|
Image sensor format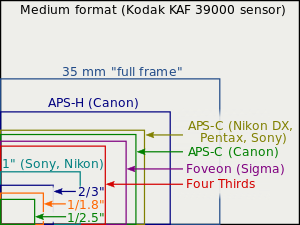 In digital photography, the image sensor format is the shape and size of the image sensor. The image sensor format of a digital camera determines the angle of view of a particular lens when used with a particular sensor. Because the image sensors in many digital cameras are smaller than the 24 mm × 36 mm image area of full-frame 35 mm cameras, a lens of a given focal length gives a narrower field of view in such cameras. Sensor size is often expressed as optical format in inches. Other measures are also used; see table of sensor formats and sizes below. Lenses produced for 35 mm film cameras may mount well on the digital bodies, but the larger image circle of the 35 mm system lens allows unwanted light into the camera body, and the smaller size of the image sensor compared to 35 mm film format results in cropping of the image. This latter effect is known as field-of-view crop. The format size ratio (relative to the 35 mm film format) is known as the field-of-view crop factor, crop factor, lens factor, focal-length conversion factor, focal-length multiplier, or lens multiplier. Sensor size and depth of fieldThree possible depth-of-field comparisons between formats are discussed, applying the formulae derived in the article on depth of field. The depths of field of the three cameras may be the same, or different in either order, depending on what is held constant in the comparison. Considering a picture with the same subject distance and angle of view for two different formats: so the DOFs are in inverse proportion to the absolute aperture diameters and . Using the same absolute aperture diameter for both formats with the "same picture" criterion (equal angle of view, magnified to same final size) yields the same depth of field. It is equivalent to adjusting the f-number inversely in proportion to crop factor – a smaller f-number for smaller sensors (this also means that, when holding the shutter speed fixed, the exposure is changed by the adjustment of the f-number required to equalise depth of field. But the aperture area is held constant, so sensors of all sizes receive the same total amount of light energy from the subject. The smaller sensor is then operating at a lower ISO setting, by the square of the crop factor). This condition of equal field of view, equal depth of field, equal aperture diameter, and equal exposure time is known as "equivalence".[1] And, we might compare the depth of field of sensors receiving the same photometric exposure – the f-number is fixed instead of the aperture diameter – the sensors are operating at the same ISO setting in that case, but the smaller sensor is receiving less total light, by the area ratio. The ratio of depths of field is then where and are the characteristic dimensions of the format, and thus is the relative crop factor between the sensors. It is this result that gives rise to the common opinion that small sensors yield greater depth of field than large ones. An alternative is to consider the depth of field given by the same lens in conjunction with different sized sensors (changing the angle of view). The change in depth of field is brought about by the requirement for a different degree of enlargement to achieve the same final image size. In this case the ratio of depths of field becomes
In practice, if applying a lens with a fixed focal length and a fixed aperture and made for an image circle to meet the requirements for a large sensor is to be adapted, without changing its physical properties, to smaller sensor sizes neither the depth of field nor the light gathering will change. Sensor size, noise and dynamic rangeDiscounting photo response non-uniformity (PRNU) and dark noise variation, which are not intrinsically sensor-size dependent, the noises in an image sensor are shot noise, read noise, and dark noise. The overall signal to noise ratio of a sensor (SNR), expressed as signal electrons relative to rms noise in electrons, observed at the scale of a single pixel, assuming shot noise from Poisson distribution of signal electrons and dark electrons, is where is the incident photon flux (photons per second in the area of a pixel), is the quantum efficiency, is the exposure time, is the pixel dark current in electrons per second and is the pixel read noise in electrons rms.[2] Each of these noises has a different dependency on sensor size. Exposure and photon fluxImage sensor noise can be compared across formats for a given fixed photon flux per pixel area (the P in the formulas); this analysis is useful for a fixed number of pixels with pixel area proportional to sensor area, and fixed absolute aperture diameter for a fixed imaging situation in terms of depth of field, diffraction limit at the subject, etc. Or it can be compared for a fixed focal-plane illuminance, corresponding to a fixed f-number, in which case P is proportional to pixel area, independent of sensor area. The formulas above and below can be evaluated for either case. Shot noiseIn the above equation, the shot noise SNR is given by
