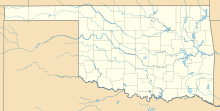
Antelope Hills expedition
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Arena Ski Tateyama Sanroku Gokurakuzaka, Jepang. Olahraga musim dingin adalah olahraga yang umum dimainkan selama musim dingin. Istilah ini dipakai untuk olahraga yang dilakukan di udara terbuka pada permukaan salju atau es.[1] Olahraga musim dingin yang umum dikenal, misalnya: ski, hoki es, dan skating indah. Daftar olahraga musim dingin Biatlon, kombinasi ski dan menembak. Catatan: olahraga Olimpiade Musim Dingin diberi tanda asteris. Skating es Artikel utama: Skating es Skating indah …

Logo perusahaan Bruno Senna mengemudikan mobil Formula Tiga Dallara F304 dalam balapan pendukung Grand Prix Australia 2006 Dallara Automobili adalah manufaktur sasis dari Italia untuk berbagai macam balap mobil, tetapi lebih dikenal karena hampir memonopoli Formula 3 sejak tahun 1993. Dallara juga memproduksi sasis yang digunakan di dalam IndyCar Series, Indy Lights, Grand-Am Rolex Sports Car Series, GP2 Series (sekarang Kejuaraan FIA Formula 2), World Series by Renault, GP3 Series (sekarang Kej…
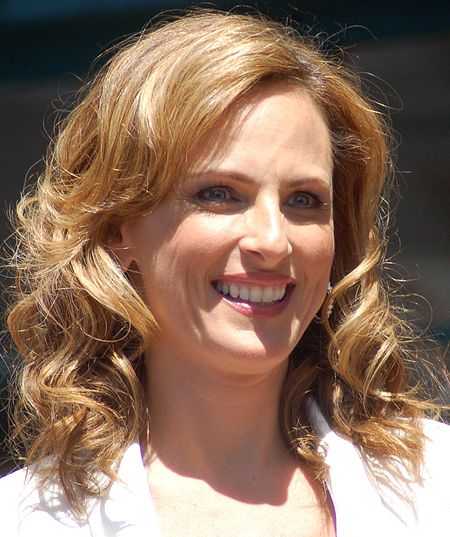

Marlee MatlinMarlee Matlin menerima Motion Pictures Star di Hollywood Walk of Fame tahun 2009Lahir24 Agustus 1965 (umur 58)Morton Grove, Illinois, Amerika SerikatPekerjaanAktris, penulis, aktivisTahun aktif1986–sekarangSuami/istriKevin Grandalski (m. 1993)Anak4Situs webmarleematlinsite.com Marlee Beth Matlin (lahir 24 Agustus 1965) merupakan seorang aktris, penulis dan aktivis berkebangsaan Amerika Serikat yang memenangkan nominasi Academy Award. Ia ber…

Goebbels visita la mostra Arte degenerata allestita a Monaco di Baviera nel 1937 Arte degenerata (in tedesco entartete Kunst) è un termine che nel contesto della Germania del regime nazista indicava quelle forme d'arte che riflettevano valori o estetiche contrarie alle concezioni naziste, le quali si opponevano a molte forme di arte contemporanea, nell'intento di conservare i valori della razza ariana e della sua tradizione culturale. Indice 1 Origine del concetto 2 Le mostre naziste 3 La colle…

John Leslie Breck, oleh James Carroll Beckwith. John Leslie Breck (1859–1899) adalah seorang seniman Amerika yang meninggal pada usia 39 tahun. Selama hidupnya yang singkat, ia melukis sejumlah karya terkenal, dan dikreditkan dengan memperkenalkan Impresionisme ke Amerika Serikat dengan sebuah pertunjukan di Boston pada tahun 1890. Ia meninggal pada tahun 1899 , dilaporkan sebagai kematian karena keracunan gas, dan dikebumikan di Pemakaman Forest Hills di Boston. Karya-karyanya tetap di sejuml…

S. K. Das Hakim Mahkamah Agung IndiaMasa jabatan30-04-1956–02-09-1963 Informasi pribadiKebangsaanIndiaProfesiHakimSunting kotak info • L • B S. K. Das adalah hakim Mahkamah Agung India. Ia mulai menjabat sebagai hakim di mahkamah tersebut pada 30-04-1956. Masa baktinya sebagai hakim berakhir pada 02-09-1963.[1] Referensi ^ Daftar Hakim di Mahkamah Agung India. Mahkamah Agung India. Diakses tanggal 10 Juni 2021. Artikel bertopik biografi India ini adalah sebuah rinti…

