|
Coat of arms of Germany
 The coat of arms of Germany, also known as Bundesrepublik Deutschland displays a black eagle with a red beak, a red tongue and red feet on a golden field, which is blazoned: Or, an eagle displayed sable beaked langued and membered gules. This is the Bundesadler (German for 'Federal Eagle'), formerly known as Reichsadler (German: [ˈʁaɪ̯çsˌʔaːdlɐ] ⓘ, German for 'Imperial Eagle'). It is one of the oldest coats of arms in the world, and today the oldest national symbol used in Europe. It is a re-introduction of the coat of arms of the Weimar Republic (in use 1919–1935), which was adopted by the Federal Republic of Germany in 1950.[1] The current official design is due to Karl-Tobias Schwab (1887–1967) and was originally introduced in 1928. The German Empire of 1871–1918 had re-introduced the medieval coat of arms of the Holy Roman Emperors, in use during the 13th and 14th centuries (a black single-headed eagle on a golden background), before the emperors adopted the double-headed eagle, beginning with Sigismund of Luxemburg in 1433. The single-headed Prussian Eagle (on a white background; blazoned: Argent, an eagle displayed sable) was used as an escutcheon to represent the Prussian kings as dynasts of the German Empire. The Weimar Republic introduced a version in which the escutcheon and other monarchical symbols were removed. The Federal Republic of Germany adopted the Weimar eagle as its symbol in 1950. Since then, it has been known as the Bundesadler ("federal eagle"). The legal basis of the use of this coat of arms is the announcement by President Theodor Heuss, Chancellor Konrad Adenauer and Interior Minister Gustav Heinemann of 20 January 1950, which is word for word identical to the announcement by President Friedrich Ebert and Interior Minister Erich Koch-Weser by 11 November 1919:
Since the accession (1990) of the states that used to form the German Democratic Republic, the Federal Eagle has been the symbol of the reunified Germany. Official depictions of the eagle can be found not only in the federal coat of arms but also on the federal institutions flag, the standard of the president of Germany and official seals. These are designs by various artists of the Weimar period and differ primarily in the shape and position of the wings. A large and rather plump version of the eagle decorates the chamber of the Bundestag, the German parliament; it is sometimes called Fette Henne ("Fat Hen"), with a similar representation found on the German euro coins. In addition to the official depictions, artistic renderings of the federal eagle are permitted and have found their way onto coins, stamps and the letterhead of federal authorities. In 1997 the Federal Press Office implemented a slightly simplified version of the original von Weech seal design which has since been used as a corporate design of the Federal government especially for publications and media appearances. It has no official status though as it is not mentioned in any ordinance or shown in the binding patterns of 1952 still in effect.[3]
The arms emblazoned on the German 1 euro coin (l.), as well Ludwig Gies's sculpture of the eagle charge, as displayed previously in the Federal parliament in Bonn (m.) and presently in the Reichstag building in Berlin (r.), respectively Previous versionsHoly Roman Empire The German Imperial Eagle (Reichsadler) originates from a proto-heraldic emblem believed to have been used by Charlemagne, the first Frankish ruler crowned Holy Roman Emperor by the Pope in 800, and derived ultimately from the Aquila or eagle standard, of the Roman army. By the 13th century the imperial coat of arms was generally recognized as: Or, an eagle displayed sable beaked and membered gules (a black eagle with wings expanded with red beak and legs on a gold field). During the medieval period the imperial eagle was usually single-headed. A double-headed eagle is attributed as the arms of Frederick II in the Chronica Majora (c. 1250). In 1433 the double-headed eagle was adopted by Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor. Thereafter the double-headed eagle was used as the arms of the German emperor, and hence as the symbol of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation. From the 12th century the Emperors also used a personal coat of arms separate from the imperial arms. From the reign of Albert II (reigned 1438–39), the Emperors bore the old Imperial arms with an inescutcheon of pretence of his personal family arms, which appears as the black eagle with an escutcheon on his breast.
