György Márkus
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
Għargħur Ħal GħargħurDewan lokal BenderaLambang kebesaranLokasi di MaltaNegara MaltaLuas • Total2 km2 (0,8 sq mi)Populasi (2014) • Total2.768 • Kepadatan1,400/km2 (3,600/sq mi)Kode ISO 3166-2MT-15Situs webhttp://www.gharghur.gov.mt/ Għargħur adalah salah satu dewan lokal di Malta. Menurut sensus 2014, Għargħur memiliki luas 2 kilometer persegi dan populasi 2.768 jiwa. Kode ISO 3166-2 daerah ini adalah MT-15. Referensi Cit…

Jesús Gallardo Jesús Gallardo con México en la Copa del Mundo de 2018.Datos personalesNombre completo Jesús Daniel Gallardo Vasconcelos[1]Apodo(s) Vegeta[2][3]Nacimiento Heroica Cárdenas, Tabasco15 de agosto de 1994 (29 años)Nacionalidad(es) MexicanaAltura 1,74 m (5′ 9″)[4]Peso 74 kg (163 lb)Carrera deportivaDeporte FútbolClub profesionalDebut deportivo 2014(C. Universidad Nacional)Club C. F. MonterreyLiga Liga MXPosición Extremo o Late…

KurasaoJenisLiqueurProdusenBervariasiNegara asalCuraçaoDiperkenalkanAbad ke-19Alkohol menurut volume40% Kurasao (Spanyol: Curaçaocode: es is deprecated ) adalah sebuah likeur dengan rasa buah sitrus laraha, yang ditanam di Curaçao. Buah ini sangat mirip dengan jeruk, laraha merupakan hasil cangkokan dari pelaut Spanyol yang ingin menanam jeruk Valencia yang manis di Curaçao. Dikarenakan tanah yang tidak bernutrisi dan keringnya iklim Curaçao, buah yang dihasilkan sangat kecil dan sangat pah…

Stasiun Tsurusaki鶴崎駅Stasiun Tsurusaki pada 2008LokasiKota Ōita, Prefektur ŌitaJepangKoordinat33°14′33″N 131°41′15″E / 33.24250°N 131.68750°E / 33.24250; 131.68750Koordinat: 33°14′33″N 131°41′15″E / 33.24250°N 131.68750°E / 33.24250; 131.68750Operator JR KyushuJalur■ Jalur Utama NippōLetak141.0 km dari KokuraJumlah peron1 peron pulauKonstruksiJenis strukturAtas tanahInformasi lainStatusMemiliki stafSitus webSitus w…

Artikel ini mungkin mengandung riset asli. Anda dapat membantu memperbaikinya dengan memastikan pernyataan yang dibuat dan menambahkan referensi. Pernyataan yang berpangku pada riset asli harus dihapus. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Gaya atau nada penulisan artikel ini tidak mengikuti gaya dan nada penulisan ensiklopedis yang diberlakukan di Wikipedia. Bantulah memperbaikinya berdasarkan panduan penulisan artikel. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk mengh…

Legislative branch of the state government of Ohio For the current General Assembly, see 135th Ohio General Assembly. Ohio General Assembly135th Ohio General AssemblyTypeTypeBicameral HousesSenateHouse of RepresentativesLeadershipPresident of the SenateMatt Huffman (R) since January 4, 2021 President pro tempore (Senate)Kirk Schuring (R) since January 3, 2023 Speaker of the Ohio House of RepresentativesJason Stephens (R) since January 3, 2023 Speaker pro temporeScott Oelslager (R) si…

Lion Air Group IATA ICAO Kode panggil * Lion Air : JT Wings Air : IW Batik Air : ID Super Air Jet : IU Batik Air Malaysia : OD Thai Lion Air : SL * Lion Air : LNI Wings Air : WON Batik Air : BTK Super Air Jet : SJV Batik Air Malaysia : MXD Thai Lion Air : TLM * Lion Air : LION INTER Wings Air : WINGS ABADI Batik Air : BATIK Super Air Jet : PROSPER Batik Air Malaysia : MALINDO Thai Lion Air : MENTARI Anak pe…