Apart from the quantum efficiency it depends on the incident photon flux and the exposure time, which is equivalent to the exposure and the sensor area; since the exposure is the integration time multiplied with the image plane illuminance, and illuminance is the luminous flux per unit area. Thus for equal exposures, the signal to noise ratios of two different size sensors of equal quantum efficiency and pixel count will (for a given final image size) be in proportion to the square root of the sensor area (or the linear scale factor of the sensor). If the exposure is constrained by the need to achieve some required depth of field (with the same shutter speed) then the exposures will be in inverse relation to the sensor area, producing the interesting result that if depth of field is a constraint, image shot noise is not dependent on sensor area. For identical f-number lenses the signal to noise ratio increases as square root of the pixel area, or linearly with pixel pitch. As typical f-numbers for lenses for cell phones and DSLR are in the same range f/1.5–2 it is interesting to compare performance of cameras with small and big sensors. A good cell phone camera with typical pixel size 1.1 μm (Samsung A8) would have about 3 times worse SNR due to shot noise than a 3.7 μm pixel interchangeable lens camera (Panasonic G85) and 5 times worse than a 6 μm full frame camera (Sony A7 III). Taking into consideration the dynamic range makes the difference even more prominent. As such the trend of increasing the number of "megapixels" in cell phone cameras during last 10 years was caused rather by marketing strategy to sell "more megapixels" than by attempts to improve image quality. Read noiseThe read noise is the total of all the electronic noises in the conversion chain for the pixels in the sensor array. To compare it with photon noise, it must be referred back to its equivalent in photoelectrons, which requires the division of the noise measured in volts by the conversion gain of the pixel. This is given, for an active pixel sensor, by the voltage at the input (gate) of the read transistor divided by the charge which generates that voltage, . This is the inverse of the capacitance of the read transistor gate (and the attached floating diffusion) since capacitance .[3] Thus . In general for a planar structure such as a pixel, capacitance is proportional to area, therefore the read noise scales down with sensor area, as long as pixel area scales with sensor area, and that scaling is performed by uniformly scaling the pixel. Considering the signal to noise ratio due to read noise at a given exposure, the signal will scale as the sensor area along with the read noise and therefore read noise SNR will be unaffected by sensor area. In a depth of field constrained situation, the exposure of the larger sensor will be reduced in proportion to the sensor area, and therefore the read noise SNR will reduce likewise. Dark noiseDark current contributes two kinds of noise: dark offset, which is only partly correlated between pixels, and the shot noise associated with dark offset, which is uncorrelated between pixels. Only the shot-noise component Dt is included in the formula above, since the uncorrelated part of the dark offset is hard to predict, and the correlated or mean part is relatively easy to subtract off. The mean dark current contains contributions proportional both to the area and the linear dimension of the photodiode, with the relative proportions and scale factors depending on the design of the photodiode.[4] Thus in general the dark noise of a sensor may be expected to rise as the size of the sensor increases. However, in most sensors the mean pixel dark current at normal temperatures is small, lower than 50 e- per second,[5] thus for typical photographic exposure times dark current and its associated noises may be discounted. At very long exposure times, however, it may be a limiting factor. And even at short or medium exposure times, a few outliers in the dark-current distribution may show up as "hot pixels". Typically, for astrophotography applications sensors are cooled to reduce dark current in situations where exposures may be measured in several hundreds of seconds. Dynamic rangeDynamic range is the ratio of the largest and smallest recordable signal, the smallest being typically defined by the 'noise floor'. In the image sensor literature, the noise floor is taken as the readout noise, so [6] (note, the read noise is the same quantity as referred to in the SNR calculation[2]). Sensor size and diffractionThe resolution of all optical systems is limited by diffraction. One way of considering the effect that diffraction has on cameras using different sized sensors is to consider the modulation transfer function (MTF). Diffraction is one of the factors that contribute to the overall system MTF. Other factors are typically the MTFs of the lens, anti-aliasing filter and sensor sampling window.