Executive Order 10450
| |||||||||||||||

Bunda Maria jatuh pingsan saat Penyaliban, salinan dari Taddeo Zuccari Bunda Maria jatuh pingsan (Italia: Lo Spasimo della Vergine) adalah sebuah gagasan yang berkembang pada akhir Abad Pertengahan yang menyatakan bahwa Bunda Maria jatuh pingsan saat Kesengsaraan Yesus, sering kali ditempatkan saat ia menyaksikan Penyaliban Yesus. Gagasan tersebut berdasarkan pada penyebutan dalam teks-teks injil apokrifa Acta Pilati, yang menyatakan bahwa Maria jatuh pingsan. Gagasan tersebut menjadi populer da…

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento centri abitati del Giappone non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Aomoricittà青森市 Aomori – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Giappone RegioneTōhoku Prefettura Aomori SottoprefetturaNon presente DistrettoNon presente TerritorioCoordinate40°49′N 140°45′E / 40.816667°N 140.75°E40.…
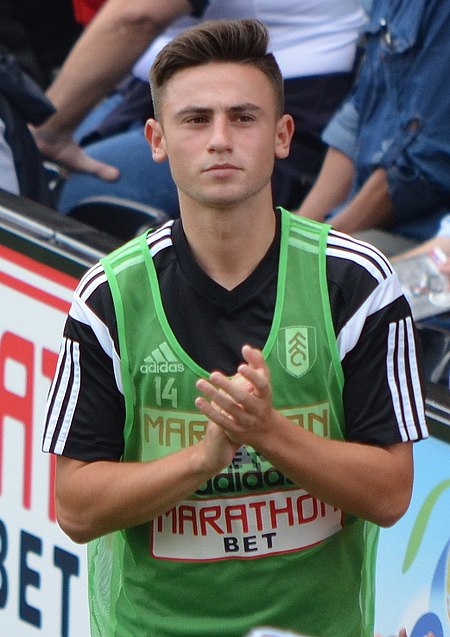

Patrick Roberts Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Patrick John Joseph Roberts[1]Tanggal lahir 5 Februari 1997 (umur 27)[2]Tempat lahir Kingston upon Thames, Inggris[2]Tinggi 1,67 m (5 ft 5+1⁄2 in)[2]Posisi bermain Penyerang Sayap Penyerang Kedua[2]Informasi klubKlub saat ini SunderlandNomor 10Karier junior000?–2010 AFC Wimbledon2010–2014 Fulham[2][3]Karier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2014–2015 Fulham 19 (0)2015�…

Nasi lemakNasi lemak yang disajikan bersama sambal cumi, sambal teri, teri kacang, separuh telur rebus, dan irisan mentimun.SajianHidangan utama, umumnya disajikan sebagai sarapanTempat asalMalaysia[1][2][3][4][5]DaerahDunia Melayu—meliputi Pulau Sumatra di Indonesia (terutama Sumatera Utara, Riau dan Kepulauan Riau), Semenanjung Malaya, Singapura, Brunei, Filipina Selatan, dan Thailand SelatanMasakan nasional terkaitMalaysiaDibuat olehOrang MelayuS…

Untuk pemain sepak bola Australia, lihat Jack Williamson (pemain sepak bola). Untuk uskup Anglikan, lihat Will Stewart (uskup). Untuk orang lain dengan nama yang sama, lihat John Williamson. Jack WilliamsonLahirJohn Stewart Williamson(1908-04-29)29 April 1908Bisbee, Teritorial Arizona, ASMeninggal10 November 2006(2006-11-10) (umur 98)Portales, New Mexico, ASNama penaWill StewartNils O. SonderlundPekerjaanPenulis, Profesor Sastra InggrisKebangsaanAmerikaPeriode1928–2006[1]Genr…
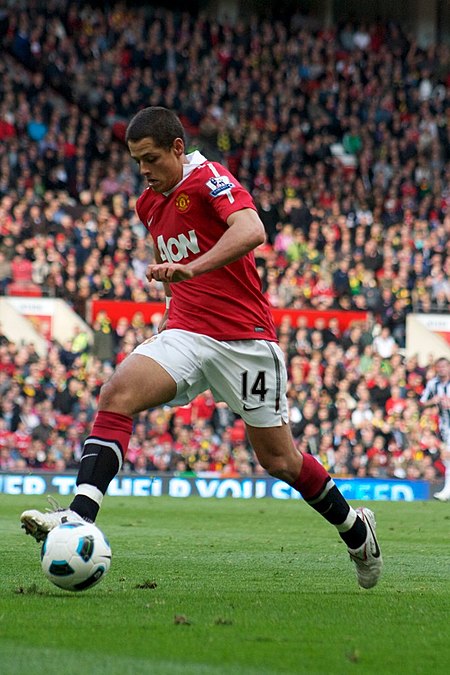

