Energy in Myanmar
|

Delegate Joseph Marion Hernández of the Florida Territory, elected in 1822, the first Hispanic or Latino American to serve in the United States Congress in any capacity. Hispanic and Latino Americans have served in the United States Congress since the early 19th century. The first group elected to serve in the Congress were incorporated as part of the United States territorial expansion into previous Spanish territories of the North American mainland as part of American campaigns of Manifest de…

Ed ZoelverdiLahir(1943-03-12)12 Maret 1943Banda Aceh, Masa Pendudukan JepangMeninggal4 Januari 2012(2012-01-04) (umur 68)Jakarta, IndonesiaKebangsaanIndonesiaPekerjaanWartawan, fotografer, pengajarDikenal atasAhli Fotografi Ed Zoelverdi (12 Maret 1943 – 4 Januari 2012) adalah wartawan dan fotografer asal Indonesia. Ia yang mempopulerkan istilah Mat Kodak untuk juru foto.[1] Kehidupan Ed lahir dari keluarga Minangkabau yang berasal dari Koto Gadang, Agam, Sumatera Bar…

After Met YouPoster filmSutradaraPatrick EffendyProduserRaffi AhmadRoni PariniSkenarioPatrick EffendyHaqi AhmadCeritaAri IrhamDwitasariBerdasarkanAfter Met You karya Ari Irham dan DwitasariPemeranAri IrhamYoriko AngelineNaufan Raid AzkaYudha KelingWulan GuritnoSurya SaputraPenata musikHaris PranowoDimas WibisanaSinematograferFerry RusliPenyuntingDinda AmandaPerusahaanproduksiRA PicturesTanggal rilis 10 Januari 2019 (2019-01-10) Durasi107 menitNegaraIndonesiaBahasaBahasa IndonesiaPenda…

Peta menunjukan lokasi Balilihan Balilihan adalah munisipalitas yang terletak di provinsi Bohol, Filipina. Pada tahun 2007, munisipalitas ini memiliki populasi sebesar 18.380 jiwa. Pembagian wilayah Balilihan terbagi menjadi 31 barangay, yaitu: Baucan Norte Baucan Sur Boctol Boyog Norte Boyog Proper Boyog Sur Cabad Candasig Cantalid Cantomimbo Cogon Datag Norte Datag Sur Del Carmen Este (Pob.) Del Carmen Norte (Pob.) Del Carmen Weste (Pob.) Del Carmen Sur (Pob.) Del Rosario Dorol Haguilanan Gran…

HyenaPoster promosiHangul하이에나 GenreDramaHukumDitulis olehKim Roo-riSutradaraJang Tae-yooPemeranKim Hye-sooJu Ji-hoonNegara asalKorea SelatanBahasa asliKoreaJmlh. episode16ProduksiPengaturan kameraSingle-cameraDurasi70 menitRumah produksiKeyEastDistributorSBSNetflix[1]Rilis asliJaringanSBS TVFormat gambar1080i (HDTV)Format audioDolby DigitalRilis21 Februari (2020-02-21) –11 April 2020 (2020-4-11) Hyena (Hangul: 하이에나; RR: Haiena) adala…

ShōmuKaisar JepangBerkuasa3 Maret 724 – 19 Agustus 749PendahuluGenshōPenerusKōkenInformasi pribadiKelahiran700Kematian4 Juni 756(756-06-04) (umur 55–56)Nara, JepangPemakamanSahoyama no minami no misasagi (Nara)WangsaYamatoAyahKaisar MonmuIbuFujiwara no MiyakoPasangan Fujiwara no Asukabe-hime (Kōmyō) Agatainukai no Hirotoji Tachibana-no-Hirooka no Konakachi Anak Kaisar Wanita Kōken Pangeran Motoi Putri Inoe Putri Fuwa Pangeran Asaka Kaisar Shōmu (聖武天皇code: ja is deprecated…

24th chapter of the second part of the Book of Kings in the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament 2 Kings 24← chapter 23chapter 25 →The pages containing the Books of Kings (1 & 2 Kings) Leningrad Codex (1008 CE).BookSecond Book of KingsHebrew Bible partNevi'imOrder in the Hebrew part4CategoryFormer ProphetsChristian Bible partOld TestamentOrder in the Christian part12 2 Kings 24 is the twenty-fourth chapter of the second part of the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible or the Second Boo…

Sultanat de Sennar 1504–1821 Le sultanat de Sennar et ses voisins vers 1750Informations générales Statut Monarchie Capitale Sannar (après 1790) Langue(s) Arabe Monnaie Troc Histoire et événements 1504 Établissement 1821 Démantèlement Sultan (1e) 1504 Amara Dunqas (De) 1821 Badi VII Entités précédentes : Peuple Funj MakurieAlodie Entités suivantes : Égypte ottomane Khédivat d'Égypte modifier - modifier le code - voir Wikidata (aide) Le sultanat (des) Funj de Sennar éta…

Body of water Greenland SeaGreenland Sea icebergGreenland SeaLocationNorthern America and Northern EuropeCoordinates76°N 8°W / 76°N 8°W / 76; -8TypeSeaBasin countriesGreenland, Iceland, and NorwaySurface area1,205,000 km2 (465,300 sq mi)Average depth1,444 m (4,738 ft)Max. depth4,846 m (15,899 ft)Water volume1,747,250 km3 (419,000 cu mi)References[1][2] The Greenland Sea is a body of water that bord…

