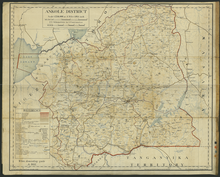
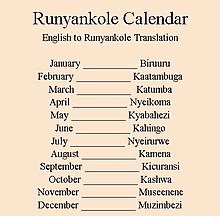
Ankole
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Disambiguazione ‚Äì Antonio da Padova rimanda qui. Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Antonio da Padova (disambigua). Sant'Antonio di PadovaSant'Antonio da Padova col Bambino (Guercino) Religioso e Dottore della Chiesa NascitaLisbona, 15 agosto 1195 MortePadova, 13 giugno 1231 (35 anni) Venerato daChiesa cattolica CanonizzazioneSpoleto, 30 maggio 1232 da papa Gregorio IX Santuario principaleBasilica di Sant'Antonio di Padova Ricorrenza13 giugno AttributiLibro, pesce…

Polytechnic in Ibadan, Nigeria The Polytechnic, IbadanIse loogun iseTypePublic polytechnicEstablished1970RectorProf. Kazeem A. AdebiyiLocationIbadan, NigeriaCampusUrbanWebsitewww.polyibadan.edu.ng The Polytechnic, Ibadan Entrance Gate The Polytechnic, Ibadan Exit Gate The Polytechnic, Ibadan The Polytechnic, Ibadan (also called Poly Ibadan) is an institution of higher learning in Ibadan in Oyo State, Nigeria.[1] Founded on August 1970, Poly Ibadan is similar to other polytechnics in Nige…

Bhagwaan DadaPosterSutradaraJ. Om PrakashProduserRakesh RoshanDitulis olehRahi Masoom Reza (cerita)Ramesh Pant (skenario & dialog)PemeranRakesh RoshanDanny DenzongpaRajinikanthSrideviPenata musikRajesh Roshan (komponis)Indivar (lirik)Farooq KaiserSinematograferPushpal DuttaPenyuntingNand KumarTanggal rilis 25 April 1986 (1986-04-25) BahasaHindiPendapatankotor‚Çπ4.1 juta Bhagwaan Dada adalah sebuah film fitur berbahasa Hindi India tahun 1986 garapan J. Om Prakash. Film tersebu…

Halaman ini memuat daftar penyanyi country. Daftar ini tidak dimaksudkan sebagai suatu daftar yang lengkap atau selalu terbarui. Jika Anda melihat artikel yang seharusnya tercantum di sini, silakan sunting halaman ini dan tambahkan pranala ke artikel tersebut. Gunakan perubahan terkait untuk melihat perubahan terbaru dari artikel-artikel yang tercantum pada halaman ini. Daftar isi A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0-9 3 of Hearts 4 Runner 8 Ball Aitken A Gene Autry ca. 1940s Ed…

Artikel atau sebagian dari artikel ini mungkin diterjemahkan dari 55 Cancri e di en.wikipedia.org. Isinya masih belum akurat, karena bagian yang diterjemahkan masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Jika Anda menguasai bahasa aslinya, harap pertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menyempurnakan terjemahan ini. Anda juga dapat ikut bergotong royong pada ProyekWiki Perbaikan Terjemahan. (Pesan ini dapat dihapus jika terjemahan dirasa sudah cukup tepat. Lihat pula: panduan penerjemahan ar…

Adi Winarso Wali Kota Tegal ke-15Masa jabatan23 Maret 1999 ‚Äì 23 Maret 2009PresidenB.J. HabibieAbdurrahman WahidMegawati SukarnoputriSusilo Bambang YudhoyonoGubernurMardiyantoBibit WaluyoWakilDr. Maufur, M.Pd. PendahuluMuhammad ZakirPenggantiIkmal Jaya Informasi pribadiLahir(1950-12-11)11 Desember 1950Panggang, Jepara, Jepara, Jawa TengahMeninggal8 September 2023(2023-09-08) (umur 72)Surabaya, Jawa TimurAlma materAkademi Angkatan Laut (1974)Karier militerPihak IndonesiaDi…

Multi-parasport event in Tokyo, Japan II Paralympic GamesHost cityTokyo, JapanNations21Athletes375Events144 in 9 sportsOpening3 NovemberClosing12 NovemberOpened byCrown Prince AkihitoStadiumOda Field← Rome 1960Tel Aviv 1968 → 1964 Summer Olympics The 1964 Summer Paralympics (Japanese: 1964Âπ¥Â§èÂ≠£„Éë„É©„É™„É≥„Éî„ÉÉ„ÇØ, Hepburn: 1964-Nen Kaki Pararinpikku), originally known as the 13th International Stoke Mandeville Games and also known as Paralympic Tokyo 1964,[1] …

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento Microbiologia √® priva o carente di note e riferimenti bibliografici puntuali. Sebbene vi siano una bibliografia e/o dei collegamenti esterni, manca la contestualizzazione delle fonti con note a pi√® di pagina o altri riferimenti precisi che indichino puntualmente la provenienza delle informazioni. Puoi migliorare questa voce citando le fonti pi√π precisamente. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Le informazioni riportate non sono consigli …

