|
George Bellas Greenough
George Bellas Greenough FRS FGS (18 January 1778 – 2 April 1855) was a pioneering English geologist. He is best known as a synthesizer of geology rather than as an original researcher. Trained as a lawyer, he was a talented speaker and his annual addresses as founding president of the Geological Society of London were influential in identifying and guiding contemporary geological research. He also courted controversy, after using his presidential address in 1834 to cast aspersions on a paper on great earthquakes by Maria Graham.[1] Greenough advocated an empirical approach to the early science; his scepticism of theoretical thinking courted controversy amongst some contemporaries, especially his doubts of the usefulness of fossils in correlating strata. He compiled a geological map of England and Wales, published in 1820, and in the penultimate year of his life used similar methods to produce the first geological map of British India. Greenough characterised himself as follows: ʻbright eyes, silver hair, large mouth, ears and feet; fondness for generalisation, for system and clearliness; great diligence, patience and zeal; goodnature but hasty; firmness of principle; hand for gardening.ʼ[2] Early lifeGreenough was born in London, as George Bellas, named after his father, George Bellas, who had a profitable business in the legal profession as a proctor in Doctor's Commons, St Paul's Churchyard Doctors' Commons and some real estate in Surrey. His mother was the only daughter of the apothecary Thomas Greenough, whose very successful business was located on Ludgate Hill near to St Paul's. A younger brother died in infancy.[3] At the age of six he was orphaned with his father dying first, and the cause, recorded by Greenough in a biographical sketch, was 'By neglect of business, by carelessness, extravagance, dissipation and by party zeal, my father's fortune was soon squandered away—family dissention followed; his constitution was broken, his prospects blighted and he died of decline at Clifton in 1784'.[4] His mother followed only a few months later.[3] He was adopted by his maternal grandfather, who had made a fortune through selling popular preparations, the most popular of which were "Pectoral Lozenge from Balsam of Tolu", for coughs and colds, and various tinctures for cleaning teeth and gums and curing tooth ache.[5][6] His grandfather sent him to Mr Cotton's school at Salthill near Slough and then to Eton at the age of ten. He stayed there only one year, suggesting he was perhaps too delicate a child for the robust life at the boarding schools of the day. In September 1789 he entered Dr Thompson's school at Kensington where he studied for the next six years. Whilst he was at school he took the name Greenough at the request of his grandfather.[3] EducationHe left school in 1795 and went up to Pembroke Hall, Cambridge to study law for three years, but he did not take a degree.[7][8] In September 1798, he went to the University of Göttingen to continue his legal studies, thinking that the lectures would be in Latin, but found instead they were all in German. In order to improve his language skills Greenough attended the lectures of Johann Friedrich Blumenbach on natural history and these inspired a passion for mineralogy and geology. At Göttingen Samuel Coleridge was one of his closer friends. A few years later, Greenough was instrumental in securing a government post for Coleridge during his period in Malta.[9] In 1799, Greenough made at least two tours of the Harz; one in the Easter vacation with Clement Carlyon and Charles and Frederic Parry; and the other in the late summer with Carlyon and Coleridge. These tours were mainly to collect minerals, but he also studied geological collections in the towns he visited.[10] In 1801, Greenough returned to England and his interest in geology deepened when he toured England with Carlyon and met Humphry Davy in Penzance. Later he attended Davy's lectures at the Royal Institution in London. The following year he travelled to France and Italy and 'noted what I saw of geology on my way'.[4] He went on a geological tour of Scotland with James Skene in 1805,[10] and of Ireland with Davy in 1806. On the Ireland tour he also made a study of social conditions which aroused a deep interest in political questions. Politics1807 was a significant year for Greenough as this was the founding year of the Geological Society in which he deployed considerable political skill in its establishment and its subsequent organisation and debates on controversial aspects of the emerging science. He was elected member of parliament for the ("rotten"[11]) borough of Gatton, continuing to hold this seat until 1812,[8] although Hansard does not record he made any contributions to the House. During the time he helped to found and forge the Geological Society, Greenough served in the militia in the Light Horse Volunteers of London and Westminster. This was a corps of volunteers, originated by a group of city businessmen, and rather than being paid for their services members had to pay to join and maintain an annual subscription. The unit has an obligation to be called out in support of the civil power when necessary. It was rather different from other regiments in organising itself democratically through a committee. All prospective members had to be proposed by one of the committee and if admitted all served as private soldiers, with officers elected by ballot. Greenough enlisted as a private soldier in 1803, but in 1808 he was elected a commissioned officer with the rank of Lieutenant and he served for the next 11 years. Greenough resigned his commission in 1819 as a matter of principle following the Peterloo massacre in Manchester, which he regarded as an abuse of military power for political ends. He published his resignation letters in The Morning Chronicle and The Times. Clearly, Greenough was a man of conscience.