Floyd Lavinius Parks
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Diva (disambiguasi). Diva Diva (Aksara Ibrani: דיווה) adalah lagu pemenang Kontes Lagu Eurovision 1998 yang dinyanyikan dengan bahasa Ibrani oleh Dana International yang mewakili Israel. Lagu ini diciptakan oleh Tzvika Pick, dan lirik diciptakan oleh Yoav Ginai. Lagu ini mendapat nilai 172 poin dalam pemilihan. Pranala luar Lyrics of Diva Artikel bertopik lagu, musik, atau alat musik ini adalah sebuah rintisan. Anda dapat membantu Wikipedia dengan mengembangkannya…

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut). …

American politician Frank B. KlepperMember of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom Missouri's 3rd districtIn officeMarch 4, 1905 – March 3, 1907Preceded byJohn DoughertySucceeded byJoshua Willis Alexander Personal detailsBorn(1864-06-22)June 22, 1864Cameron, MissouriDiedAugust 4, 1933(1933-08-04) (aged 69)Liberty, MissouriPolitical partyRepublican Frank B. Klepper (June 22, 1864 – August 4, 1933) was a U.S. Representative from Missouri. Born in St. John, Putnam Cou…

Bayinnaung Raja Burma Hanthawaddy (1552–1581)Ava (1555–1581)Negara Shan (1557–1581)Manipur (1560–1581)Kerajaan Mao Shan China (1562–1581)Arakan Selatan (1580–1581) Berkuasa30 April 1550 – 10 Oktober 1581Penobatan11 Januari 1551 di Toungoo 12 January 1554 at PeguPendahuluTabinshwehtiPenggantiNandaKetua MenteriBinnya Dala (1559–1573)Kaisar LannaBerkuasa2 April 1558 – 10 Oktober 1581PendahuluJabatan baruPenerusNandaRajaMekuti (1558–1563) Visuddhadevi (1565–1579) Nawrahta Minsa…

Katedral CumanáKatedral Metropolitan Hati Kudus YesusSpanyol: Catedral Metropolitana del Corazón de JesúsKatedral CumanáLokasiCumanáNegaraVenezuelaDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaArsitekturStatusKatedralStatus fungsionalAktifAdministrasiKeuskupan AgungKeuskupan Agung Cumaná Katedral Cumaná[1][2] (Spanyol: Catedral Metropolitana de Cumaná) disebut juga Katedral Metropolitan Cumaná adalah sebuah gereja katedral Katolik yang terletak di Rivas jalan di seberang Plaza An…

Letak Fayetteville di Carolina Utara Fayetteville merupakan sebuah kota di Amerika Serikat. Kota ini letaknya di bagian timur. Tepatnya di negara bagian Carolina Utara. Pada tahun 2010, kota ini memiliki jumlah penduduk sebesar 200.564 jiwa dan memiliki luas wilayah 155,3 km². Kota ini memiliki angka kepadatan penduduk sebesar 795,1 jiwa/km². Pranala luar Wikimedia Commons memiliki media mengenai Fayetteville, North Carolina. Official Fayetteville, NC website Diarsipkan 2011-05-11 di Wayb…

نصوح النكدلي معلومات شخصية الميلاد 15 يونيو 1993 (العمر 30 سنة)حمص الطول 1.70 م (5 قدم 7 بوصة) مركز اللعب مهاجم الجنسية سوريا معلومات النادي النادي الحالي تشرين مسيرة الشباب سنوات فريق الكرامة المسيرة الاحترافية1 سنوات فريق مشاركات (أهداف) 2010–2014 الكرامة 2012 →زاخو (إعارة) 17…

Bürgerhaus Hauptstraße 43 Portalschmuck Das Haus Hauptstraße 43 in Gundelfingen an der Donau, einer Stadt im schwäbischen Landkreis Dillingen an der Donau in Bayern, wurde in der zweiten Hälfte des 18. Jahrhunderts errichtet. Das Gebäude ist ein geschütztes Baudenkmal. Architektur Das zweigeschossige Giebelhaus mit fünf Achsen wurde in der zweiten Hälfte des 18. Jahrhunderts errichtet. Es besitzt einen glatten Giebel mit Profilrand, das Traufgesims ist an der Giebelfassade ver…

A small tectonic plate in the Mediterranean Geology of the AlpsThe Alps Tectonic subdivision Helvetic Zone Penninic nappes Austroalpine nappes Southern Alps Formation & rocks Bündner schist flysch molasse Geological structures Aarmassif Dent Blanche klippe Engadine Line Engadine window Flysch zone Giudicárie line Greywacke zone Hohe Tauern window Molasse basin Penninic thrustfront Periadriatic Seam Ivrea zone Lepontin dome Rechnitz window Rhône-Simplon line Sesia unit Paleogeographic term…

When potential energy difference depends only on displacement This article is about a general description of a function used in mathematics and physics to describe conservative fields. For the scalar potential of electromagnetism, see electric potential. For all other uses, see potential. In mathematical physics, scalar potential, simply stated, describes the situation where the difference in the potential energies of an object in two different positions depends only on the positions, not upon t…