Wuhan MIRInfoWilayahWuhan dan sekitarnyaJenisKereta kecepatan tinggiOperasiDimulai2013OperatorKereta api Tiongkok/Kereta kecepatan tinggi TiongkokTeknisLebar sepur1.435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) sepur standarListrikAC 25 kV listrik aliran atas Peta rute Kereta antarkota Wilayah Metropolitan Wuhan Hanzi tradisional: 武漢城市圈城際軌道交通 Hanzi sederhana: 武汉城市圈城际轨道交通 Alih aksara Mandarin - Hanyu Pinyin: Wǔhàn Chéngshì Quān Chéngjì Guǐdà…

Arus Balik PengarangPramoedya Ananta ToerNegaraIndonesiaBahasaIndonesiaGenreFiksiPenerbitWira KaryaTanggal terbit17 Mei 2008Halaman724ISBNISBN 9789839960556 Arus Balik Arus Balik (1995) adalah novel sejarah karangan Pramoedya Ananta Toer yang menceritakan Kedatangan Portugis di Bumi Nusantara dengan latar awal Abad XVI, yaitu ketika surutnya pengaruh Majapahit dan naiknya pamor Kesultanan Demak. Tokoh utama dalam novel ini adalah Wiranggaleng, seorang pemuda desa yang ikut berjuang dalam In…

جزء من سلسلة عليالحرب التاريخ ما قبل التاريخ الحروب القديمة ما بعد الكلاسيكية أوائل العصر الحديث أواخر العصر الحديث الصناعية الجيل الرابع ساحة المعركة الجوية الإلكترونية المعلومات البرية المناطق الباردة الصحراء الغابة الجبال حضرية البحرية الفضاء الأسلحة المدرعات المدفع…
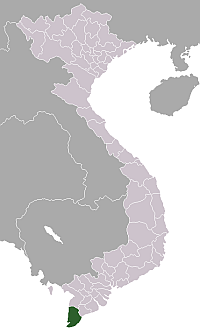
Cà Mau (Vietnam: [kaː˨˩ maw˧˧] simakⓘ) merupakan sebuah provinsi di Vietnam. Provinsi ini terletak di bagian selatan di negara itu. Provinsi ini memiliki luas wilayah 5.201 km² dengan memiliki jumlah penduduk 1.200.800 jiwa (2004). Provinsi ini memiliki angka kepadatan penduduk 230 jiwa/km². Provinsi ini terbagi menjadi 9 distrik yaitu Cai Nuoc, Phu Tan, Dam Doi, Ngoc Hien, Thoi Binh, Tran Van Thoi, U Minh. Pranala luar Situs resmi lbsPembagian administratif Vietnam Wila…

American criminal duo This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Harpe brothers – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2018) (Learn how…

1850 killing of over 40 Native Americans by Mormon settlers Provo River MassacreLocationProvo River, Rock Canyon, and Utah Lake near Provo, Utah[1]Coordinates40°15′18″N 111°39′58″W / 40.255°N 111.666°W / 40.255; -111.666DateFebruary 8–17, 1850TargetTimpanogos peopleAttack typeMass murderWeaponsGuns, cannonDeaths40–100 men and 1–2 woman; 1 militiaman killedPerpetratorsOrders of Brigham Young to the Mormon militiaMotiveRetaliation for cattle theft …

Cet article concerne la ville de Lausanne. Pour le bateau à vapeur du même nom, voir Lausanne (bateau à vapeur). Pour les articles ayant des titres homophones, voir Lauzanne et Lozanne. Lausanne De haut en bas et de gauche à droite : le musée olympique, la cathédrale de Lausanne, le Tribunal fédéral, vue aérienne de la ville et du parc de Milan. Blason Logo Administration Pays Suisse Canton Vaud District Lausanne Localité(s) Quartiers de Lausanne Communes limitrophes Bottens, …

Tyrone Power Tyrone Power (5 Mei 1914-15 November 1958) adalah aktor Amerika yang sangat terkenal pada zamannya.[1] Ia berasal dari keluarga yang berkecimpung di dunia teater dan selama beberapa waktu terjun ke bidang tersebut.[1] Lalu, ia pindah ke bidang radio bersama dengan Don Amache dan kembali lagi ke panggung sandiwara.[1] Film-filmnya yang terkenal antara lain Tom Brown of Culver (1932), Ladies in Love (1936), In Old Chicagao (1938), The Raine Came (1939), Mark of…

Dr. Ghananand Pandeडॉ. घनानंदा पांडेLahir(1902-01-01)1 Januari 1902Ranikhet, distrik Almora, UttarakhandKebangsaanIndiaPendidikanB.E. dalam bidang Teknik SipilAlmamater IIT Roorkee (saat itu Thomson College of Civil Engineering) Tempat kerja Ketua Railway Board (1954-57) Ketua Hindustan Steel (1957-60) Wakil Kanselir Universitas Roorkee (1961-66) Ghananand Pande (1 Januari 1902 – sebelum 1995)[1] adalah seorang ilmuwan India. Ia tak hanya menjabat di jabatan…

Branch of biology studying prenatal biology This article is about the development of embryos in animals. For the development of plant embryos, see Sporophyte. 1 - morula, 2 - blastula 1 - blastula, 2 - gastrula with blastopore; orange - ectoderm, red - endoderm Embryology (from Greek ἔμβρυον, embryon, the unborn, embryo; and -λογία, -logia) is the branch of animal biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos and fetu…

Canadian land designated as a First Nations reserve within an urban area The term Indian in this article refers to Indigenous peoples in Canada; not to be confused with Indian people from India Not to be confused with Indian colony or Little India. Indigenous peoplesin Canada First Nations Inuit Métis History Timeline Paleo-Indians Pre-colonization Genetics Residential schools gravesites Indian hospitals Conflicts First Nations Inuit Truth and Reconciliation Commission Politics Indigenous law B…
