Classical demography
|
Read other articles:

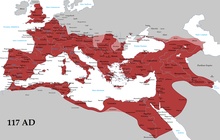
Kaisar Kekaisaran Romawi Bekas Kerajaan Imperial Vexillum Augustus Penguasa pertama Augustus Penguasa terakhir Theodosius I (Bersatu/klasikal),Romulus Augustulus (Barat),Konstantinus XI (timur) Gelar Imperator, Augustus, Caesar, Princeps, Dominus Noster, atau Autokrator (menurut periode) Pendirian 27 SM Pembubaran 395 (Bersatu/klasikal),476 (Barat),1453 (Timur) Penuntut takhta Tidak ada Romawi Kuno Artikel ini adalah bagian dari seri Politik dan KetatanegaraanRomawi Kuno Zaman Kerajaan Romawi753…
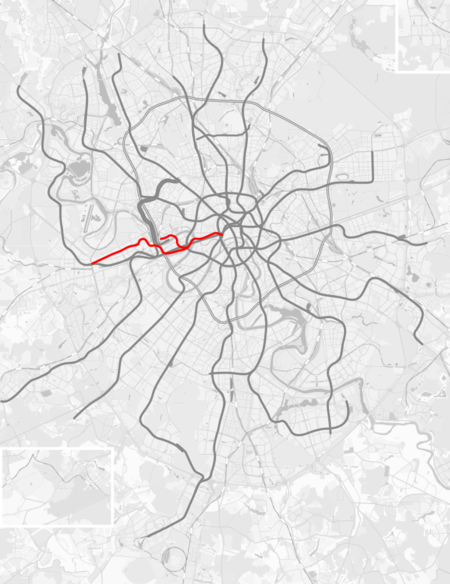
!B9986137056388 4 Jalur Filyovskaya IkhtisarJenisAngkutan cepatSistemMetro MoskwaLokasiMoskwaTerminusAleksandrovsky Sad (pusat)Kuntsevskaya (barat); Mezhdunarodnaya (pusat)Stasiun13Penumpang harian320.600OperasiDibuka15 Mei 1935 (sebagai cabang !C 1 )7 November 1958 (terpisah) PemilikMoskovsky MetropolitenOperatorMoskovsky MetropolitenKarakteristik lintasAt-grade, undergroundRangkaian81-740/74181-717/714Data teknisPanjang lintas149 km (93 mi)Lebar …

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Somerset (homonymie) et Comté de Somerset. Cet article est une ébauche concernant l’Angleterre. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Somerset Administration Pays Royaume-Uni Nation Angleterre Région Angleterre du Sud-Ouest Statut Comté non-métropolitainComté cérémonialComté traditionnel Démographie Population 910 200 hab. (2011) Densité 218 hab…
Daftar keuskupan di Latvia adalah sebuah daftar yang memuat dan menjabarkan pembagian terhadap wilayah administratif Gereja Katolik Roma yang dipimpin oleh seorang uskup ataupun ordinaris di Latvia. Konferensi uskup di wilayah Latvia bergabung dalam Konferensi Waligereja Latvia. Saat ini terdapat 4 buah yurisdiksi, di mana 1 merupakan keuskupan agung dan 3 merupakan keuskupan sufragan. Daftar keuskupan Provinsi Gerejawi Riga Keuskupan Agung Riga: Zbigņev Stankevičs Uskup Auksilier, Andris Krav…

Waktu Standar Natal atau UTC+07:00 adalah zona waktu standar yang dipakai di Pulau Natal, wilayah eksternal Australia. Zona waktu ini sama dengan yang dipakai di Indonesia, yaitu Waktu Indonesia Barat.[1] Waktu di Pulau Natal Standar Zona UTC+07:00 Waktu Standar Natal Referensi ^ Official government website [1] Diarsipkan 2008-08-20 di Wayback Machine. Pranala luar Artikel bertopik waktu ini adalah sebuah rintisan. Anda dapat membantu Wikipedia dengan mengembangkannya.lbs