Квітконіжка Будова квітки Квітконіжка (лат. pedicellus) — розгалуження стебла або бічний квітконосний пагін (який розвивається у пазусі листка); частина квітконоса у суцвітті, що несе на собі поодиноку квітку[1]. Більше або менше відрізняється від тих частин стебла, що не�…

Reproduksi uang kertas, mungkin Jiaozi, zaman Dinasti Song, dapat ditukarkan dengan 770 mò. Jiaozi (Hanzi: 交子; Pinyin: jiāozǐ) adalah semacam Surat sanggup bayar yang muncul sekitar abad ke-11 di kota Chengdu, ibu kota provinsi Sichuan, Tiongkok. Numismatis menganggapnya sebagai uang kertas pertama dalam sejarah, suatu perkembangan masyarakat Tiongkok di masa Dinasti Song (960-1279 M). Uang kertas Jiaozi awalnya tidak memiliki denominasi standar tetapi didenominasi sesuai dengan k…

This article is about the 2018 science fiction film. For the 1950 German documentary film, see The Titan: Story of Michelangelo. For other uses, see Titan. 2018 filmThe TitanOfficial release posterDirected byLennart RuffScreenplay byMax HurwitzStory byArash AmelProduced by Arash Amel Fred Berger Leon Clarance Brian Kavanaugh-Jones Ben Pugh Starring Sam Worthington Taylor Schilling Tom Wilkinson Agyness Deyn Nathalie Emmanuel Corey Johnson Aleksandar Jovanovic Diego Boneta CinematographyJan-Marce…

Australian Idol is an Australian talent reality television series that first aired in 2003. As of December 2008, there have been six seasons. During every season, the final round of competition features twelve singers, except for season three when it had thirteen finalists. A total of 73 contestants have reached the finals of their season. The show's age requirements only allow people to enter if they are between 16 and 29 years of age. Out of the 73 contestants listed, 19 of them were under the…

Vincent van Gogh adalah pelukis pasca-impresionis Belanda yang merupakan salah satu pelukis terbesar dalam sejarah seni Eropa. Berikut lukisan-lukisan yang dibuat oleh Vincent van Gogh dengan judul dalam bahasa Indonesia. Lukisan Jalan setapak di taman Di ambang kekekalan Augustine Roulin dengan bayinya Petani dengan pekerjaannya Gubuk petani di Auvers Batang pohon Pemandangan desa pada waktu subuh Pemandangan Arles Pemandangan Arles dengan bunga lili Pemandangan Montmartre Pohon yang berbunga P…

Fredrik Stoor Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Fredrik Olof Esaias Stoor[1]Tanggal lahir 28 Februari 1984 (umur 40)Tempat lahir Stockholm, SwediaTinggi 1,83 m (6 ft 0 in)Posisi bermain Bek kananInformasi klubKlub saat ini LillestrømNomor 27Karier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2002–2006 Hammarby 51 (2)2006–2008 Rosenborg 30 (0)2008–2011 Fulham 4 (0)2009 → Derby County (pinjaman) 11 (0)2011– Vålerenga 15 (0)2012– → Lillestrøm (pinjaman) 1 (0)Tim nasional‡…

Masa Depan Cerah Björt framtíðKetuaKosong[1]Dibentuk4 Februari 2012[2]Dibubarkan2019IdeologiLiberalismeLiberalisme sosial[3]Pro-EropanismePosisi politikTengahAfiliasi EropaAlliance of Liberals and Democrats for EuropeWarnaUngu, putihLambang pemiluASitus webwww.bjortframtid.is Masa Depan Cerah (Islandia: Björt framtíðcode: is is deprecated ) adalah partai politik berhaluan liberal[4] di Islandia yang didirikan pada tahun 2012. Partai ini merupakan anggot…

