Emblem of Iran
| |||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Katedral Campo GrandeKatedral Metropolitan Bunda Biara dan Santo AntoniusPortugis: Catedral Metropolitana Nossa Senhora da Abadia e Santo Antôniocode: pt is deprecated Katedral Campo Grande20°27′42″S 54°36′55″W / 20.46167°S 54.61528°W / -20.46167; -54.61528Koordinat: 20°27′42″S 54°36′55″W / 20.46167°S 54.61528°W / -20.46167; -54.61528LokasiCampo GrandeNegaraBrasilDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaArsitekturStatusKatedralStatus f…

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع كريس هارينجتون (توضيح). هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (نوفمبر 2019) كريس هارينجتون معلومات شخصية الميلاد 7 مايو 1982 (42 سنة) سانت كلاود مواطنة الولايات المتحدة الوزن 18…

Lahti LahtisCityLahden kaupunki Lambang kebesaranJulukan: Finland's Chicago, Business CityLocation of Lahti in FinlandNegaraFinlandiaRegionPäijänne TavastiaSubregionLahti sub-regionCharter1905-11-01Pemerintahan • City managerJyrki MyllyvirtaLuas(1 Januari 2016)[1] • Total459,43 km2 (17,739 sq mi) • Luas daratan135,05 km2 (5,214 sq mi) • Luas perairan19,53 km2 (754 sq mi)Peringkatke-191 di …
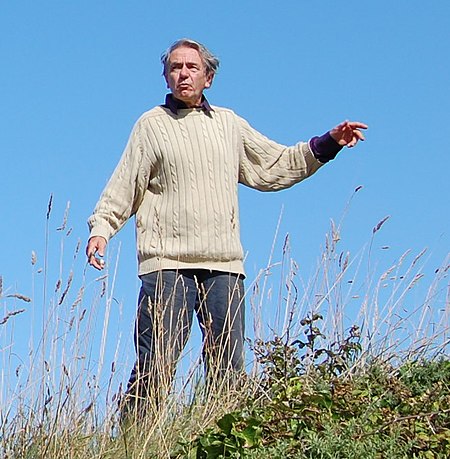

Jacques RancièreLahir1940Algiers, Aljazair PrancisAlmamaterÉcole Normale SupérieureEraAbad ke-20KawasanFilsafat baratAliranFilsafat kontinentalMarxisme StrukturalInstitusiUniversitas Paris VIIIMinat utamaPolitik, EstetikaGagasan pentingDemokrasi radikal, pertentangan, estetika visual, bagian dari tanpa bagian (la part de sans part), partage du sensible Dipengaruhi Plato, Aristotle, Marx, Althusser, Foucault, Lacan, Lyotard, Badiou Memengaruhi Laclau, Žižek, Critchley, Bernard Aspe…

Aggregate stock market valuation metric Not to be confused with Buffett Rule. Wilshire 5000 to GDP ratio The Buffett indicator (or the Buffett metric, or the Market capitalization-to-GDP ratio)[1] is a valuation multiple used to assess how expensive or cheap the aggregate stock market is at a given point in time.[1][2] It was proposed as a metric by investor Warren Buffett in 2001, who called it probably the best single measure of where valuations stand at any…

Ada usul agar Austria Hilir diganti judulnya dan dipindahkan ke Niederösterreich (Diskusikan). Peta Austria menunjukkan lokasi Austria Hilir Austria Hilir adalah sebuah negara bagian di Austria yang memiliki luas wilayah 19.174 km² dan populasi 1.545.804 jiwa (2001). Ibu kotanya ialah St. Pölten. lbsNegara bagian di Austria Austria Hulu · Austria Hilir · Burgenland · Kärnten · Salzburg · Steiermark · Tirol · …

Untuk kota di Portugal, lihat Porto. Artikel ini mungkin mengandung riset asli. Anda dapat membantu memperbaikinya dengan memastikan pernyataan yang dibuat dan menambahkan referensi. Pernyataan yang berpangku pada riset asli harus dihapus. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) PortoSamasuru Amalatu Poru AmarimaNegeriNegara IndonesiaProvinsiMalukuKabupatenMaluku TengahKecamatanSaparuaLuaskm2Jumlah pendudukjiwaKepadatanjiwa/km2 Porto, adalah salah satu dari tujuh…