Artikel biografi ini ditulis menyerupai resume atau daftar riwayat hidup (Curriculum Vitae). Tolong bantu perbaiki agar netral dan ensiklopedis. Achmad Afzan Arslan Djunaid Wali Kota Pekalongan ke-24PetahanaMulai menjabat 26 Februari 2021PresidenJoko WidodoGubernurGanjar PranowoNana Sudjana (Pj.)WakilSalahudin PendahuluSaelany Machfudz Sri Ruminingsih (Plh.)PenggantiPetahana Wakil Wali Kota Pekalongan ke-5Masa jabatan12 April 2019 – 17 Februari 2021PresidenJoko WidodoGuber…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Jalur rempah di Nusantara telah dikenal sejak berabad-abad lamanya di mana jalur khayal ini merupakan jalur yang biasa pada masa itu dilalui oleh para pedagang dari berbagai belahan di dunia. Tome pires menyebutkan dalam bukunya Summa Oriental que trata d…

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Stade Municipal Ouagadougou – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) The stadium in 2008 Stade Dr. Issoufou Joseph Conombo[1] is a multi-use stadium in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso…
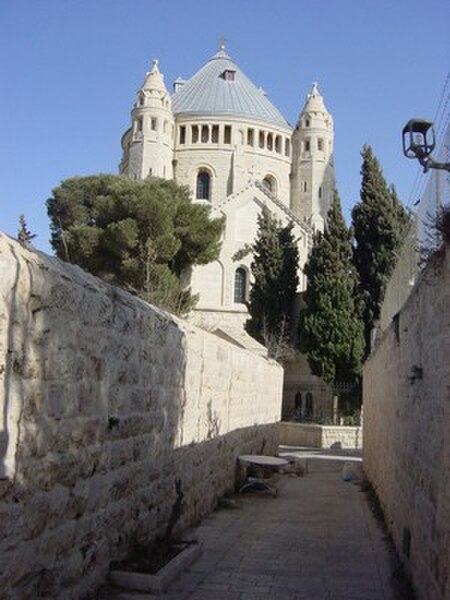

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Gunung Sion. Gunung Zion, atau juga dieja sebagai bukit Sion (dari Bahasa Ibrani: ציון, Tziyyon, Bahasa Arab: صهيون Ṣahyūn) adalah bukit di mana kota Yerusalem berdiri. Sekarang ini, perkampungan Yahudi di Kota Lama Yerusalem berdiri di atas bukit Zion. Nama Zion biasanya merujuk ke kota Yerusalem dan tanah Israel. Identifikasi sekarang Hagia Maria Sion Abbey (Dormition Church), terletak di daerah Mount Zion modern Sekarang ini, nama Gunung Zion (Mount Zion…

Barrière à sédiments installée sur un chantier de construction. Aux États-Unis, le contrôle des alluvions (en anglais : sediment control) sont une pratique ou un dispositif conçu pour maintenir un sol érodé sur un chantier de construction, afin qu'il ne se lave pas et n'occasionne pas de pollution de l'eau à un ruisseau, une rivière, un lac ou une mer à proximité. Le contrôle des alluvions va généralement de pair avec la lutte contre l'érosion, qui est conçu pour prévenir…

Jamaah TablighIjtima Tahunan Jamaah Tabligh Malaysia 2009Sepang Selangor, MalaysiaTotal populasi12 hingga 80 juta[1]PendiriMuhammad Ilyas al-Kandhlawi[2]AgamaIslam Deobandi[2][3][4]Kitab suciQuran, Hadis, dan Sunnah Bagian dari seriIslam Rukun Iman Keesaan Allah Malaikat Kitab-kitab Allah Nabi dan Rasul Allah Hari Kiamat Qada dan Qadar Rukun Islam Syahadat Salat Zakat Puasa Haji Sumber hukum Islam al-Qur'an Sunnah (Hadis, Sirah) Tafsir Akidah Fikih Syariat…