[7] The spatial cut-off frequency due to diffraction through a lens aperture is where λ is the wavelength of the light passing through the system and N is the f-number of the lens. If that aperture is circular, as are (approximately) most photographic apertures, then the MTF is given by for and for [8] The diffraction based factor of the system MTF will therefore scale according to and in turn according to (for the same light wavelength). In considering the effect of sensor size, and its effect on the final image, the different magnification required to obtain the same size image for viewing must be accounted for, resulting in an additional scale factor of where is the relative crop factor, making the overall scale factor . Considering the three cases above: For the 'same picture' conditions, same angle of view, subject distance and depth of field, then the f-numbers are in the ratio , so the scale factor for the diffraction MTF is 1, leading to the conclusion that the diffraction MTF at a given depth of field is independent of sensor size. In both the 'same photometric exposure' and 'same lens' conditions, the f-number is not changed, and thus the spatial cutoff and resultant MTF on the sensor is unchanged, leaving the MTF in the viewed image to be scaled as the magnification, or inversely as the crop factor. Sensor format and lens sizeIt might be expected that lenses appropriate for a range of sensor sizes could be produced by simply scaling the same designs in proportion to the crop factor.[9] Such an exercise would in theory produce a lens with the same f-number and angle of view, with a size proportional to the sensor crop factor. In practice, simple scaling of lens designs is not always achievable, due to factors such as the non-scalability of manufacturing tolerance, structural integrity of glass lenses of different sizes and available manufacturing techniques and costs. Moreover, to maintain the same absolute amount of information in an image (which can be measured as the space-bandwidth product[10]) the lens for a smaller sensor requires a greater resolving power. The development of the 'Tessar' lens is discussed by Nasse,[11] and shows its transformation from an f/6.3 lens for plate cameras using the original three-group configuration through to an f/2.8 5.2 mm four-element optic with eight extremely aspheric surfaces, economically manufacturable because of its small size. Its performance is 'better than the best 35 mm lenses – but only for a very small image'. In summary, as sensor size reduces, the accompanying lens designs will change, often quite radically, to take advantage of manufacturing techniques made available due to the reduced size. The functionality of such lenses can also take advantage of these, with extreme zoom ranges becoming possible. These lenses are often very large in relation to sensor size, but with a small sensor can be fitted into a compact package. Small body means small lens and means small sensor, so to keep smartphones slim and light, the smartphone manufacturers use a tiny sensor usually less than the 1/2.3" used in most bridge cameras. At one time only Nokia 808 PureView used a 1/1.2" sensor, almost three times the size of a 1/2.3" sensor. Bigger sensors have the advantage of better image quality, but with improvements in sensor technology, smaller sensors can achieve the feats of earlier larger sensors. These improvements in sensor technology allow smartphone manufacturers to use image sensors as small as 1/4" without sacrificing too much image quality compared to budget point & shoot cameras.[12] Active area of the sensorFor calculating camera angle of view one should use the size of active area of the sensor. Active area of the sensor implies an area of the sensor on which image is formed in a given mode of the camera. The active area may be smaller than the image sensor, and active area can differ in different modes of operation of the same camera. Active area size depends on the aspect ratio of the sensor and aspect ratio of the output image of the camera. The active area size can depend on number of pixels in given mode of the camera. The active area size and lens focal length determines angles of view.[13] Sensor size and shading effectsSemiconductor image sensors can suffer from shading effects at large apertures and at the periphery of the image field, due to the geometry of the light cone projected from the exit pupil of the lens to a point, or pixel, on the sensor surface. The effects are discussed in detail by Catrysse and Wandell.