Glenn Research Center
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando lo scrittore e giornalista, vedi Paolo Negro (scrittore). Paolo Negro Negro alla Lazio nella stagione 1995-1996 Nazionalità Italia Altezza 182 cm Peso 73 kg Calcio Ruolo Allenatore (ex difensore) Termine carriera 2011 - giocatore Carriera Giovanili 1986-1988 Chiampo1988-1990 Brescia Squadre di club1 1989-1990 Brescia0 (0)1990-1992 Bologna49 (0)1992-1993 Brescia26 (1)1993-2005 Lazio264 (19)2005-2007 Siena50 (4)2010-201…

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri aeroporti di Manchester o con nomi simili, vedi Aeroporto di Manchester (disambigua). Aeroporto di ManchesteraeroportoL'aeroporto. Codice IATAMAN Codice ICAOEGCC Nome commercialeManchester International Airport DescrizioneTipoCivile GestoreManchester Airport Group Stato Regno Unito Regione/area/distrettoManchester PosizioneGreater Manchester Base Aer Lingus UK easyJet Jet2 Ryanair Virgin Atlantic TUI Altitudine78 m s.l.m. Coordinate53°21…

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (يوليو 2023) نابليون جوزيف شارل بول بونابارت (بالفرنسية: Napoléon Joseph Charles Paul Bonaparte)، و(بالفرنسية: Napoléon-Jérôme Bonaparte) معلو…

Para wartawan yang sedang bertugas. Wartawan atau pewarta (Inggris: journalist) adalah orang yang melakukan pekerjaan kewartawanan dan atau tugas-tugas jurnalistik secara rutin, atau dalam definisi lain, wartawan dapat dikatakan sebagai orang yang pekerjaannya mencari dan menyusun berita, baik dalam media cetak, media elektronik, maupun media daring. Seseorang yang melakukan pekerjaan kewartawanan, kegiatan kewartawanan secara rutin atau orang yang secara teratur menuliskan berita (berupa la…

Chronologie de la France ◄◄ 1666 1667 1668 1669 1670 1671 1672 1673 1674 ►► Chronologies Portrait mythologique de la famille de Louis XIV, Jean Nocret, 1670.Données clés 1667 1668 1669 1670 1671 1672 1673Décennies :1640 1650 1660 1670 1680 1690 1700Siècles :XVe XVIe XVIIe XVIIIe XIXeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies thématiques Art Architecture, Arts plastiques (Dessin, Gravure, Peinture et Sculpture), Littér…

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع الثورة (توضيح). صحيفة الثورةAl-Thawra (بالغير المعروفة) معلومات عامةالنوع إلكترونية وورقيةالتأسيس 1962 القطع القطع الكبير الثمن 50 ريال يمني التحريراللغة العربيةالإدارةالمقر الرئيسي صنعاءالناشر مؤسسة الثورةتعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات صحيفة ال�…

For the computer system, see NABU Network. 52°31′23″N 13°22′43″E / 52.523136°N 13.378625°E / 52.523136; 13.378625 This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Naturschutzbund Deutschland – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2020) (Learn how and when to remo…

Election for the governorship of the U.S. state of Minnesota 1873 Minnesota gubernatorial election ← 1871 November 4, 1873 1875 → Nominee Cushman Kellogg Davis Ara Barton Party Republican Democratic Popular vote 40,741 35,245 Percentage 52.90 47.56% County resultsDavis: 50-60% 60-70% 70-80% 80-90% 90-100%Barton: &#…

Cet article est une ébauche concernant un coureur cycliste danois. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?). Pour plus d’informations, voyez le projet cyclisme. Pour les articles homonymes, voir Pedersen. Alex PedersenInformationsNom de naissance Alex Kjeld PedersenNaissance 15 novembre 1966 (57 ans)IkastNationalité danoiseDistinctions Cycliste danois de l'année (1984, 1987 et 1994)Équipes professionnelles 1988R.M.O.-Mavic-Liberia1988JBS Indertøj1989…

Kebijakan sosial adalah salah satu bentuk dari kebijakan publik[1] yang merupakan ketetapan pemerintah yang dibuat untuk merespon isu-isu yang bersifat publik, yakni mengatasi masalah sosial atau memenuhi kebutuhan masyarakat banyak.[1] Kebijakan sosial juga adalah ketetapan yang dirancang secara kolektif untuk mencegah terjadinya masalah sosial (fungsi preventif), mengatasi masalah sosial (fungsi kuratif) dan mempromosikan kesejahteraan (fungsi pengembangan) sebagai wujud kewaji…