Mohammed Abdellaoue Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Mohammed AbdellaoueTanggal lahir 23 Oktober 1985 (umur 38)Tempat lahir Oslo, NorwegiaTinggi 1,82 m (5 ft 11+1⁄2 in)Posisi bermain PenyerangInformasi klubKlub saat ini VålerengaKarier junior1997–2000 Hasle-Løren2001–2003 SkeidKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2003–2007 Skeid 86 (40)2008–2010 Vålerenga 67 (30)2010–2013 Hannover 96 80 (29)2013–2015 VfB Stuttgart 12 (1)2015 VfB Stuttgart II 4 (0)2015– Vål…

Beringin Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae Divisi: Magnoliophyta Kelas: Magnoliopsida Ordo: Urticales Famili: Moraceae Genus: Ficus Subgenus: Conosycea Spesies: F. benjamina Nama binomial Ficus benjaminaL. 1767[1] Peta persebaran spesies Ficus benjamina. Sinonim[1] Sinonim Ficus benjamina var. bracteata Corner Ficus benjamina var comosa (Roxb.) Kurz Ficus benjamina subsp. comosa (Roxb.) Panigrahi & Murti Ficus benjamina var. comosa King Ficus benjamina var. haematocar…

Kembang PerawanSutradaraJoko NugrohoPemeranAdly FayruzIndah KalaloRyana DeaOlivia Lubis JensenMarrio MerdhitiaKris AnjarDimas AnggaraTiti QadarsihAgung UdijanaDistributorFrame Ritz PictureTanggal rilis22 Oktober 2009Durasi... menitNegaraIndonesia Kembang Perawan adalah film Indonesia yang dirilis pada 22 Oktober 2009 dengan disutradarai oleh Joko Nugroho dan dibintangi oleh Adly Fayruz, Ryana Dea, Indah Kalalo, Olivia Lubis Jensen, Marrio Merdhitia, Kris Anjar, Dimas Anggara, Titi Qadarsih dan A…

Untuk kapal lain dengan nama serupa, lihat Kapal perusak Jepang Isonami. Isonami Sejarah Kekaisaran Jepang Nama IsonamiAsal nama Kapal perusak Jepang Isonami (1908)Dipesan 1923 (Tahun Fiskal)Pembangun Perusahaan Dok UragaNomor galangan Perusak No. 43Pasang lunas 19 Oktober 1926Diluncurkan 24 November 1927Mulai berlayar 30 Juni 1928Dicoret 1 Agustus 1943Nasib Tenggelam pada 9 April 1943 Ciri-ciri umum Kelas dan jenis Kapal perusak kelas-FubukiBerat benaman 1.750 ton panjang (1.780 …

Butterfly World TourTur oleh Mariah CareyButterflyMulai11 Januari 1998 (1998-01-11)Berakhir21 Februari 1998 (1998-02-21)Putaran3Penampilan5 di Asia6 di Australia1 di Amerika UtaraTotal 12Kronologi konser Mariah Carey Daydream World Tour(1996) Butterfly World Tour(1998) Rainbow World Tour(2000) Butterfly World Tour adalah tur konser ketiga oleh penyanyi asal Amerika, Mariah Carey. Tur dimulai pada tanggal 11 Januari 1998. Sepanjang tur, Mariah Carey melakukan gaya yang variasi untuk ram…

Salah satu slogan Boikot barang-barang Tiongkok dari gerakan Tibet merdeka di Internet. Boikot produk-produk Tiongkok (Boikot Made in China atau berhenti menggunakan produk-produk Tiongkok, berhenti membeli barang-barang Tiongkok) adalah sebuah slogan populer di Internet yang dibuat untuk kampanye sampai pemboikotan produk-produk Tiongkok di berbagai negara. Umumnya alasan yang dikutip untuk pemboikotan tersebut adalah kualitas yang dianggap rendah dari produk tersebut dan konflik wilayah.[1…

Bagian dari seriGereja Katolik menurut negara Afrika Afrika Selatan Afrika Tengah Aljazair Angola Benin Botswana Burkina Faso Burundi Chad Eritrea Eswatini Etiopia Gabon Gambia Ghana Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guinea Khatulistiwa Jibuti Kamerun Kenya Komoro Lesotho Liberia Libya Madagaskar Malawi Mali Maroko Mauritania Mauritius Mesir Mozambik Namibia Niger Nigeria Pantai Gading Republik Demokratik Kongo Republik Kongo Rwanda Sao Tome dan Principe Senegal Seychelles Sierra Leone Somalia Somaliland Sud…