American baseball player and manager (born 1964) For the Venezuelan baseball pitcher, see David Martínez (baseball). For other people with similar names, see David Martínez (disambiguation). Baseball player Dave MartinezMartinez with the Nationals in 2022Washington Nationals – No. 4Outfielder / ManagerBorn: (1964-09-26) September 26, 1964 (age 59)Brooklyn, New York, U.S.Batted: LeftThrew: LeftMLB debutJune 15, 1986, for the Chicago CubsLast MLB appearanceOctober 7, 2…
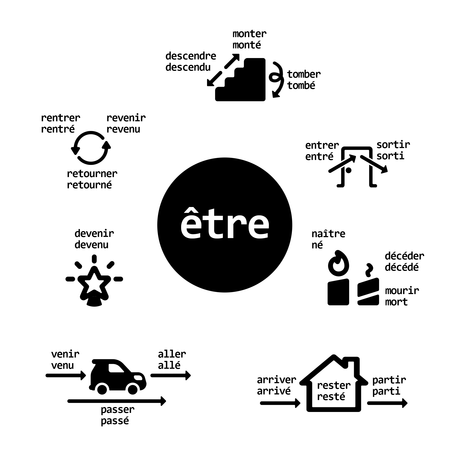
Common past tense in French Diagram showing which verbs (apart from pronomial verbs) are conjugated with être; below each verb in infinitive form is the past participle. This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Passé composé – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this t…

2001 2017 Élections sénatoriales de 2011 dans les Landes 25 septembre 2011 Type d’élection Élections sénatoriales Postes à élire 2 sièges de sénateur Jean-Louis Carrère – PS Voix 635 61,89 % Danielle Michel – PS Voix 587 57,21 % Marie-Françoise Nadau – UMP Voix 220 21,44 % Pierre Mallet – MoDem Voix 189 18,42 % Sénateurs des Landes Sortant Élu Jean-Louis Carrère et Philippe Labeyrie PS et PS Jean…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Expert (homonymie). Roger-Henri Expert Présentation Naissance 18 avril 1882Arcachon (Gironde) Décès 13 avril 1955 (à 72 ans)Cérons (Gironde) Nationalité France Activités Architecte, enseignant à l'ENSBA Diplôme 1912 Formation École des beaux-arts de BordeauxÉcole nationale supérieure des beaux-arts, ateliers Umbdenstock et Redon Élèves Jean Balladur, Claude Ferret Œuvre Réalisations Fontaine du TrocadéroÉglise Sainte-Thérèse-de-l'Enfant-…

Short-lived Polish political alliance Politics of Poland Government Constitution of Poland Law Human rights Legislature Parliament of Poland Current Parliament Sejm Marshal Szymon Hołownia (PL2050) Deputy Marshals Senate Marshal Małgorzata Maria Kidawa- Błońska (PO) Deputy Marshals Executive President of Poland Andrzej Duda (I) Prime Minister of Poland Donald Tusk (PO) Cabinet Ministries Judiciary Supreme Court of Poland First President Małgorzata Manowska Constitutional Tribunal President …

Final Piala FA 1939TurnamenPiala FA 1938–1939 Portsmouth Wolverhampton Wanderers 4 1 Tanggal29 April 1939StadionStadion Wembley, LondonWasitTommy Thompson (Lemington, Newcastle upon Tyne)Penonton99.370← 1938 1946 → Final Piala FA 1939 adalah pertandingan sepak bola antara Portsmouth dan Wolverhampton Wanderers yang diselenggarakan pada 29 April 1939 di Stadion Wembley, London. Pertandingan ini merupakan pertandingan final ke-64 Piala FA sebagai pertandingan penentu pemenang musim 1…