[14] In the context of this discussion the most important result from the above is that to ensure a full transfer of light energy between two coupled optical systems such as the lens' exit pupil to a pixel's photoreceptor the geometrical extent (also known as etendue or light throughput) of the objective lens / pixel system must be smaller than or equal to the geometrical extent of the microlens / photoreceptor system. The geometrical extent of the objective lens / pixel system is given by where wpixel is the width of the pixel and (f/#)objective is the f-number of the objective lens. The geometrical extent of the microlens / photoreceptor system is given by where wphotoreceptor is the width of the photoreceptor and (f/#)microlens is the f-number of the microlens. In order to avoid shading, therefore If wphotoreceptor / wpixel = ff, the linear fill factor of the lens, then the condition becomes Thus if shading is to be avoided the f-number of the microlens must be smaller than the f-number of the taking lens by at least a factor equal to the linear fill factor of the pixel. The f-number of the microlens is determined ultimately by the width of the pixel and its height above the silicon, which determines its focal length. In turn, this is determined by the height of the metallisation layers, also known as the 'stack height'. For a given stack height, the f-number of the microlenses will increase as pixel size reduces, and thus the objective lens f-number at which shading occurs will tend to increase.[a] In order to maintain pixel counts smaller sensors will tend to have smaller pixels, while at the same time smaller objective lens f-numbers are required to maximise the amount of light projected on the sensor. To combat the effect discussed above, smaller format pixels include engineering design features to allow the reduction in f-number of their microlenses. These may include simplified pixel designs which require less metallisation, 'light pipes' built within the pixel to bring its apparent surface closer to the microlens and 'back side illumination' in which the wafer is thinned to expose the rear of the photodetectors and the microlens layer is placed directly on that surface, rather than the front side with its wiring layers.[b] Common image sensor formats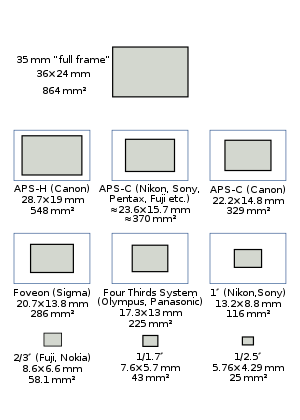 For interchangeable-lens camerasSome professional DSLRs, SLTs and mirrorless cameras use full-frame sensors, equivalent to the size of a frame of 35 mm film. Most consumer-level DSLRs, SLTs and mirrorless cameras use relatively large sensors, either somewhat under the size of a frame of APS-C film, with a crop factor of 1.5–1.6; or 30% smaller than that, with a crop factor of 2.0 (this is the Four Thirds System, adopted by OM System (formerly Olympus) and Panasonic). As of November 2013[update], there was only one mirrorless model equipped with a very small sensor, more typical of compact cameras: the Pentax Q7, with a 1/1.7" sensor (4.55 crop factor). See section § Smaller sensors section below. Many different terms are used in marketing to describe DSLR/SLT/mirrorless sensor formats, including the following:
Obsolescent and out-of-production sensor sizes include:
When full-frame sensors were first introduced, production costs could exceed twenty times the cost of an APS-C sensor. Only twenty full-frame sensors can be produced on an 8 inches (20 cm) silicon wafer, which would fit 100 or more APS-C sensors, and there is a significant reduction in yield due to the large area for contaminants per component. Additionally, full frame sensor fabrication originally required three separate exposures during each step of the photolithography process, which requires separate masks and quality control steps. Canon selected the intermediate APS-H size, since it was at the time the largest that could be patterned with a single mask, helping to control production costs and manage yields.[18] Newer photolithography equipment now allows single-pass exposures for full-frame sensors, although other size-related production constraints remain much the same. Due to the ever-changing constraints of semiconductor fabrication and processing, and because camera manufacturers often source sensors from third-party foundries, it is common for sensor dimensions to vary slightly within the same nominal format. For example, the Nikon D3 and D700 cameras' nominally full-frame sensors actually measure 36 × 23.9 mm, slightly smaller than a 36 × 24 mm frame of 35 mm film. As another example, the Pentax K200D's sensor (made by Sony) measures 23.5 × 15.7 mm, while the contemporaneous K20D's sensor (made by Samsung) measures 23.4 × 15.6 mm. Most of these image sensor formats approximate the 3:2 aspect ratio of 35 mm film. Again, the Four Thirds System is a notable exception, with an aspect ratio of 4:3 as seen in most compact digital cameras (see below). Smaller sensorsMost sensors are made for camera phones, compact digital cameras, and bridge cameras. Most image sensors equipping compact cameras have an aspect ratio of 4:3. This matches the aspect ratio of the popular SVGA, XGA, and SXGA display resolutions at the time of the first digital cameras, allowing images to be displayed on usual monitors without cropping. As of December 2010[update] most compact digital cameras used small 1/2.3" sensors. Such cameras include Canon PowerShot SX230 IS, Fujifilm Finepix Z90 and Nikon Coolpix S9100. Some older digital cameras (mostly from 2005–2010) used even smaller 1/2.5" sensors: these include Panasonic Lumix DMC-FS62, Canon PowerShot SX120 IS, Sony Cyber-shot DSC-S700, and Casio Exilim EX-Z80. As of 2018 high-end compact cameras using one inch sensors that have nearly four times the area of those equipping common compacts include Canon PowerShot G-series (G3 X to G9 X), Sony DSC-RX100 series, Panasonic Lumix DC-TZ200 and Panasonic DMC-LX15. Canon has an APS-C sensor on its top model PowerShot G1 X Mark III.  