Nama ini menggunakan cara penamaan Spanyol: nama keluarga pertama atau paternalnya adalah Hernández dan nama keluarga kedua atau maternalnya adalah Balcázar. Javier Hernández Hernández pada tahun 2019Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Javier Hernández Balcázar[1]Tanggal lahir 1 Juni 1988 (umur 35)[2]Tempat lahir Guadalajara, MeksikoTinggi 1,75 m (5 ft 9 in)[3]Posisi bermain PenyerangKarier junior1997–2005 GuadalajaraKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tamp…

Rene Seebacher Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Rene SeebacherTanggal lahir 24 Juli 1988 (umur 35)Tempat lahir Klagenfurt, AustriaPosisi bermain BekInformasi klubKlub saat ini Admira WackerNomor 23Karier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2007–2008 Kärnten 30 (0)2010– Admira Wacker 21 (0)2010–2011 → TSV Hartberg (pinjaman) 44 (0) * Penampilan dan gol di klub senior hanya dihitung dari liga domestik dan akurat per 20:26, 17 August 2011 (UTC) Rene Seebacher (lahir 24 Juli 1988) adalah pe…

Grand Prix Kanada 2017 Lomba ke-7 dari 20 dalam Formula Satu musim 2017← Lomba sebelumnyaLomba berikutnya → Tata letak Sirkuit Gilles Villeneuve.Detail perlombaanTanggal 11 Juni 2017Nama resmi Formula 1 Grand Prix du Canada 2017[1][2][3]Lokasi Sirkuit Gilles VilleneuveMontreal, Quebec, KanadaSirkuit Sirkuit jalan rayaPanjang sirkuit 4.361 km (2.710 mi)Jarak tempuh 70 putaran, 305.270 km (189.686 mi)Cuaca Cerah dan panas dengan suhu yang mencapai 29…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. I've Fallen For YouGenreKomedi romansa SejarahBerdasarkanJin Xin Jioleh Han XuefeiDitulis olehZhou Tong Dai MengyingSutradaraZhou Tong Dai MengyingPemeranYu Shuxin Liu Yichang Lou Mingjie Chen HaolanNegara asalTiongkokBahasa asliMandarinJmlh. musim2Jmlh.…

Further information: 4th millennium BC, 3rd millennium BC, and 2nd millennium BC This article or section possibly contains synthesis of material which does not verifiably mention or relate to the main topic. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. (October 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and …

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Dua dashcam Dashcam, kamera dashboard, DVR mobil, perekam kemudi atau event data recorder (EDR) adalah sebuah kamera onboard yang terus merekam pemandangam dari layar depan kendaraan dan terkadang layar belakang atau jendela lainnya. Beberapa dashcam meli…

Pandemi COVID-19 di AntarktikaPenyakitCOVID-19Galur virusSARS-CoV-2LokasiAntarktikaKasus pertamaBase General Bernardo O'Higgins, Teritorial Antarktika ChiliTanggal kemunculan21 Desember 2020(3 tahun, 2 bulan dan 4 hari ago)AsalWuhan, Hubei, TiongkokKasus terkonfirmasi58 Pandemi COVID-19 di Antarktika adalah bagian dari pandemi seluruh dunia penyakit koronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) yang disebabkan oleh sindrom penapasan akut berat koronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Karena terpencil, Antarktik…

SirCharlie ChaplinKBEChaplin sekitar tahun 1920-anLahirCharles Spencer Chaplin(1889-04-16)16 April 1889 Walworth, London, Britania RayaMeninggal25 Desember 1977(1977-12-25) (umur 88) Manoir de Ban, Distrik Riviera-Pays-d'Enhaut, Vaud, SwissMakamCimetière de Corsier-sur-Vevey, Corsier-sur-Vevey, Distrik Riviera-Pays-d'Enhaut, Vaud, SwissPekerjaanPemeranSutradaraKomposerPenulis skenarioProduserPenyuntingTahun aktif1899–1976Suami/istriMildred Harris (m. 1918…
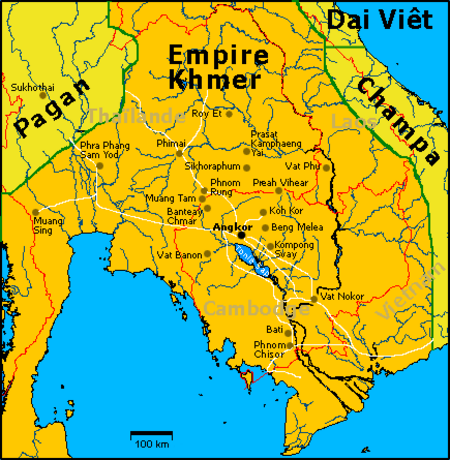
Kerajaan Khmerចក្រភពខ្មែរ802–1431 Bendera900 AD Merah:Kerajaan Khmer Hijau : Haripunjaya Kuning: ChampaStatusKekaisaranIbu kotaYasodharapura Hariharalaya AngkorBahasa yang umum digunakanKhmer Lama SanskritAgama Hindu Buddha Mahayana Buddha TheravadaPemerintahanMonarki absolutRaja • 802–850 Jayawarman II• 1113–1150 Suryavarman II• 1181–1218 Jayawarman VII• 1393–1463 Ponhea Yat Era SejarahAbad Pertengahan• Suksesi dari Ch…

