Japanese destroyer Momo (1944)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
Bundorf Lambang kebesaranLetak Bundorf di Haßberge NegaraJermanNegara bagianBayernWilayahUnterfrankenKreisHaßbergeMunicipal assoc.Hofheim in UnterfrankenPemerintahan • MayorHubert Endres (FW)Luas • Total40,24 km2 (1,554 sq mi)Ketinggian326 m (1,070 ft)Populasi (2013-12-31)[1] • Total916 • Kepadatan0,23/km2 (0,59/sq mi)Zona waktuWET/WMPET (UTC+1/+2)Kode pos97494Kode area telepon09763 bzw. 09523Pelat kenda…

هذه المقالة بحاجة لصندوق معلومات. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة صندوق معلومات مخصص إليها. يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) نحو 3 مل�…

تاريخ آسيا الوسطى تعديل مصدري - تعديل دول وسط آسيا إن تاريخ آسيا الوسطى يتعلق بتاريخ الشعوب المختلفة التي سكنت آسيا الوسطى. لقد تم تحديد نمط حياة هؤلاء الأشخاص في المقام الأول من خلال مناخ المنطقة وجغرافيتها. إن جفاف المنطقة يجعل الزراعة صعبة ، كما أن المسافة من البحر …

إليزافيتينسكوي الإحداثيات 45°00′29″N 43°21′07″E / 45.0080504°N 43.3518791°E / 45.0080504; 43.3518791 تقسيم إداري البلد روسيا[2][3][1] عدد السكان عدد السكان 2998 (2017)[4] معلومات أخرى منطقة زمنية ت ع م+03:00 356407 رمز جيونيمز 467850 تعديل مصدري - تعديل ييليزا…

Mata telanjang Mata telanjang atau mata bugil adalah majas yang merujuk pada penglihatan manusia tanpa menggunakan alat optik apapun seperti mikroskop dan teleskop (tidak termasuk kacamata). Istilah ini sering digunakan dalam astronomi ketika merujuk kepada peristiwa yang dapat dilihat oleh orang awam, seperti sebagian komet dan hujan meteor. Sastra Davidson, N.: Sky Phenomena: A Guide to Naked Eye Observation of the Heavens. FlorisBooks (208p), ISBN 0-86315-168-X, Edinburgh 1993. Gerstbach G.: …

العلاقات العراقية الغامبية العراق غامبيا العراق غامبيا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات العراقية الغامبية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين العراق وغامبيا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة العرا�…

European free trade zone established in 1994 Not to be confused with European Free Trade Association. European Economic Area Европейска икономическа зона (Bulgarian)Europski gospodarski prostor (Croatian)Evropský hospodářský prostor (Czech)Det Europæiske Økonomiske Samarbejdsområde (Danish)Europese Economische Ruimte (Dutch)Euroopa Majanduspiir…

County in Wyoming, United States County in WyomingSublette CountyCountyPinedale, WyomingLocation within the U.S. state of WyomingWyoming's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 42°46′N 109°55′W / 42.76°N 109.92°W / 42.76; -109.92Country United StatesState WyomingFoundedFebruary 15, 1921(authorized)1923 (organized)Named forWilliam SubletteSeatPinedaleLargest townPinedaleArea • Total4,936 sq mi (12,780 km2) • Land4,887…
Enormous hall located in Asgard, in Norse mythology For other uses, see Valhalla (disambiguation). Valhalla (1896) by Max Brückner in a scenic backdrop for Richard Wagner's Der Ring des Nibelungen In Norse mythology Valhalla (/vælˈhælə, vɑːlˈhɑːlə/[1]) is the anglicised name for Old Norse: Valhǫll (hall of the slain).[2] It is described as a majestic hall located in Asgard and presided over by the god Odin. Half of those who die in combat enter Valhalla, while the oth…

Get RightSingel oleh Jennifer Lopezdari album RebirthSisi-B Feelin' So Good Hold You Down Dirilis03 Januari 2005 (2005-01-03)Direkam2004Genre Dance R&B Durasi3:45LabelEpicPencipta Rich Harrison James Brown Produser Rich Harrison Cory Rooney Kronologi singel Jennifer Lopez Baby I Love U! (2003) Get Right (2005) Hold You Down (2005) Video musikGet Right di YouTube Get Right adalah lagu oleh penyanyi asal Amerika Serikat, Jennifer Lopez, untuk album studio keempatnya, Rebirth (2005). Lagu …