PT Bakrie Indo Infrastructure TbkIndustriInfrastrukturDidirikan2008 (2008) di Jakarta, IndonesiaKantorpusatJakarta, IndonesiaTokohkunciAD Erlangga, Direktur Chandra Devi Muharam, Head Of Legal & Admin Krisnaraga Syarfuan, Direktur Bambang Banyudoyo, Direktur Bakrie Oil & Gas Infrastructure Ali Herman, Direktur Utama Bakrie Power.IndukBakrie & BrothersAnakusahaPT Bakrie Power PT Bakrie Oil & Gas Infrastructure PT Bakrie Toll Indonesia PT Bakrie Port Indonesia PT Bakrie Telco …
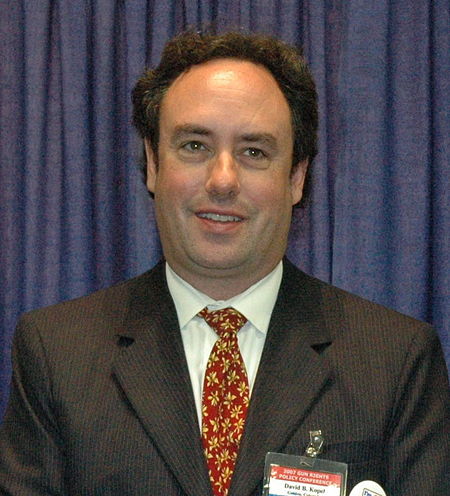

American journalist Dave KopelBornDavid B. Kopel (1960-01-07) January 7, 1960 (age 64)NationalityAmericanEducationBrown University (BA)University of Michigan Law SchoolOccupations Author attorney gun rights advocate journalist Political partyDemocraticWebsitedavekopel.org David B. Kopel[1] (born January 7, 1960) is an American author, attorney, gun rights advocate, and contributing editor to several publications. As of August 2021, he is research director of the Independence Institu…

Swedish rap metal band ClawfingerClawfinger performing in 2009. From left to right: André Skaug, Zak Tell, Micke Dahlénn, Jocke Skog and Bård Torstensen.Background informationOriginStockholm, SwedenGenres Rap metal[1] nu metal[2][3] industrial metal[4] alternative metal[5] Years active1989–2013, 2017–presentLabelsNuclear Blast, WEA/WMGMembersZak TellJocke SkogBård TorstensenAndré SkaugMicke DahlénPast membersHenka JohanssonErlend OttemMorten Skau…

Area between liver and right kidney Hepatorenal recessDetailsIdentifiersLatinrecessus hepatorenalis, recessus subhepaticiTA98A10.1.02.427TA23721FMA14715Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] The hepatorenal recess[1] (subhepatic recess, pouch of Morison or Morison's pouch) is the subhepatic space that separates the liver from the right kidney. As a potential space, the recess is not normally filled with fluid. However, fluid can collect here in circumstances where the abdomen fills…

Cinema of Poland List of Polish films Interwar Period Pre 1930 1930s 1940s 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s 2010s 2020svte List of films produced in the Cinema of Poland. For an A-Z list of films currently covered on Wikipedia see Polish films. Interwar List of films made in Poland in the Interwar Period 1902–1929 List of Polish films pre 1930 1930s List of Polish films of the 1930s 1940s List of Polish films of the 1940s 1950s List of Polish films of the 1950s 1960s List of Polish films of…

Державний комітет телебачення і радіомовлення України (Держкомтелерадіо) Приміщення комітетуЗагальна інформаціяКраїна УкраїнаДата створення 2003Керівне відомство Кабінет Міністрів УкраїниРічний бюджет 1 964 898 500 ₴[1]Голова Олег НаливайкоПідвідомчі орг�…

Boxing competitions Boxing at the 2023 SEA GamesVenueChroy Changvar Convention CentreLocationPhnom Penh, CambodiaDates6–14 MayCompetitors95 from 10 nations← 20212025 → Boxing competitions at the 2023 SEA Games took place in Chroy Changvar Convention Centre in Phnom Penh, Cambodia.[1][2] Medal table * Host nation (Cambodia)RankNationGoldSilverBronzeTotal1 Thailand921122 Philippines451103 Vietna…

















![First version used from 30 January 1980 to 9 May 1980.[18]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8d/Emblem_of_Iran_%281980%29.svg/150px-Emblem_of_Iran_%281980%29.svg.png)