2005 single by Slipknot The NamelessSingle by Slipknotfrom the album 9.0: Live ReleasedNovember 1, 2005RecordedAugust 22, 2005VenueHouse of Blues (Las Vegas)Length3:44LabelRoadrunnerSongwriter(s) Shawn Crahan Chris Fehn Paul Gray Craig Jones Joey Jordison Jim Root Corey Taylor Mick Thomson Sid Wilson Producer(s)Joey JordisonSlipknot singles chronology Before I Forget (2005) The Nameless (2005) The Blister Exists (2006) Music videoThe Nameless on YouTube The NamelessSong by Slipknotfrom the album…

Kota Taoyuan di Republik Tiongkok Kota Taoyuan (Hantzu: 桃園市; Tongyong Pinyin: Táoyuán Shì; Taiwanese POJ: Thô-hn̂g-kōan; Jhuyin Fuhao: ㄊㄠˊ ㄩㄢˊ ㄒㄧㄢˋ) adalah sebuah kota di Taiwan, Republik Tiongkok. Secara geografis, kota ini terletak di Taiwan bagian utara, berbatasan dengan: Utara: Selat Taiwan Timur: Kota Taipei Baru Selatan: Kabupaten Yilan dan Kabupaten Hsinchu Barat: Kabupaten Hsinchu Di kota ini pula terletak Bandar Udara Internasional Taoyuan Taiwan yang merup…

1919 film The Sheriff's SonPosterDirected byVictor SchertzingerScreenplay byJ.G. HawksWilliam MacLeod RaineProduced byThomas H. InceStarringCharles RaySeena OwenJ. P. LockneyCharles K. FrenchOtto HoffmanLamar JohnstoneCinematographyChester LyonsProductioncompanyFamous Players–Lasky CorporationDistributed byParamount PicturesRelease date March 30, 1919 (1919-03-30) Running time50 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguagesSilentEnglish intertitles The Sheriff's Son is a 1919 American si…

Sporting event delegationSouth Korea at the2012 Summer OlympicsIOC codeKORNOCKorean Olympic CommitteeWebsitewww.sports.or.kr (in Korean and English)in LondonCompetitors248 in 22 sportsFlag bearers Yoon Kyung-shin (opening)Song Dae-nam (closing)MedalsRanked 5th Gold 13 Silver 9 Bronze 8 Total 30 Summer Olympics appearances (overview)19481952195619601964196819721976198019841988199219962000200420082012201620202024 South Korea (officially the Republic of Korea) competed at the 2012 Summer …

2009 video game For the 2020 remake, see Demon's Souls (2020 video game). 2009 video gameDemon's SoulsPackaging artwork used for most regionsDeveloper(s)FromSoftware[a]Publisher(s)JP: Sony Computer EntertainmentNA: Atlus USAPAL: Namco Bandai PartnersDirector(s)Hidetaka MiyazakiProducer(s)Masanori TakeuchiTakeshi KajiiDesigner(s)Takashi NakamuraProgrammer(s)Jun ItoArtist(s)Makoto SatohMasato MiyazakiHisao YamadaComposer(s)Shunsuke KidaPlatform(s)PlayStation 3ReleaseJP: February 5, 200…

American politician Senator Downey redirects here. For the New York State Senate member, see John V. Downey. Sheridan DowneyDowney in 1939United States Senatorfrom CaliforniaIn officeJanuary 3, 1939 – November 30, 1950Preceded byThomas M. StorkeSucceeded byRichard Nixon Personal detailsBorn(1884-03-11)March 11, 1884Laramie, Wyoming, U.S.DiedOctober 25, 1961(1961-10-25) (aged 77)San Francisco, California, U.S.Political partyDemocraticSpouseHelen SymonsChildren5Alma materUniversity…