American BSL-4 research facility National Bio and Agro-Defense FacilityNBAF logoFront of the NBAFEstablished2015Laboratory typeBiosafety level 4 research laboratoryResearch typeScientific research and biodefenseBudgetUS$1.25 billion (2021)Field of researchHuman, zoonotic, and foreign animal diseasesDirectorAlfonso ClavijoStaff250–350LocationManhattan, Kansas, U.S.39°12′11″N 96°35′03″W / 39.20306°N 96.58417°W / 39.20306; -96.58417ZIP code66506Campus…
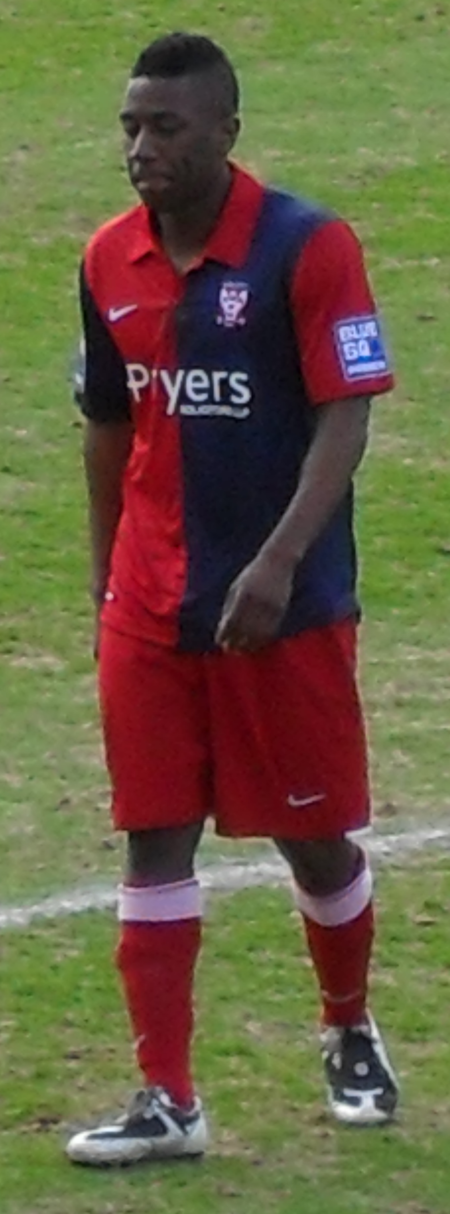

English footballer Courtney Pitt Pitt playing for York City in 2010Personal informationFull name Courtney Leon Pitt[1]Date of birth (1981-12-17) 17 December 1981 (age 42)[1]Place of birth Paddington, EnglandHeight 5 ft 7 in (1.70 m)Position(s) MidfielderYouth career000?–2001 ChelseaSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2001–2004 Portsmouth 39 (3)2003 → Luton Town (loan) 12 (0)2003–2004 → Coventry City (loan) 1 (0)2004 Oxford United 8 (0)2004–2005 Bost…

Big Jacks Creek WildernessIUCN category Ib (wilderness area)LocationOwyhee County, Idaho, USANearest cityBoise, IdahoCoordinates42°27′43″N 116°4′46″W / 42.46194°N 116.07944°W / 42.46194; -116.07944Area52,826 acres (21,378 ha)Established2009Governing bodyBureau of Land Management The Big Jacks Creek Wilderness is located on the high basalt plateaus of Owyhee County in southwestern Idaho in the western United States.[1][2] Little J…