علي رضا شابور شهبازي معلومات شخصية الميلاد 4 سبتمبر 1942(1942-09-04)شيراز، إيران الوفاة يوليو 15, 2006 (عن عمر ناهز 63 عاماً)واشنطن العاصمة سبب الوفاة سرطان مكان الدفن ضريح حافظ الشيرازي الجنسية IRN الحياة العملية المؤسسات جامعة شيراز جامعة غوتنغن جامعة طهران جامعة هارفا�…
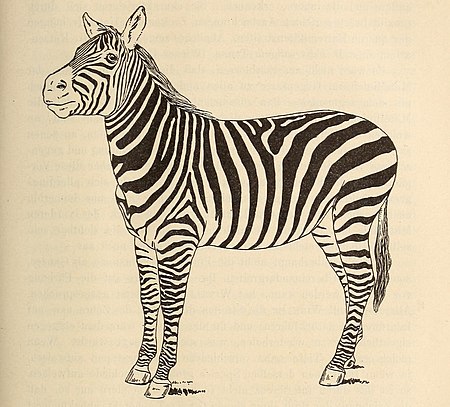

Zebra Selous Equus quagga selousi TaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumChordataKelasMammaliaOrdoPerissodactylaFamiliEquidaeGenusEquusSpesiesEquus quaggaSubspesiesEquus quagga selousi Sinonim takson[1]lbs Zebra Selous (Equus quagga selousi) adalah sebuah subspesies zebra dataran yang tersebar di belahan tenggara Afrika. Subspesies tersebut banyak ditemukan di Mozambik.[2] Referensi ^ Zicha, Ondrej (2005-09-01). Equus quagga borensis (Selous' Zebra). BioLib.cz (dalam bahasa Latin). Diakse…

This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (February 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) For the 1980s airline operating to Europe as American Overseas Airlines, see Guy-America Airways. American Overseas Airlines IATA ICAO Callsign - - AM OVER Founded1945Ceased operations1950 (merged into Pan American World Airways)Fleet size33 (2 SV-…

US Navy Rear Admiral Paul SohlRear Admiral Paul A. Sohl in 2014Born1963 (age 60–61)AllegianceUnited StatesService/branchUnited States NavyYears of service1986–2019RankRear AdmiralCommands heldOperational Test and Evaluation ForceFleet Readiness Center SoutheastUnited States Naval Test Pilot SchoolBattles/warsGulf WarWar in AfghanistanAwardsLegion of Merit (3)Defense Meritorious Service Medal (2) Paul Alan Sohl[1] (born 1963)[2] is a retired rear admiral in the U…

ESPN Deportes.com is a Spanish language sports website launched by ESPN in 2000.[1] Currently, it has regional editions for the Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Mexico, United States and Venezuela. The website features news, analysis and results of several sports, including association football, American football, baseball, basketball, boxing, motorsport, tennis, rugby union, golf and polo, as well as the Olympic Games and X Games. Some sections are branded, such as ESPN FC (association footb…

United States Template‑class United States portalThis template is within the scope of WikiProject United States, a collaborative effort to improve the coverage of topics relating to the United States of America on Wikipedia. If you would like to participate, please visit the project page, where you can join the ongoing discussions. Template Usage Articles Requested! Become a Member Project Talk Alerts United StatesWikipedia:WikiProject United StatesTemplate:WikiProject United StatesUnited Stat…

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府與�…

منتخب بولندا لاتحاد الرغبي اللقب (بالبولندية: Biało-czerwoni) بلد الرياضة بولندا تاريخ التأسيس 24 أبريل 1958 الموقع الرسمي الموقع الرسمي[1] أكبر فوز أكبر خسارة تعديل مصدري - تعديل منتخب بولندا الوطني لاتحاد الرغبي (بالبولندية: Reprezentacja Polski w rugby) هو المنتخب الرياض…

本表是動態列表,或許永遠不會完結。歡迎您參考可靠來源來查漏補缺。 潛伏於中華民國國軍中的中共間諜列表收錄根據公開資料來源,曾潛伏於中華民國國軍、被中國共產黨聲稱或承認,或者遭中華民國政府調查審判,為中華人民共和國和中國人民解放軍進行間諜行為的人物。以下列表以現今可查知時間為準,正確的間諜活動或洩漏機密時間可能早於或晚於以下所歸類�…
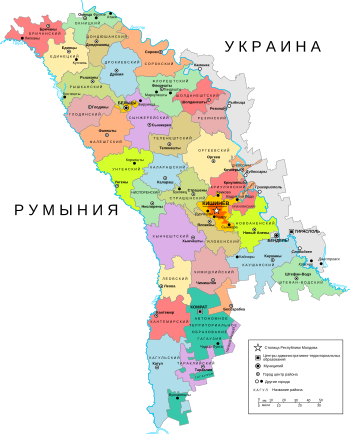
Административное деление Молдавии[1] Топонимия Молдавии — совокупность географических названий, включающая наименования природных и культурных объектов на территории Молдавии. Структура и состав топонимии обусловлены такими факторами, как географическое полож�…
