDurasi41.58LabelIndonesia Musik NusantaraProduserYasushi AkimotoKronologi JKT48 -String Module Error: Match not foundString Module Error: Match not found He…

A Touch of ZenFilm posterSutradaraKing HuProduserJung-Feng ShaShiqing YangDitulis olehKing HuPemeranHsu FengShih JunPai YingRoy ChiaoTanggal rilisNovember 18, 1971 (Hong Kong)Durasi200 minNegara TaiwanBahasaTionghoaIMDbInformasi di IMDbAMGProfil All Movie Guide A Touch of Zen (Hanzi tradisional: 俠女; Hanzi: xiá nǚ) adalah sebuah wuxia film buatan tahun 1971 yang disutradari King Hu, dan dibuat di Taiwan. Film ini mendapatkan banyak pujian dan menjadi film aksi China pertama yang pernah …

Wakil Menteri Agama IndonesiaLogo Kementerian Agama IndonesiaBendera Kementerian Agama IndonesiaPetahanaSaiful Rahmat Dasukisejak 17 Juli 2023Kementerian Agama IndonesiaDitunjuk olehPresiden IndonesiaPejabat perdanaNasaruddin UmarDibentuk19 Oktober 2011; 12 tahun lalu (2011-10-19)Situs webkemenag.go.id Wakil Menteri Agama Indonesia, umumnya disingkat Wamenag adalah pembantu Menteri Agama Indonesia. Sejak 17 Juli 2023, Wakil Menteri Agama Indonesia dijabat oleh Saiful Rahmat Dasuki.[…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Anthus spinoletta Anthus spinoletta Anthus spinoletta spinolettaStatus konservasiRisiko rendahIUCN22718571 TaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumChordataKelasAvesOrdoPasseriformesFamiliMotacillidaeGenusAnthusSpesiesAnthus spinoletta (Linnaeus, 1758) Tata namaSin…

Roman Catholic diocese in the Philippines Diocese of DumagueteDioecesis DumaguetensisDiyosesis sa DumagueteCatholic Dumaguete CathedralCoat of armsLocationCountryPhilippinesTerritoryNegros Oriental (except Canlaon, Guihulngan City, Municipality of Vallehermoso, Municipality of La Libertad)SiquijorEcclesiastical provinceCebuCoordinates9°18′19.2″N 123°18′24.2″E / 9.305333°N 123.306722°E / 9.305333; 123.306722StatisticsArea4,955 km2 (1,913 sq mi)Po…

BaengnyeongdoNama KoreaHangul백령도 Hanja白翎島 Alih AksaraBaengnyeongdoMcCune–ReischauerPaengnyŏngdo Pulau Baengnyeong (kadang dieja Baekryeong; Pengucapan Korea: [pɛŋnjʌŋ-do]) adalah pulau sepanjang 458-kilometer-persegi (177 sq mi), 845 kilometer (525 mi) dan selebar 1.256 kilometer (780 mi) di County Ongjin, Incheon, Korea Selatan, di dekat Garis Batas Utara.[1] Berdasarkan Persetujuan Gencatan Senjata Korea 1953 yang mengakhiri Perang Korea, lim…

Abdul HamidLahirAbdoel Hamid(1948-12-03)3 Desember 1948Jakarta, IndonesiaMeninggal28 Desember 2022(2022-12-28) (umur 74)Bekasi, IndonesiaNama lainPak OgahTahun aktif1981–2022TelevisiSi UnyilSuami/istriYuyun Abdul Hamid (3 Desember 1948 – 28 Desember 2022) adalah pemeran dan pengisi suara Pak Ogah dalam serial Si Unyil.[1] Pak Ogah terkenal karena perannya sebagai pengangguran pemalas di Si Unyil. Karakternya menjadi populer dan menjadi ikon di kalangan an…

Astro BoyPoster rilisSutradaraDavid BowersProduserMaryann GargerDitulis olehOsamu Tezuka (manga) Timothy Harris (screenplay)PemeranFreddie Highmore Nicolas Cage Donald Sutherland Kristen Bell Eugene Levy Nathan Lane Bill Nighy Madeline Carroll Matt LucasPenata musikJohn OttmanPenyuntingRobert Anich ColePerusahaanproduksiImagi Animation Studios[1]DistributorSummit Entertainment (AS) Hoyts Distribution (Australia) E1 Entertainment (UK) Kadokawa Pictures (Jepang)Tanggal rilis10 Oktobe…
