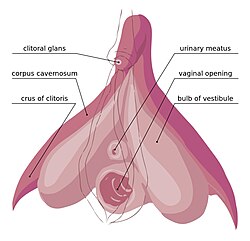
One of two erectile tissue structures of the human clitoris
The clitoral crura (sg. : clitoral crus ) are two erectile tissue structures, which together form a "V" shape. Crus is a Latin word that means "leg". Each "leg" of the V converges on the clitoral body . At each divergent point is a corpus cavernosum . Together with the vestibular bulbs , they form the clitoral root . The crura are attached to the pubic arch , and are adjacent to the vestibular bulbs. The crura flank the urethra , urethral sponge , and vagina and extend back toward the pubis . Each clitoral crus connects to the rami of the pubis and the ischium .[ 1]
During sexual arousal , the crura become engorged with blood, as does all of the erectile tissue of the clitoris.[ 2] [ 3]
The clitoral crura are each covered by an ischiocavernosus muscle .[ 4]
Shows the sub-areas of the clitoris. Areas include clitoral glans, body, crura. Also shows vestibular bulbs and corpora cavernosa
See also
References
^ Ginger, VA; Cold, CJ; Yang, CC (March 2011). "Surgical anatomy of the dorsal nerve of the clitoris". Neurourology and Urodynamics . 30 (3): 412– 6. doi :10.1002/nau.20996 . PMID 21298720 . S2CID 22501531 . ^ Hite, Shere (2006). The Shere Hite reader sex, globalization, and private life ISBN 1609800362 . Retrieved 17 October 2015 . ^ Wessells, Norman K.; Center, Elizabeth M.; Kistler, Henry B. (1992). Vertebrates, a laboratory text (2nd ed.). Boston: Jones and Bartlett. p. 201. ISBN 0867208538 ^ "Anatomy Atlases: Atlas of Human Anatomy in Cross Section: Section 6: Pelvis, Perineum, Hip, and Upper Thigh" . anatomyatlases.org .