Central Railroad of New Jersey
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang negara di Amerika Utara. Untuk bahasa di India, lihat Bahasa Kannada. KanadaCanada (Inggris dan Prancis) Bendera Lambang Semboyan: A mari usque ad mare (Latin)Dari Laut ke LautLagu kebangsaan: O Canada (Oh Kanada) Lagu kerajaan: God Save the King (Tuhan Jaga sang Raja) Perlihatkan BumiPerlihatkan peta BenderaIbu kotaOttawa45°24′N 75°40′W / 45.400°N 75.667°W / 45.400; -75.667Kota terbesarToronto 45°42′N 79°24�…

Gerbang Kuil Fawang Pagoda Kuil Fawang Kuil Fawang (Hanzi: 法王寺) adalah kuil Buddha Tiongkok yang terletak 5 km (3,1 mi) di barat laut kota Dengfeng, Provinsi Henan, Tiongkok. Kuil ini berada di kaki Puncak Yuzhu, salah satu puncak yang ada di Gunung Song. Kuil Fawang memiliki Pagoda Tiongkok yang dibangun selama Dinasti Tang (618–907). Pagoda ini merupakan pagoda yang paling menonjol di awal era Tang, menaranya berbentuk persegi terbuat dari batu setinggi 40 m (131…

Badan Informasi Geospasial BIGGambaran umumDasar hukumPeraturan Presiden Nomor 94 Tahun 2011KepalaProf. Dr.rer.nat. Muh Aris Marfai, M.Sc.[1]Sekretaris UtamaDr. Ir. RA. Belinda Arunarwati Margono, M.Sc.DeputiDeputi Bidang Informasi Geospasial DasarIr. Mohamad Arief Syafi'i, M.Eng.Sc.Deputi Bidang Informasi Geospasial TematikDr. Antonius Bambang WijanartoDeputi Bidang Infrastruktur Informasi GeospasialDr. Ibnu Sofian, M.Eng.InspekturHabib Subagio, S.Si., M.Si.Kantor pusatJl.Raya Jaka…

Laima Balaišytė (Amelin)Balaišytė-Amelina (1971)Informasi pribadiKewarganegaraan LituaniaLahir03 Januari 1948 (umur 76)VilniusPasanganAnatoly Amelin Rekam medali Putri Tenis Meja Mewakili Uni Soviet Kejuaraan Tenis Meja Dunia 1967 Stockholm Women's team 1969 Munich Women's team Laima Balaišytė (nama lain Laima Amelin; lahir 3 Januari 1948) adalah mantan pemain tenis meja putri asal Lithuania. Karier tenis meja Dia memenangkan medali perak di Kejuaraan Tenis Meja Dunia 1967 …

Monumen Pembebasan Irian BaratMonumen Pembebasan Irian Barat di Lapangan Banteng.LetakSawah Besar, Jakarta, IndonesiaKoordinat6°10′13″S 106°50′06″E / 6.170298°S 106.834925°E / -6.170298; 106.834925Koordinat: 6°10′13″S 106°50′06″E / 6.170298°S 106.834925°E / -6.170298; 106.834925Dibangun1963ArsitekFriedrich SilabanHenk NgantungPemahatEdhi Sunarso Monumen Pembebasan Irian Barat adalah monumen yang dibangun untuk mengenang para…

PrayaKecamatanNegara IndonesiaProvinsiNusa Tenggara BaratKabupatenLombok TengahPemerintahan • CamatBaiq MurniatiPopulasi (30 Juni 2023) • Total131.929 jiwa • Kepadatan4.239/km2 (10,980/sq mi)Kode Kemendagri52.02.01 Kode BPS5202060 Situs webkec-praya.lomboktengahkab.go.id Praya adalah sebuah kecamatan di kabupaten Lombok Tengah, Nusa Tenggara Barat, Indonesia yang juga merupakan ibu kota dari Kabupaten Lombok Tengah terletak antara 115°46 - 119�…