Bakal JuluDesaKantor Kepala Desa Bakal JuluNegara IndonesiaProvinsiSumatera UtaraKabupatenDairiKecamatanSiempat Nempu HuluKode pos22254Kode Kemendagri12.11.07.2011 Luas... km¬≤Jumlah penduduk... jiwaKepadatan... jiwa/km¬≤ Bakal Julu merupakan salah satu desa yang ada di kecamatan Siempat Nempu Hulu, Kabupaten Dairi, provinsi Sumatera Utara, Indonesia. Pemerintahan Desa Bakal Julu terdiri dari Dusun Bakal Julu, Jumagunung, Namontrep I, Namontrep II, dan dusun lainnya. Galeri Gapura selamat d…

Genus of fishes Botia Botia striata Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Actinopterygii Order: Cypriniformes Family: Botiidae Genus: BotiaJ. E. Gray, 1831 Type species Botia almorhaeGray 1831 Species See text Synonyms Hymenphysa Botia (Indian loaches) is a genus of freshwater fish in the loach family (Botiidae). It was a large genus with about 20 species. In 2004 Maurice Kottelat proposed in his paper (along with the description of Botia kubotai, …

2002 American animated short film by Eric Armstrong The ChubbChubbs!PosterDirected byEric ArmstrongWritten byJeff WolvertonProduced byJacquie BarnbookStarringBradford SimonsenJeff WolvertonEric ArmstrongMortonette JenkinsPeter LurieRick ZieffEdited byRobert GordonMusic byChance ThomasProductioncompanies Columbia Pictures Sony Pictures Imageworks Distributed bySony Pictures ReleasingRelease date July 3, 2002 (2002-07-03) (with Men in Black II) Running time5 minutesCountryUnited…

1998 agreements between the United Kingdom and Ireland British‚ÄìIrish Agreement redirects here. For the 1921 treaty, see Anglo-Irish Treaty. For the 1985 treaty, see Anglo-Irish Agreement. Multi-Party AgreementTypeMultilateral agreementSigned10 April 1998 (1998-04-10)LocationBelfast, Northern IrelandEffective2 December 1999 (1999-12-02)PartiesGovernment of the Republic of IrelandGovernment of the United KingdomParties in Northern IrelandLanguageEnglish British‚ÄìIr…

Bendera dan logo The Southeast Asian Games Federation Pesta Olahraga Semenanjung Asia Tenggara (bahasa Inggris: Southeast Asian Peninsular Games) atau sering disingkat SEAP Games adalah cikal bakal Pesta Olahraga Asia Tenggara (SEA Games). Acara ini pertama kali dicetuskan oleh Laung Sukhumnaipradit dari Thailand. SEAP Games mula-mula diikuti oleh Thailand, Burma (sekarang Myanmar), Malaysia, Laos, Vietnam dan Kamboja (dengan Singapura ikut kemudian). Para pelopor itu pun setuju menyelenggarakan…

Ini adalah nama Melayu; nama Yacob merupakan patronimik, bukan nama keluarga, dan tokoh ini dipanggil menggunakan nama depannya, Halimah. Halimah YacobNama dalam bahasa asli(ms) Halimah Binti Yacob / ÿ≠ÿߟџäŸÖŸá ÿ®ŸÜÿ™ Ÿäÿß(zh) ÂìàËéâÁéõ¬∑ÈõÖÂêÑÂ∏É(ta) ýÆπýÆ≤ýÆøýÆÆýÆæ ýÆ™ýÆøýÆ©ýØçýƧýÆø ýÆØýÆæýÆïýØäýÆ™ýØç BiografiKelahiran23 Agustus 1954 (69 tahun)Singapura 8a Presiden Singapura 14 September 2017 ‚Äì 13 September 2023 ← Tony Tan Keng Yam ‚Äì Tharman Shanmugaratna…

ŸäŸÅÿ™ŸÇÿ± ŸÖÿ≠ÿ™ŸàŸâ Ÿáÿ∞Ÿá ÿߟџ֟ÇÿߟÑÿ© ÿ•ŸÑŸâ ÿߟÑÿßÿ≥ÿ™ÿ¥ŸáÿßÿØ ÿ®ŸÖÿµÿßÿØÿ±. ŸÅÿ∂ŸÑÿߟãÿå ÿ≥ÿߟáŸÖ ŸÅŸä ÿ™ÿ∑ŸàŸäÿ± Ÿáÿ∞Ÿá ÿߟџ֟ÇÿߟÑÿ© ŸÖŸÜ ÿÆŸÑÿßŸÑ ÿ•ÿ∂ÿߟÅÿ© ŸÖÿµÿßÿØÿ± ŸÖŸàÿ´ŸàŸÇ ÿ®Ÿáÿß. ÿ£Ÿä ŸÖÿπŸÑŸàŸÖÿßÿ™ ÿ∫Ÿäÿ± ŸÖŸàÿ´ŸÇÿ© ŸäŸÖŸÉŸÜ ÿߟÑÿ™ÿ¥ŸÉŸäŸÉ ÿ®Ÿáÿß Ÿàÿ•ÿ≤ÿߟÑÿ™Ÿáÿß. (ŸÖÿßÿ±ÿ≥ 2016) ÿ±Ÿàÿ≥Ÿäÿß ÿߟÑÿ®Ÿäÿ∂ÿßÿ° ŸÖÿπŸÑŸàŸÖÿßÿ™ ÿπÿߟÖÿ© ÿ®ŸÑÿØ ÿߟÑÿ±Ÿäÿßÿ∂ÿ© ÿ®ŸäŸÑÿßÿ±Ÿàÿ≥ ÿߟџÅÿ¶ÿ© ŸÉÿ±ÿ© ÿߟџÇÿØŸÖ ŸÑŸÑÿ≥ŸäÿØÿßÿ™ ÿ±ŸÖÿ≤ ÿߟџşäŸÅÿß BLR ÿߟÑÿßÿ™ÿ≠ÿßÿØ ÿßÿ™ÿ≠ÿßÿØ…