2023 Swedish-Norwegian drama film OpponentPromotional release posterSwedishMotståndaren Directed byMilad AlamiWritten byMilad AlamiProduced byAnnika RogellStarringPayman MaadiMarall NasiriBjörn ElgerdCinematographySebastian WinterøEdited byOlivia Neergaard-HolmMusic byCarl-Johan SevedagJan EkstrandProductioncompaniesApe&BjørnTangyDistributed byTriArt FilmRelease date 18 February 2023 (2023-02-18) (Berlin) Running time119 minutesCountriesSwedenNorway Opponent (Swedish: …
此條目介紹的是拉丁字母中的第2个字母。关于其他用法,请见「B (消歧义)」。 提示:此条目页的主题不是希腊字母Β、西里尔字母В、Б、Ъ、Ь或德语字母ẞ、ß。 BB b(见下)用法書寫系統拉丁字母英文字母ISO基本拉丁字母(英语:ISO basic Latin alphabet)类型全音素文字相关所属語言拉丁语读音方法 [b][p][ɓ](适应变体)Unicode编码U+0042, U+0062字母顺位2数值 2歷史發展…

Rappresentazione visiva del grafico di una funzione cubica su R {\displaystyle \mathbb {R} } : y = x 3 − 9 x {\displaystyle y=x^{3}-9x} Rappresentazione visiva del grafico di: f ( x , y ) = sin ( x 2 ) cos ( y 2 ) {\displaystyle f(x,y)=\sin(x^{2})\cos(y^{2})} In matematica, il grafico di una funzione è l'insieme delle coppie ordinate costituite dagli elementi del dominio e dalle rispettive immagini. Indice 1 Definizione 2 Grafici di funzioni reali 3 Grafici di funzioni …

Keigo SonodaInformasi pribadiKebangsaan JepangLahir20 Februari 1990 (umur 34)Yatsushiro, Kumamoto, JepangTinggi169 m (554 ft 6 in)Berat70 kg (154 pon)PeganganKananTunggal putra & gandaPeringkat tertinggi69 (MS 1 Desember 2011) 2 (MD 26 Januari 2017) 19 (XD 31 Maret 2016)Peringkat saat ini6 bersama Takeshi Kamura (21 Desember 2021[1])Profil di BWF Keigo Sonoda (園田 啓悟code: ja is deprecated , Sonoda Keigo, lahir 20 Februari 1990) adalah pe…

Trains Template‑class Trains Portal This template is within the scope of WikiProject Trains, an attempt to build a comprehensive and detailed guide to rail transport on Wikipedia. If you would like to participate, you can visit the project page, where you can join the project and/or contribute to the discussion. See also: WikiProject Trains to do list and the Trains Portal.TrainsWikipedia:WikiProject TrainsTemplate:WikiProject Trainsrail transport articlesTemplateThis template does not requir…
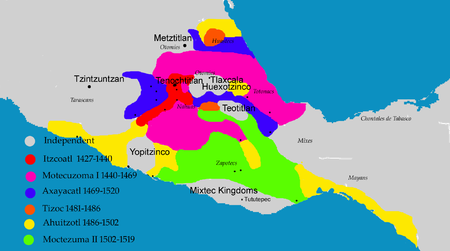
AxayacatlTlatoani TenochtitlanAxayacatl di Codex AzcatitlanBerkuasa1469–1481PendahuluMoctezuma IPenerusTizocKematian1481AyahPangeran TezozomocIbuPutri Atotoztli II Axayacatl ([aːʃaː'jakat͡ɬ] (namanya berarti topeng air atau wajah air) adalah penguasa Aztek keenam yang berkuasa dari tahun 1469 hingga 1481. Ia dikenang karena berhasil menundukkan Tlatelolco pada tahun 1473. Biografi Axayacatl adalah putra dari putri Atotoztli II dan sepupunya, pangeran Tezozomoc. Ia adalah cucu dari kaisar …

Neanderthal fossil discovered in the early 19th-century in modern day Belgium Engis 2Lateral view of juvenileCommon nameEngis 2SpeciesNeanderthalAge35,350 years (aged c. 3)Place discoveredFlemalle, Liege, BelgiumDate discovered1829Discovered byPhilippe-Charles SchmerlingEngis 2 refers to part of an assemblage, discovered in 1829 by Dutch physician and naturalist Philippe-Charles Schmerling in the lower of the Schmerling Caves. The pieces that make up Engis 2 are a partially preserved calvaria (c…

Australian bookseller, book publisher and book printer Not to be confused with Angus Robertson. Angus & RobertsonIndustryOnline (Specialty)Founded1884 in Sydney, AustraliaFounderDavid AngusGeorge RobertsonHeadquartersSydney, AustraliaProductsBooks and DVDsOwnerBooktopiaWebsiteangusrobertson.com.au Angus & Robertson (A&R) is a major Australian bookseller, publisher and printer. As book publishers, A&R has contributed substantially to the promotion and development of Australian lit…

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6] 得…

2000 studio album by Alan JacksonWhen Somebody Loves YouStudio album by Alan JacksonReleasedNovember 7, 2000GenreCountryLength33:56LabelArista NashvilleProducerKeith StegallAlan Jackson chronology Under the Influence(1999) When Somebody Loves You(2000) Drive(2002) Singles from When Somebody Loves You www.memoryReleased: October 2, 2000 When Somebody Loves YouReleased: March 5, 2001 Where I Come FromReleased: July 9, 2001 It's Alright to Be a RedneckReleased: November 5, 2001 Professional…