Typical boogie woogie bassline on 12 bar blues progression in C, chord roots in red Playⓘ. In music, a rewrite rule is a recursive generative grammar, which creates a chord progression from another. Steedman (1984)[1] has proposed a set of recursive rewrite rules which generate all well-formed transformations of jazz, basic I–IV–I–V–I twelve-bar blues chord sequences, and, slightly modified, non-twelve-bar blues I–IV–V sequences (rhythm changes). The typical 12-bar blues pr…

Catherine Colonna Duta Besar Prancis untuk Britania RayaMasa jabatan2019 – kiniPresidenEmmanuel Macron PendahuluJean-Pierre JouyetPenggantiPetahanaDuta Besar Prancis untuk ItaliaMasa jabatan2014–2017PresidenFrançois HollandeEmmanuel Macron PendahuluAlain Le RoyPenggantiChristian MassetDuta Besar Prancis untuk UNESCOMasa jabatan26 Maret 2008 – 22 Desember 2010Menteri Urusan EropaMasa jabatan2 Juni 2005 – 15 Mei 2007PresidenJacques ChiracPerdana MenteriDominique…
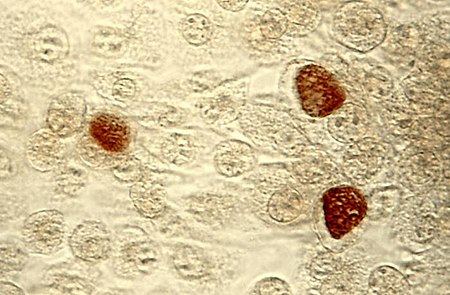
Untuk penyakit pada manusia, lihat Infeksi chlamydia. Chlamydia Badan inklusi C. trachomatis (coklat) pada kultur sel McCoy. Klasifikasi ilmiah Domain: Bakteri Filum: Chlamydiae Kelas: Chlamydiae Ordo: Chlamydiales Famili: Chlamydiaceae Genus: Chlamydia Spesies Chlamydia avium Sachse dkk. 2015[1] Chlamydia felis Sachse dkk. 2015[1] Chlamydia gallinacea Sachse dkk. 2015[1] Chlamydia muridarum Everett dkk. 1999Chlamydophila pecorum Fukushi & Hirai 1992, gen. nov. Everet…

Milly & Mamet: Ini Bukan Cinta & RanggaPoster filmSutradaraErnest PrakasaProduser Chand Parwez Servia Mira Lesmana Fiaz Servia SkenarioErnest PrakasaMeira AnastasiaPemeran Sissy Priscillia Dennis Adhiswara Ernest Prakasa Julie Estelle Yoshi Sudarso Dian Sastrowardoyo Titi Kamal Adinia Wirasti Penata musikAndhika TriyadiSinematograferRoby HerbiPenyuntingRyan PurwokoPerusahaanproduksi Starvision Plus Miles Films HOOQ Originals Tanggal rilis20 Desember 2018Durasi101 menitNegaraIndones…

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (نوفمبر 2019) دوري جزر فارو الممتاز 1986 تفاصيل الموسم دوري جزر فارو الممتاز النسخة 45، و44 البلد جزر فارو التا�…

Karakter dalam seri NarutoUzumaki NarutoうずまきナルトNarutoNarutoPenampilan perdanaMangaBab 1AnimeNaruto episode 1Tampil diAnime, manga, film, OVA, dan permainanPengisi suaraIndonesiaHanna Bahagiana[3]Ridawati[4]Mirna Haryati[4]Leni M Tarra[4]Wiwiek Supadmi[4]InggrisMaile Flanagan[2]JepangJunko Takeuchi[1] Informasi karakter ProfilUlang tahun10 OktoberJenis kelamin Laki-lakiUsiaBagian I: 12-13Bagian II: 16-17Tinggi145,3–147,5 …