[12] GeologyIn 1807 Greenough's interest in science in general, and geology in particular, increased : he joined a number of eminent scientific and cultural societies and he was elected fellow of the Royal Society. He also became associated with a group of mineralogists to which Davy referred in a letter to William Pepys, dated 13 November 1807, when he said 'We are forming a little talking Geological Club'. This club rapidly developed into a learned society devoted to geology and Greenough became the chief founder with others of the Geological Society of London. He was the first chairman of that Society, and in 1811, when it was more regularly constituted, he was the first president. In this capacity he served on two subsequent occasions, and did much to promote the advancement of geology.[10][8] In 1819, he published A Critical Examination of the First Principles of Geology,[13] a work which was useful mainly in refuting erroneous theories. In the following year, the Geological Society issued his famous Geological Map of England and Wales, in six sheets[8] (published 1 May 1820, although the date 1 November 1819 appears on the map). A second edition was issued in 1840 (the date on this map is 1 November 1839) and a third edition was published in 1865. 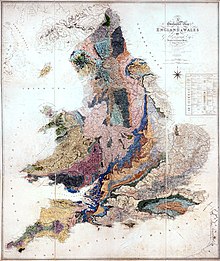 This map was the culmination of a major cooperative project of the early Geological Society, who had established a Committee of Maps in April 1809, led by Greenough. Members of the society out in the provinces of England and Wales submitted details of local rocks and strata which were collated by Greenough, entered in his notebooks and plotted on a topographical map. Greenough was an inductivist in the Baconian tradition, so he eschewed 'theory' and systematically collected information and details with the aim of discovering the distribution of rocks.[14] Greenough received assistance in the collection of his geological facts chiefly from William Buckland, Reverend W. D. Conybeare, Henry Warburton, and Thomas Webster, and amongst others from Henry Thomas De la Beche, John Farey, the Rev. J. Hailstone, David Mushet, Thomas Biddle and Arthur Aikin.[15] A first draft of the geological map was presented to the Geological Society as early as 1812, but there was dissatisfaction with the quality of the engraving of the topographical map, resulting in the base map not being ready until 1814. In 1815, William Smith published his famous geological map and when Greenough finally published his map five years later[16] it was clear he was heavily indebted to Smith's work in delineating strata (although not acknowledged and thus plagiarized until the 1865 edition); nevertheless Greenough's map contained more geological detail and was better cartographically.[17] Smith had relied on a theory about the linear arrangement of strata identified by characteristic fossils to extrapolate from his observations (Smith himself was indebted to John Strachey's theory of strata for his ideas[18]), and so was able to map out the distribution of strata across the country. Greenough, on the other hand, did not go by theory, and this aversion was probably one of the factors that delayed the preparation of his map. It has been claimed that Greenough and the Geological Society failed to work with William Smith in the production of a geological map due to snobbishness,[19] but Rachel Lauden argues that a more compelling reason is that Greenough did not consider that fossils could reveal anything about the nature of rocks.[20] Greenough (incorrectly) considered that fossils had been very overrated in their usefulness, as fossil species were different from modern species, so fossils could not be used to 'theorise' about or deduce the relative age and the conditions of deposition of the rocks. Indeed, he was suspicious of the concepts of 'stratum' and 'formation', much used by Smith. For this reason Greenough wanted to dissociate himself and the Geological Society map from the man who was using fossils to identify strata. Seemingly, Greenough had intellectual reasons rather than primarily social reasons for not collaborating with Smith.[21] This did not, however, stop Greenough from using Smith's map as a source of material for the Geological Society's version of the map and there is debate about how much Smith's map influenced Greenough.[22] Both maps now hang side by side on the main staircase in the entrance hall of The Geological Society apartments in Burlington House, London.[23] An anonymous 1855 obituarist noted that Greenough's geology was based mainly on "mineralogical views" and that his habitual skepticism of new theories made him a "drag" on the progress of geological science.[3][11] A common narrative in some recent accounts of William Smith's life and his map asserts that rivalry built up between Greenough and Smith.[24][25][26] However original sources point to this narrative not being the case and indicate Smith was used by John Farey Sr., another 'practical man'(i.e. mineral surveyor), to prosecute Farey's own grievances against the Geological Society in an article in The Philosophical Magazine by which he both started and fuelled the story that Smith was disrespected and there was ill-feeling towards him by the Geological Society men and Greenough in particular.[27] In the following issue Greenough replied, publicly declaring his view as being non-antagonistic by stating: "Your correspondent considers me, in common with many other persons, actuated by feelings of hostility towards Mr. Smith. Now my feelings towards that gentleman are directly the reverse. I respect him for the important services he has rendered to geology, and I esteem him for the example of dignity, meekness, modesty, and candour, which he continually, though ineffectually, exhibits to his self-appointed champion."