Keuskupan Nardò-GallipoliDioecesis Neritonensis-GallipolitanaKatolik Katedral NardòLokasiNegaraItaliaProvinsi gerejawiLecceStatistikLuas587 km2 (227 sq mi)Populasi- Total- Katolik(per 2013)211.352210,417 (99.6%)Paroki66Imam124 (diosesan)18 (Ordo Relijius)InformasiDenominasiGereja KatolikRitusRitus RomaPendirian13 Januari 1413 (611 tahun lalu)KatedralBasilica Cattedrale di S. Maria AssuntaKonkatedralBasilica Concattedrale di S. Agata VergineKepemimpinan kiniPa…

Danish annual music festival held in Roskilde Roskilde FestivalGenre Rock pop electronic reggae hip hop world DatesFour days, starting from first Wednesday in July, or last Wednesday in June with a 4-day warm-upLocation(s)Roskilde, DenmarkYears active1971–presentFounded by Mogens Sandfær Jesper Switzer Møller Carl Fischer[1] Websiteroskilde-festival.dk/en The Roskilde Festival is a Danish music festival held annually south of Roskilde. It is one of the largest music festivals in Euro…

La BoissièrecomuneLa Boissière – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Francia Regione Normandia Dipartimento Calvados ArrondissementLisieux CantoneMézidon-Canon TerritorioCoordinate49°08′N 0°09′E / 49.133333°N 0.15°E49.133333; 0.15 (La Boissière)Coordinate: 49°08′N 0°09′E / 49.133333°N 0.15°E49.133333; 0.15 (La Boissière) Superficie2,03 km² Abitanti185[1] (2009) Densità91,13 ab./km² Altre informazioniCod. postale14340…

Musang bulan Status konservasi Risiko Rendah (IUCN 3.1)[1] Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Mammalia Ordo: Carnivora Famili: Viverridae Subfamili: Paradoxurinae Genus: PagumaGray, 1831 Spesies: P. larvata Nama binomial Paguma larvata(C. E. H. Smith, 1827) Habitat Musang galing Musang bulan / galing / musang bertopeng (Paguma larvata) adalah jenis musang yang berasal dari Asia Timur and Asia Tenggara. Spesies ini diklasifikasikan oleh IUCN pada 2008 …

British book publisher This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Virgin Books – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Virgin BooksStatusActiveFounded1979 (1979)[1]FounderRichard BransonCountry of originUnited KingdomHeadquarters lo…

Voce principale: Dexter (serie televisiva). La terza stagione della serie televisiva Dexter è stata trasmessa in prima visione negli Stati Uniti d'America da Showtime dal 28 settembre al 14 dicembre 2008. In Italia è stata trasmessa in prima visione satellitare su FX dal 18 settembre al 4 dicembre 2009, e in chiaro da Cielo dal 13 dicembre 2010. Gli antagonisti principali della stagione sono Miguel Prado e lo Scorticatore alias George W. King. nº Titolo originale Titolo italiano Prima TV USA …

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁地�…

City in Uttarakhand, IndiaLohaghatCityView of the region around Lohaghat after SnowfallLohaghatLocation in Uttarakhand, IndiaShow map of UttarakhandLohaghatLohaghat (India)Show map of IndiaCoordinates: 29°25′N 80°06′E / 29.42°N 80.10°E / 29.42; 80.10CountryIndiaStateUttarakhandDistrictChampawatArea • Total4.5 km2 (1.7 sq mi)Elevation1,754 m (5,755 ft)Population (2011) • Total7,954 • Density1,800/km2…

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府與�…

Industrial Bank of KoreaNama asli중소기업은행 中小企業銀行 (hanja)TokohkunciYoon Jong-won (Direktur Utama)Total aset$201 miliar (2015)[1]Situs webhttp://global.ibk.co.kr Industrial Bank of Korea (IBK) (bahasa Korea:중소기업은행, KRX: 024110) adalah sebuah bank industri yang berpusat di Jung-gu, Seoul, Korea Selatan. Bank ini berdiri pada tahun 1961. Slogannya adalah Global Leading Bank. Bank ini dimiliki oleh Pemerintah Korea Selatan. Direktur utama IBK dari tahun 2013 …