MöslestadionThe Möslestadion in FreiburgLocationFreiburg, GermanyCapacity5,400 (1000 in covered seating area)SurfaceGrassConstructionOpenedOctober 1st, 1922RenovatedJune–August, 2013TenantsSC Freiburg second men's teamFreiburg Soccer SchoolSC Freiburg (women) The Möslestadion is a soccer stadium in Freiburg im Breisgau. The stadium used to be home to the Freiburger FC. Today it is used by the second men's team and the Freiburg soccer school of the SC Freiburg. Since the 2008/09 season, the …

This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (October 2021) Darts playerMark McGrathPersonal informationNicknameThe CowboyBorn (1968-07-15) 15 July 1968 (age 55)Leeds, EnglandHome townRongoteaDarts informationPlaying darts since1988Darts25 GramLateralityRight-handedWalk-on musicCowboy Up by Dry CountyOrganisation (see split in d…

追晉陸軍二級上將趙家驤將軍个人资料出生1910年 大清河南省衛輝府汲縣逝世1958年8月23日(1958歲—08—23)(47—48歲) † 中華民國福建省金門縣国籍 中華民國政党 中國國民黨获奖 青天白日勳章(追贈)军事背景效忠 中華民國服役 國民革命軍 中華民國陸軍服役时间1924年-1958年军衔 二級上將 (追晉)部队四十七師指挥東北剿匪總司令部參謀長陸軍總�…
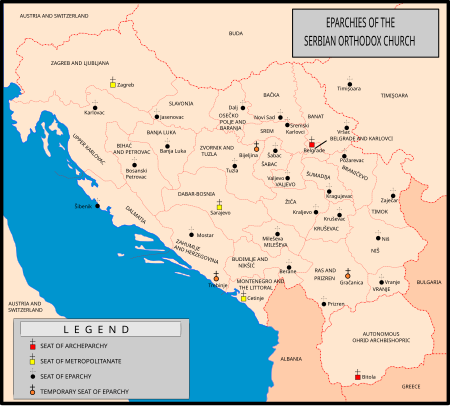
Diocese in Eastern Christianity For other uses, see Eparchy (disambiguation). Eparchy (Greek: ἐπαρχία eparchía overlordship) is an ecclesiastical unit in Eastern Christianity that is equivalent to a diocese in Western Christianity. An eparchy is governed by an eparch, who is a bishop. Depending on the administrative structure of a specific Eastern Church, an eparchy can belong to an ecclesiastical province (usually a metropolis), but it can also be exempt. Each eparchy is divided into p…

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (March 2013) This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise cit…

Irish food in Newfoundland This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Jiggs dinner – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Jiggs dinner: cabbage, turnip, carrot, salt meat, mashed turnip, dressing, potatoes Part of a series onCanadian cuisi…

Сельское поселение России (МО 2-го уровня)Новотитаровское сельское поселение Флаг[d] Герб 45°14′09″ с. ш. 38°58′16″ в. д.HGЯO Страна Россия Субъект РФ Краснодарский край Район Динской Включает 4 населённых пункта Адм. центр Новотитаровская Глава сельского посел…

烏克蘭總理Прем'єр-міністр України烏克蘭國徽現任杰尼斯·什米加尔自2020年3月4日任命者烏克蘭總統任期總統任命首任維托爾德·福金设立1991年11月后继职位無网站www.kmu.gov.ua/control/en/(英文) 乌克兰 乌克兰政府与政治系列条目 宪法 政府 总统 弗拉基米尔·泽连斯基 總統辦公室 国家安全与国防事务委员会 总统代表(英语:Representatives of the President of Ukraine) 总理…

La Libre ParoleStato Francia Linguafrancese Periodicitàquotidiano GenereStampa politica FondatoreÉdouard Drumont Fondazione1892 Chiusura1924 SedeParigi Tiratura300000 Record vendite300000 DirettoreÉdouard Drumont ISSN1256-0294 (WC · ACNP) e 2592-4125 (WC · ACNP) Sito webwww.retronews.fr/titre-de-presse/libre-parole Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Frontespizio de La Libre Parole, 1893 La Libre Parole o La Libre Parole illustrée (francese; La parola libera) è…