German Confederation In 1815, a German Confederation (Bund) of 39 loosely united German states was founded on the territory of the former Holy Roman Empire. Until 1848, the confederation did not have a coat of arms of its own. The Federal Diet (Bundestag) meeting at Frankfurt am Main used a seal which carried the emblem of the Austrian Empire, since Austria had taken over the union's leadership. It showed a black, double-headed eagle, which Austria had adopted just before the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation. During the 1848 revolution, a new Reich coat of arms was adopted by the National Assembly that convened in St. Paul's Church in Frankfurt. The black double-headed eagle was retained, but without the four symbols of the emperor: the sword, the imperial orb, the sceptre and the crown. The eagle rested on a golden shield; above was a five-pointed golden star. On both sides the shield was flanked by three flags with the colors black-red-gold. The emblem, however, never gained general acceptance. The coat of arms itself was the result of a decision of the federal assembly:
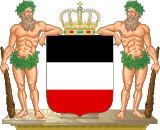
North German ConfederationIn 1867, the North German Confederation was established without Austria and the four southern German states (Bavaria, Württemberg, Baden, Hesse-Darmstadt with only its southern half) and under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia (see Coat of arms of Prussia). A new coat of arms was adopted, which consisted of a shield with the colors black-white-red, flanked by two wild men holding cudgels and standing on a pedestal.
German Empire The Reichsadler had already been introduced at the Proclamation of Versailles, although the first version had been only a provisional one. The design of the eagle was altered at least twice during the German Empire (1871–1918). It shows the imperial eagle, a comparatively realistic black eagle, with the heraldic crown of the German Empire. The eagle has a red beak, tongue and claws, with open wings and feathers. In contrast to its predecessor, the eagle of the German Confederation, it has only one head, looking to the right, symbolising that important parts of the old empire, Austria and Bohemia, were not part of this new empire. Its legal basis was an imperial rescript:
Weimar Republic After the introduction of the republic the coat of arms of Germany was also altered accounting for the political changes. The Weimar Republic (1918–1933), retained the Reichsadler without the symbols of the former Monarchy (Crown, Collar, Breast shield with the Prussian Arms). This left the black eagle with one head, facing to the right, with open wings but closed feathers, with a red beak, tongue and claws and white highlighting. The republican Reichsadler is based on the Reichsadler introduced by the Paulskirche Constitution of 1849, which was decided by the Germany National Assembly in Frankfurt upon Main, at the peak of the German civic movement demanding parliamentary participation and the unification of the German states. The achievements and signs of this movement had been mostly done away after its downfall and the political reaction in the 1850s. Only the tiny German Principality of Waldeck-Pyrmont upheld the tradition and continued to use the German colours called Schwarz-Rot-Gold in German (English: Black-Red-Or). These signs had remained symbols of the Paulskirche movement and Weimar Germany wanted to express its view of being also originated in that political movement between 1848 and 1852. The republican coat of arms took up the idea of the German crest established by the Paulskirche movement, using the same charge animal, an eagle, in the same colors (black, red and or), but modernising its form, including a reduction of the heads from two to one. The artistic rendition of the eagle was very realistic. This eagle is mounted on a yellow (golden) shield. The coat of arms was announced in 1919 by the President Friedrich Ebert and Interior Minister Erich Koch-Weser:
However, in 1928 the Reichswappen (Reich's coat of arms) designed by Tobias Schwab (1887–1967) in 1926 (or 1924[note 1]) for the German Olympic team became the official emblem.[7][8][9] The Reichswehr adopted the new Reichswappen already in 1927.[9] Emil Doepler's earlier design then became the Reichsschild (Reich's escutcheon) with restricted use such as pennant for government vehicles. In 1920, Sigmund von Weech designed a Staatssiegel (State seal), of which the smaller version was used since 1921 by all Reich ministries and authorities on official documents as a consistent sign. It also appeared on the German passports. In 1949, the Federal Republic of Germany adopted all signs of Weimar Republic, Reichswappen, Reichsschild, Staatssiegel, Reichsflagge as Bundeswappen, Bundesschild. Bundessiegel and Bundesflagge in the 1950s.[9] Nazi GermanyNazi Germany used the Weimar coat of arms until 1935. The Nazi Party used a stylised black eagle above an oak wreath, with a swastika at its centre. With the eagle looking over its left shoulder, that is, looking to the right from the viewer's point of view, it symbolises the Nazi Party, and was therefore called the Parteiadler. After 1935 the Nazis introduced their party symbol as the national insignia (Hoheitszeichen) as well. This version symbolises the country (Reich) and was therefore called the Reichsadler. It can be distinguished from the Parteiadler because the eagle of the latter is looking over its right shoulder, that is, looking to the left from the viewer's point of view. The emblem was established by a regulation made by the Fuhrer and Reich Chancellor Adolf Hitler, 5 November 1935:
Hitler added on 7 March 1936 that:
German Democratic Republic East Germany (German Democratic Republic) used a socialist insignia from 1950 until its reunification with West Germany in 1990. In 1959 the insignia was also added to the flag of East Germany.
See also
Notes
References
Further reading
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||