Finally, Sony has the DSC-RX1 and DSC-RX1R cameras in their lineup, which have a full-frame sensor usually only used in professional DSLRs, SLTs and MILCs. Due to the size constraints of powerful zoom objectives, most current bridge cameras have 1/2.3" sensors, as small as those used in common more compact cameras. As lens sizes are proportional to the image sensor size, smaller sensors enable large zoom amounts with moderate size lenses. In 2011 the high-end Fujifilm X-S1 was equipped with a much larger 2/3" sensor. In 2013–2014, both Sony (Cyber-shot DSC-RX10) and Panasonic (Lumix DMC-FZ1000) produced bridge cameras with 1" sensors. The sensors of camera phones are typically much smaller than those of typical compact cameras, allowing greater miniaturization of the electrical and optical components. Sensor sizes of around 1/6" are common in camera phones, webcams and digital camcorders. The Nokia N8 (2010)'s 1/1.83" sensor was the largest in a phone in late 2011. The Nokia 808 (2012) surpasses compact cameras with its 41 million pixels, 1/1.2" sensor.[19] Medium-format digital sensorsThe largest digital sensors in commercially available cameras are described as "medium format", in reference to film formats of similar dimensions. Although the most common medium format film, the 120 roll, is 6 cm (2.4 in) wide, and is most commonly shot square, the most common "medium-format" digital sensor sizes are approximately 48 mm × 36 mm (1.9 in × 1.4 in), which is roughly twice the size of a full-frame DSLR sensor format. Available CCD sensors include Phase One's P65+ digital back with Dalsa's 53.9 mm × 40.4 mm (2.12 in × 1.59 in) sensor containing 60.5 megapixels[20] and Leica's "S-System" DSLR with a 45 mm × 30 mm (1.8 in × 1.2 in) sensor containing 37-megapixels.[21] In 2010, Pentax released the 40MP 645D medium format DSLR with a 44 mm × 33 mm (1.7 in × 1.3 in) CCD sensor;[22] later models of the 645 series kept the same sensor size but replaced the CCD with a CMOS sensor. In 2016, Hasselblad announced the X1D, a 50MP medium-format mirrorless camera, with a 44 mm × 33 mm (1.7 in × 1.3 in) CMOS sensor.[23] In late 2016, Fujifilm also announced its new Fujifilm GFX 50S medium format, mirrorless entry into the market, with a 43.8 mm × 32.9 mm (1.72 in × 1.30 in) CMOS sensor and 51.4MP. [24] [25] Table of sensor formats and sizes Sensor sizes are expressed in inches notation because at the time of the popularization of digital image sensors they were used to replace video camera tubes. The common 1" outside diameter circular video camera tubes have a rectangular photo sensitive area about 16 mm on the diagonal, so a digital sensor with a 16 mm diagonal size is a 1" video tube equivalent. The name of a 1" digital sensor should more accurately be read as "one inch video camera tube equivalent" sensor. Current digital image sensor size descriptors are the video camera tube equivalency size, not the actual size of the sensor. For example, a 1" sensor has a diagonal measurement of 16 mm.[26][27]  Sizes are often expressed as a fraction of an inch, with a one in the numerator, and a decimal number in the denominator. For example, 1/2.5 converts to 2/5 as a simple fraction, or 0.4 as a decimal number. This "inch" system gives a result approximately 1.5 times the length of the diagonal of the sensor. This "optical format" measure goes back to the way image sizes of video cameras used until the late 1980s were expressed, referring to the outside diameter of the glass envelope of the video camera tube. David Pogue of The New York Times states that "the actual sensor size is much smaller than what the camera companies publish – about one-third smaller." For example, a camera advertising a 1/2.7" sensor does not have a sensor with a diagonal of 0.37 in (9.4 mm); instead, the diagonal is closer to 0.26 in (6.6 mm).[28][29][30] Instead of "formats", these sensor sizes are often called types, as in "1/2-inch-type CCD." Due to inch-based sensor formats not being standardized, their exact dimensions may vary, but those listed are typical.[29] The listed sensor areas span more than a factor of 1000 and are proportional to the maximum possible collection of light and image resolution (same lens speed, i.e., minimum f-number), but in practice are not directly proportional to image noise or resolution due to other limitations. See comparisons.[31][32] Film format sizes are also included, for comparison. The application examples of phone or camera may not show the exact sensor sizes.
See also
NotesFootnotes and references
External links
|






















![{\displaystyle \mathrm {MTF} \left({\frac {\xi }{\xi _{\mathrm {cutoff} }}}\right)={\frac {2}{\pi }}\left\{\cos ^{-1}\left({\frac {\xi }{\xi _{\mathrm {cutoff} }}}\right)-\left({\frac {\xi }{\xi _{\mathrm {cutoff} }}}\right)\left[1-\left({\frac {\xi }{\xi _{\mathrm {cutoff} }}}\right)^{2}\right]^{\frac {1}{2}}\right\}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2df679bc046c28caa3d3f26b8db34e88d924319e)