2015 single by XXXTentacion Look at Me! redirects here. For other uses, see Look at Me. Look at Me!The single's cover art of the Empire release, XXXTentacion's mugshotSingle by XXXTentacionfrom the album Revenge Released December 30, 2015 (SoundCloud) January 29, 2016 (iTunes) February 20, 2017 (Empire re-release) Recorded2015GenreTrap metal[1]lo-fi[2][3][4]Length 2:31 (original) 2:06 (Revenge re-release) 2:19 (clean version) LabelEmpireSongwriter(s) Jahseh Onfroy…
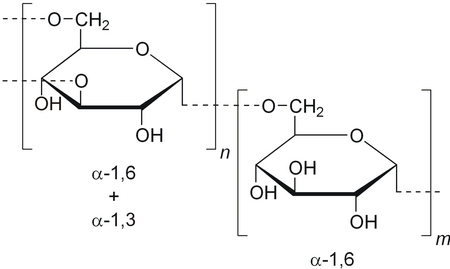
Dekstran Dekstan merupakan polisakarida (salah satu jenis dari karbohidrat) yang memiliki rantai cabang monosakarida yaitu glukosa.[1] Dekstran dibentuk dari aktivitas bakteri yang membentuk (suatu lapisan tipis, lengket pada area gigi) akibat banyaknya konsentrasi sukrosa yang akan berakibat pada kesehatan gigi.[1] Cairan dekstran sintetik komersial digunakan untuk operasi, atau pengobatan darurat terhadap shock, untuk meningkatkan volume plasma darah dalam sirkulasi darah.[…

Questa voce sull'argomento cestisti statunitensi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. A.J. Davis Nazionalità Stati Uniti Altezza 198 cm Peso 95 kg Pallacanestro Ruolo Guardia / ala piccola Termine carriera 2020 CarrieraGiovanili Linden-McKinley High School2007-2008Harmony Community School2008-2010 Wyoming Cowboys2011-2013 JMU DukesSquadre di club 2013-2014 S. Falls Skyforce…

Small comb and article of faith for Sikhs Not to be confused with Khanga. Kangha – one of the five articles of faith for the Sikhs Part of a series onSikhism People Topics Outline History Glossary Sikh gurus Guru Nanak Guru Angad Guru Amar Das Guru Ram Das Guru Arjan Guru Hargobind Guru Har Rai Guru Har Krishan Guru Tegh Bahadur Guru Gobind Singh Guru Granth Sahib Selected revered saints Bhagat Kabir Bhagat Ravidas Bhagat Farid Bhagat Ramanand Bhagat Beni Bhagat Namdev Bhagat Sadhana Bhagat Bh…

Family name Ó Caoimh arms O'Keeffe (Irish: Ó Caoimh) is an Irish Gaelic clan based most prominently in what is today County Cork, particularly around Fermoy and Duhallow. The name comes from caomh, meaning kind, gentle, noble Some reformed spellings present it as Ó Cuív and the feminine form of the original is Ní Chaoimh, as the primary sept of the Eóganacht Glendamnach, the family were once Kings of Munster from the 6th to the 8th centuries. Naming conventions Main article: Irish personal…

Part of the War of the Pacific (1879–1880) For the boundary dispute that was settled in 1929, see Treaty of Lima (1929). Tacna and Arica campaignPart of War of the PacificMovements and battles during the Tacna and Arica campaign.DateDecember 1879 – July 1880LocationDepartment of Tacna and Province of Arica, Peru (Arica currently from Chile)Result Chilean victory Chile obtains control of the territories of Tacna and Arica.Belligerents Chile Peru BoliviaCommanders and leaders Erasmo Escala Man…

إيفلين كولير معلومات شخصية اسم الولادة (بالإنجليزية: Evelyn Lucy Munro) الميلاد 16 أغسطس 1902(1902-08-16)إنجلترا الوفاة 6 نوفمبر 1930 (28 سنة)الهند الجنسية المملكة المتحدة الحياة العملية التقاعد 1930 بلد الرياضة المملكة المتحدة تعديل مصدري - تعديل إيفلين كولير (بالإنجليزية: Evelyn…

Stasiun Shimo-Ichida下市田駅Stasiun Shimo-Ichida, Juni 2008LokasiShimoichida, Takamori-machi, Shimoina-gun, Nagano-ken 399-3103 JepangKoordinat35°32′39″N 137°52′36″E / 35.5442°N 137.8766°E / 35.5442; 137.8766Koordinat: 35°32′39″N 137°52′36″E / 35.5442°N 137.8766°E / 35.5442; 137.8766Ketinggian435 meter[butuh rujukan]Operator JR CentralJalur Jalur IidaLetak135.6 km dari ToyohashiJumlah peron1 peron sisiInform…

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع النواصر (توضيح). النواصر - قرية - تقسيم إداري البلد اليمن المحافظة م�…

1808–09 United States Senate elections ← 1806 & 1807 Dates vary by state 1810 & 1811 → 12 of the 34 seats in the United States Senate (plus special elections)18 seats needed for a majority Majority party Minority party Party Democratic-Republican Federalist Last election 27 seats 7 seats Seats before 28 6 Seats won 8 4 Seats after 27 7 Seat change 1 1 Seats up 9 3 Results: Federalist hold &#…