[28] Another common but misleading narrative in some recent accounts of Smith's map has Greenough's 1820 map undercutting the price and sales of Smith's map, thereby citing Greenough as a primary cause of landing Smith in Debtors' prison. However, Greenough's map could not have contributed to the debts for which Smith was consigned to prison as the Greenough map, although dated 1819 on the map, was not published until May 1820, after Smith's incarceration. In fact Smith's maps retailed at 5 guineas, which was the same price as that privileged to Geological Society members for purchase of the Greenough 1820 map. However the Greenough map retailed to public at 6 guineas, thereby being a more expensive purchase than Smith's map.[29] Also, the number of sales of Smith's map appears to have topped those of Greenough's map (196 copies sold), although neither map sold well and there are only 15 names in common between Smith's subscribers' list and the list of those who bought the Geological Society's map.[30]  In 1843, he started to prepare a geological map of British India. This was possibly inspired by Roderich Murchison's presidential address in which he lamented the lack of a geological map of India. In 1852 Greenough produced a series of maps of Hindustan, mainly hydrographical, defining all the important elements of the ten water basins of the Indian Peninsula (for the Asiatic Society), and in 1854 a large-scale geological map of the whole of British India, published as a 'General Sketch of the Physical and Geological Features of British India.[31] Greenough never visited India but much as he had done for his earlier maps of England and Wales, he compiled his map from scraps of information gathered from many observations of officers in the East India Company who were provided forms to submit. He was assisted in this effort by Colonel William Henry Sykes of the East India Company and sixty copies of the map were purchased by the company for distribution.[32][33] One of Greenough's key strengths was his assiduous ability to collect and collate information for his empirical cause. However, this 'remote' method of map construction resulted in 53 errors on his India map, some topographical as well as geological and palaeontological, that were listed by a committee led by Thomas Oldham, Director of the Geological Survey of India, in 1856.[34] Nevertheless, Greenough's geological map of India was a pioneering effort.[35] Greenough was an active supporter of many important learned scientific societies existing in the first half of the nineteenth century. In 1831 he was one of the prime movers in establishing the British Association for the Advancement of Science (now the British Science Association). He helped found the Geographical Society of London in 1830 (later to become the Royal Geographical Society), being elected to its first council and serving as president from 1839 to 1841. Greenough was an early advocate for physical geography and the accurate delineation of physical features thereby "endeavouring to give a more scientific character to the proceedings of the Royal Geographical Society".[36] Greenough's connections and travels with Romantics of the period led to him realizing that artistic representations of physical features were imbued with emotional responses and representation which did not mix well with accuracy. On a trip through Switzerland in 1802 he noted that Mont Blanc is very difficult to reproduce artistically. He wrote: "A list of facts drawn up by a simple cold-blooded mathematician who has travelled through the country with his quadrant in his hand! may be better than a painter's sketch." Nevertheless, the influence of the Romantic poets is evident in his travels as his notebooks show how Greenough also found pleasure in allowing imagination and emotion to colour his response to grand landscapes.[37] Greenough followed the system of Sir Joseph Banks to have weekly open hours for scientific meetings at his residence (first in Parliament Street and later at Grove House).[32] ResidenceIn 1822 he built himself a villa in Regent's Park, designed by Decimus Burton, which was his home for the remainder of his life. In 1827 this was included in a series of drawings of villas in the park by Thomas H. Shepherd, although the dedication misspells the owner's name as "Greenhough". The house, now known as Grove House and structurally modified in the years since Greenough's death, stands on Prince Albert Road, NW1, with its gardens alongside the Regents Canal, which separates the property from the main part of the park. Death and legacy Greenough travelled on journeys to the continent throughout his life and at the age of 76 he set off for Italy and the East (Constantinople) with a view of connecting the geology of his researches on the geology of India with that of Europe, but he was taken ill en route with oedema ("dropsy"), probably caused by cardiac problems, and died at Naples on 2 April 1855.[32] He is buried in Kensal Green Cemetery, North London. The grave lies on the south side of the main east–west path. A marble bust by Sir Richard Westmacott commissioned for one hundred pounds in 1842 is now in the Geological Society of London.[32][38] Greenough bequeathed his fossil collection to the Geology Department at University College London (UCL) and his notebooks are in the Greenough Papers collection held at UCL Library. The student geological society at UCL is named after Greenough.[39] The Greenough River in Western Australia was so-named in 1839 by Captain George Grey, after Greenough sponsored his exploration north of Perth. Successful wheat production in the area helped establish the small town of Greenough.[40] Selected writings
References
Attribution
External links
|
||||||||||||||