Ini adalah nama Korea; marganya adalah Park. Park Se-WanLahirPark Se-Wan24 September 1994 (umur 29)Busan, Korea SelatanPendidikanUniversitas Sungkyunkwan - Departemen Akting untuk Teater, Film & TVPekerjaanAktrisTahun aktif2016-sekarangAgenHuayi BrothersNama KoreaHangul박세완 Hanja朴世完 Alih AksaraBak Se-wanMcCune–ReischauerPak Se-wan Park Se-wan lahir 24 September 1994 adalah aktris berkebangsaan Korea Selatan. Dia telah membintangi banyak drama, diantaranya School 2017, …

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (juin 2014). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références » En pratique : Quelles sources sont attendues ? Comment …

American judge John Jay Jackson Jr.The Iron Judge of West Virginia, c. 1903Judge of the United States District Court for the Northern District of West VirginiaIn officeJuly 1, 1901 – March 15, 1905Appointed byoperation of lawPreceded bySeat established by 31 Stat. 736Succeeded byAlston G. DaytonJudge of the United States District Court for the District of West VirginiaIn officeJune 11, 1864 – July 1, 1901Appointed byoperation of lawPreceded bySeat established by 13 Stat. 12…

Hafiz IndonesiaGenreAcara bakatReligiPresenterIrfan HakimJuriLulu Susanti (2013-2016, 2022, 2024)Amir Faishol Fath (2014-sekarang)Nasaruddin Umar (2014, 2016)Syekh Abdulkarim Al-Makki (2022)Syekh Ali Jaber (2014-2018, 2020) (Alm)Riza Muhammad (2013)Bachtiar Nasir (2013 & 2019)Cecep Maulana (2013)Nabila Abdul Rahim Bayan (2017-sekarang) Syekh Ahmad Al-Misry (2020-2021)Syekh Hussein Jaber (2022-Sekarang) Habib Nabil Al Musawwa (2019) Dennis Lim (2024-Sekarang) Kasif Heer (2024-Sekarang)Negara …

Bulan Sabit Merah Afganistanد افغاني سرې میاشتې ټولنېTanggal pendirian1934TipeBadan bantuanTujuanBantuan kemanusiaanKantor pusatKabul, AfganistanLokasiAfganistanPresidenMatiul Haq KhalisWakil PresidenNooruddin TurabiAfiliasiFederasi Internasional Perhimpunan Palang Merah dan Bulan Sabit MerahSitus webARCS Official Site Bulan Sabit Merah Afganistan (Pashto: د افغاني سرې میاشتې ټولنې) adalah afiliasi Afganistan dari Federasi Internasional Perhimpunan Palan…

Australian mathematician John StillwellBorn (1942-08-12) 12 August 1942 (age 81)Melbourne, AustraliaAlma materUniversity of MelbourneMassachusetts Institute of Technology (Ph.D, 1970)AwardsChauvenet Prize (2005)Scientific careerFieldsMathematicsInstitutions1970 until 2001: Monash University2002 to date: University of San FranciscoDoctoral advisorHartley Rogers, Jr John Colin Stillwell (born 1942) is an Australian mathematician on the faculties of the University of San Francisco and Mon…

Swedish writer Peder Sjögren (1905–1966), born as Gösta Sjögren, was a Swedish writer who fought in the Spanish Civil War and the Continuation War. Many of his books were based on those experiences. Life and works Peder Sjögren Gösta Tage Filip Sjögren was born in 1905, outside Växjö, in the province of Småland, and at the age of 10 moved to Stockholm. Aged 17, he was sent to Rome, after which he travelled to the Balkans, Spain, North Africa, Poland and Finland.[1] As an antif…

Kimagure PrincessLagu oleh Morning Musumedari album 10 My MeDirilis28 Oktober 2009 (CD)4 November 2009 (DVD)FormatCD, DVDDirekam2009GenreJ-popLabelZetimaProduserTsunkuVideo musikKimagure Princess di YouTube Kimagure Princess (気まぐれプリンセスcode: ja is deprecated , Putri Plin-plan) Adalah singel ke-41 Unit Hello! Project Morning Musume. Singel ini dirilis pada tanggal 28 Oktober 2009[1] dan menjadi lagu penutup untuk acara TV Tokyo, The Gyakuryū Researchers. Ini juga menjadi…













