Civil service reform in the United States
|

Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan cara menambahkan rujukan ke sumber tepercaya. Pernyataan tak bersumber bisa saja dipertentangkan dan dihapus.Cari sumber: Pesawat siluman – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR (Maret 2019) B-2 Spirit Pesawat siluman (bahasa Inggris: stealth aircraft) atau disebut pesawat amat senyap[1] adalah pesawat yang dira…

Final Piala EFL 2017TurnamenPiala EFL 2016–2017 Manchester United Southampton 3 2 Tanggal26 Februari 2017StadionStadion Wembley, LondonPemain Terbaik Zlatan Ibrahimović (Manchester United)WasitAndre Marriner (West Midlands)[1]Penonton85.264← 2016 2018 → Final Piala EFL 2017 adalah pertandingan final ke-57 dari turnamen sepak bola Piala EFL untuk menentukan juara musim 2016–2017. Pertandingan ini diselenggarakan pada 26 Februari 2017 di Stadion Wembley. Manchester United …

Ballantine'sKarakteristikJenisalcohol brand (en) dan blended whiskey (en) AsalSkotlandia Diperkenalkan1827 ProdusenPernod Ricard Kadar alkohol40 vol% Situs webhttps://www.ballantines.com/ [sunting di Wikidata]lbs Ballantine's merupakan merek wiski yang diproduksi oleh Pernod Richard. Merek ini dibuat pada tahun 1865 ketika George Ballantine mewariskan pengoperasian toko grosir whisky yang didirikannya pada tahun 1827, kepada putra sulungnya, Archibald, sementara ia membuka usah…

Fatmir Sejdiu Presiden KosovoMasa jabatan10 Februari 2006 – 27 September 2010Perdana MenteriBajram KosumiAgim ÇekuHashim Thaçi PenggantiJakup Krasniqi (Acting) Informasi pribadiLahir23 Oktober 1951 (umur 72)Pakaštica, RFS Yugoslavia (sekarang Kosovo[1])Partai politikLiga DemokratikSuami/istriNezafete SejdiuSunting kotak info • L • B Fatmir Sejdiu[2] (lahir 23 Oktober 1951) adalah Presiden kedua dari Republik Kosovo dan pemimpin Liga Demokratik Kos…

←→Апрель Пн Вт Ср Чт Пт Сб Вс 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 2024 год Содержание 1 Праздники и памятные дни 1.1 Международные 1.2 Национальные 1.3 Религиозные 1.3.1 Православие[4][5][6][7] 1.4 Именины 2 События 2.1 До XVIII века 2.2 XVIII век 2.3 XIX век 2.4 XX век 2.5 XXI век …

1962 US law on tariffs Trade Expansion Act of 1962CitationsPublic law19 U.S.C. ch. 7Legislative historyIntroduced in the House of RepresentativesCommittee consideration by House Ways and Means, Senate FinancePassed the House on June 28, 1962 (298–125)Passed the Senate on September 19, 1962 (78–8)Agreed to by the Senate on and by the House on Signed into law by President John F. Kennedy on October 11, 1962 The Trade Expansion Act of 1962 (Pub. L.Tooltip Public Law (U…
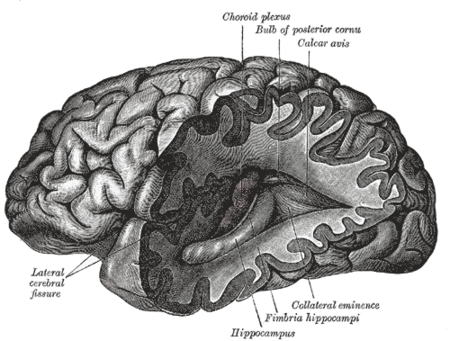
Subdiscipline of neuroscience and systems biology This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (December 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Systems neuroscience is a subdiscipline of neuroscience and systems biology that studies the structure and function of neural circuits and systems. Systems neurosc…

Indonesian hot and sweet beverage BandrekBandrek in Bandung with bits of young coconutCourseBeveragePlace of originIndonesiaRegion or stateWest JavaServing temperatureHotMain ingredientsGinger, palm sugar, cinnamon, spices, condensed milk Media: Bandrek Bandrek is a traditional hot, sweet and spicy beverage native to Sundanese of West Java, Indonesia.[1] The Sundanese people who live in the cool, highlands consume bandrek to warm themselves at night and during cold weather. Thi…

For the aircraft manufacturer, see Parnall. Parnall & Sons LtdCompany typePrivateIndustryEngineeringFoundedBristol, UK (1820 (1820))FounderWilliam ParnallFateAcquired by George Adlam & SonsHeadquartersBristol, UK Parnall & Sons Ltd was a shop and ship fitting and aircraft component manufacturer in Bristol, England. The original company was set up in 1820 by William Parnall in Narrow Wine Street, initially making weights and measures, before expanding into shop keeping equipment …

English cardinal, the last Catholic Archbishop of Canterbury His EminenceReginald PoleCardinal Archbishop of Canterbury and Primate of All EnglandPortrait by the school of Sebastiano del Piombo, c. 1549ChurchCatholic ChurchInstalled22 March 1556Term ended17 November 1558PredecessorThomas CranmerSuccessorMatthew ParkerOrdersOrdination20 March 1556Consecration22 March 1556by Nicholas HeathCreated cardinal22 December 1536by Paul IIIPersonal detailsBorn(1500-03-12)12 March 1500Stourton Ca…