Ken AnneLahirKen Anne Kartika Sari7 Maret 1994 (umur 30) Semarang, IndonesiaKebangsaan IndonesiaPekerjaanPembawa beritaTahun aktif2017-sekarang Ken Anne Kartika Suri (lahir 7 Maret 1994) merupakan seorang pembawa acara berita Indonesia. Sejak tahun 2016, dia memulai karirnya di Kompas TV Jawa Tengah. Pada tahun 2017, dia bekerja di tvOne. Pada tahun 2018, dia mendapat tugas untuk meliput gizi buruk di Asmat, Papua. Ken adalah lulusan Universitas Diponegoro Fakultas Ilmu Sosial dan…

Disused railway station in Blackhall Colliery, County Durham Blackhall RocksThe northern end of the site of the station in 1970.General informationLocationBlackhall Rocks, County DurhamEnglandCoordinates54¬∞44‚Ä≤34‚Ä≥N 1¬∞16‚Ä≤34‚Ä≥W / 54.7429¬∞N 1.2761¬∞W / 54.7429; -1.2761Grid referenceNZ467389Platforms2Other informationStatusDisusedHistoryOriginal companyNorth Eastern RailwayPre-groupingNorth Eastern RailwayPost-groupingLondon and North Eastern RailwayBritish Railways …

ŸÑŸÖÿπÿߟܟç ÿ£ÿÆÿ±Ÿâÿå ÿ∑ÿߟÑÿπ ÿ¨ŸÅÿ±ÿ≥ŸàŸÜŸÅŸäŸÑ (ÿ™Ÿàÿ∂Ÿäÿ≠). ÿ¨ŸÅÿ±ÿ≥ŸàŸÜŸÅŸäŸÑ ÿߟÑÿ•ÿ≠ÿØÿßÿ´Ÿäÿßÿ™ 41¬∞46‚Ä≤50‚Ä≥N 74¬∞55‚Ä≤56‚Ä≥W / 41.7806¬∞N 74.9322¬∞W / 41.7806; -74.9322 [1] ÿ™ŸÇÿ≥ŸäŸÖ ÿ•ÿØÿßÿ±Ÿä ÿߟÑÿ®ŸÑÿØ ÿߟџàŸÑÿߟäÿßÿ™ ÿߟџÖÿ™ÿ≠ÿØÿ©[2] ÿߟÑÿ™ŸÇÿ≥ŸäŸÖ ÿߟÑÿ£ÿπŸÑŸâ ŸÖŸÇÿßÿ∑ÿπÿ© ÿ≥ŸàŸÑŸäŸÅÿßŸÜ ÿÆÿµÿßÿ¶ÿµ ÿ¨ÿ∫ÿ±ÿߟşäÿ© ÿߟџÖÿ≥ÿßÿ≠ÿ© 1.14184 ŸÉŸäŸÑŸàŸÖÿ™ÿ± ŸÖÿ±ÿ®ÿπ1.13437 ŸÉŸäŸÑŸàŸÖÿ™ÿ± ŸÖÿ±ÿ…

Depression formed by a sinking or collapse of the surface lying above a void or empty chamber Kilauea with Halema ªuma ªu Deep pit crater on Hualalai Hawaii A pit crater (also called a subsidence crater or collapse crater) is a depression formed by a sinking or collapse of the surface lying above a void or empty chamber, rather than by the eruption of a volcano or lava vent.[1] Pit craters are found on Mercury, Venus,[2][3] Earth, Mars,[4] and the Moon.[5]…

Pangeran George, Adipati Cambridge (George William Frederick Charles; 26 Maret 1819 ‚Äì 17 Maret 1904) adalah anggota Keluarga kerajaan Inggris, cucu dari Raja George III dan sepupu dari Ratu Victoria. Dia berprofesi sebagai perwira militer dan melayani sebagai Panglima Angkatan Militer dari 1856 hingga 1895. Dia menjadi Adipati Cambridge pada 1850 dan marsekal lapangan pada 1862. Sangat mencintai Angkatan Darat yang lama, dia bekerja dengan Ratu Victoria untuk mengalahkan dan meminimalisir seti…