Éric Abidal Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Éric Sylvain Abidal[1]Tanggal lahir 11 September 1979 (umur 44)Tempat lahir Lyon, PrancisTinggi 1,84 m (6 ft 1⁄2 in)Posisi bermain BekKarier junior Lyon DuchèreKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1999–2000 Lyon Duchère 2000–2001 Monaco B 8 (0)2000–2002 Monaco 22 (0)2002–2004 Lille 62 (0)2004–2007 Lyon 76 (0)2007–2013 Barcelona 125 (0)2013–2014 Monaco 26 (0)2014 Olympiacos 9 (0)Total 328 (0)Tim nasional2…

Untuk klub sepak bola Indonesia yang bernama sama, lihat PSM Makassar. PSM MadiunNama lengkapPerserikatan Sepakbola MadiunJulukanBanteng WilisNama singkatPSMBerdiri29 Mei 1929; 94 tahun lalu (1929-05-29) (sebagai Madioensche Voetbal Bond (MVB)StadionStadion Wilis, Kota Madiun, Jawa Timur(Kapasitas: 25.000)ManajerNono DjatikusumoPelatih Kodari AmirAsisten PelatihMiftakul HudaNosa Ilvan GilisNovan Eka PrasetyaLigaLiga 3 Jawa TimurSitus webSitus web resmi klubKelompok suporterMVB (Madioen…

Betty Ford, première dame des États-Unis et du Michigan, intronisée au Temple de la renommée des femmes. Le Michigan Women's Hall of Fame (MWHOF) est un temple de la renommée qui rend hommage à des femmes remarquables, des personnalités historiques et contemporaines, qui ont un lien avec l'État américain du Michigan. Le temple de la renommée a été fondé en 1983 par Gladys Beckwith et est parrainé par la Michigan Women's Studies Association[1]. La génèse de l'Association et du Hal…

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Птиц�…

Questa voce sull'argomento stagioni delle società calcistiche italiane è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Voce principale: Associazione Calcistica Dilettantistica Rapallo Ruentes 1914. Associazione Calcio Rapallo RuentesStagione 1950-1951Sport calcio Squadra Rapallo Ruentes Allenatore Carlo Baldi Presidente Michele Rovegno Serie C10º posto nel girone A. 1949-1950 1951-1952 Si invita a s…

2012 single by Sam SparroHappinessSingle by Sam Sparrofrom the album Return to Paradise Released17 February 2012Recorded2011Genre Pop disco dance-pop Length3:06LabelEMISongwriter(s) Sam Falson Charlie Willcocks Jesse Rogg[1] Producer(s) Jesse Rogg Sam Falson Sam Sparro singles chronology The Shallow End (2012) Happiness (2012) I Wish I Never Met You (2012) Happiness is a song by Australian singer-songwriter, music producer, and former child actor Sam Sparro. The song was released on …

The San Agustin CathedralThis is a list of the tallest and largest buildings in Laredo, Texas. Laredo is the county seat and most populated city in Webb County, Texas. The city has over 230,000 residents and there are over 730,000 residents in the Laredo-Nuevo Laredo Metropolitan Area. Tallest buildings Hamilton Hotel Rio Grande Plaza Hotel The Holiday Inn The Laredo Medical Center Walker Plaza Mall del Norte Today a part of the Republic of the Rio Grande's Capitol building is used as a museum. …

Franco Venturi Franco Venturi (Roma, 16 maggio 1914 – Torino, 14 dicembre 1994) è stato uno storico italiano, professore dell'Università di Torino, studioso dell'Illuminismo italiano ed europeo e del populismo russo. Fu esule antifascista, detenuto nelle carceri fasciste e attivo nella Resistenza nelle file di Giustizia e Libertà. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Opere 3 Note 4 Bibliografia 5 Voci correlate 6 Altri progetti 7 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Nipote di Adolfo Venturi e figlio di Lionello …

American politician (1814–1891) Chester D. HubbardMember of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom West Virginia's 1st districtIn officeMarch 4, 1865 – March 3, 1869Preceded byJacob B. BlairSucceeded byIsaac H. DuvalMember of the Virginia House of Delegatesfrom the Ohio County districtIn officeJanuary 12, 1852 – December 2, 1853Serving with Charles W. Russell,John M. OldhamSucceeded byJohn C. Campbell Personal detailsBorn(1814-11-25)November…

Ini adalah nama Korea; marganya adalah Lee. Lee Tae-ranLahir25 Maret 1975 (umur 49)Yeonggwang County, Jeolla Selatan, Korea SelatanKebangsaanKorea SelatanAlmamaterUnversitas HanyangPekerjaanAktrisTahun aktif1997 – sekarangAgenSTAR PAGE EntertainmentTinggi170 m (557 ft 9 in)Suami/istriShin Seung-hwan (m. 2014)Nama KoreaHangul이태란 Alih AksaraI Tae-nanMcCune–ReischauerI T'ae-nan Lee Tae-ran (Hangul: 이태란; lahir 25 Maret 1975) adalah aktris asal Korea …




