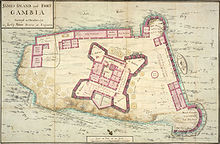
Kunta Kinteh Island
| |||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Seorang pengunjuk rasa memegang sebuah tanda yang terbaca rest in power di luar Hennepin County Government Center pada pengadilan Derek Chauvin 2021 Utamanya dalam komunitas kulit hitam dan di Amerika Serikat, rest in power (sebuah variasi dari rest in peace) adalah sebuah ekspresi yang dipakai untuk berkabung, mengingat dan memperingati seorang almarhum, khususnya seseorang yang dianggap berjuang melawan prasangka sistemik seperti rasisme dan ketidaksetaraan sosial dan diskriminasi terinstitusi…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Wurst. Conchita Wurst Conchita Wurst en 2015.Informations générales Surnom Reine d'Autriche Nom de naissance Thomas Neuwirth Naissance 6 novembre 1988 (35 ans)Gmunden, Autriche Activité principale Chanteur Genre musical Pop Années actives Depuis 2006 Labels Sony Site officiel conchitawurst.com modifier Conchita Wurst est un personnage incarné depuis 2011 par son créateur, le chanteur et drag queen autrichien Thomas Neuwirth (ou Tom Neuwirth), né le 6…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Maret 2023. DreamPoster DreamNama lainHangul드림 Alih AksaraDeurimMcCune–ReischauerTŭrim SutradaraLee Byeong-heonDitulis olehLee Byeong-heonPemeran Park Seo-joon Lee Ji-eun Penata musikTae-seong KimPerusahaanproduksiOktober Cinema Co. Ltd.DistributorMe…

City in Illinois, United StatesLebanon, IllinoisCityLebanon Historic DistrictLocation of Lebanon in St. Clair County, Illinois.Coordinates: 38°36′12″N 89°48′41″W / 38.60333°N 89.81139°W / 38.60333; -89.81139Country United StatesState IllinoisCountySt. ClairArea[1] • Total2.70 sq mi (7.00 km2) • Land2.69 sq mi (6.98 km2) • Water0.01 sq mi (0.02 km2)Elevation[2…

City in Razavi Khorasan province, Iran For the administrative divisions, see Torqabeh and Shandiz County, Shandiz District, and Shandiz Rural District. City in Razavi Khorasan, IranShandiz Persian: شانديزCityShandizCoordinates: 36°23′46″N 59°18′33″E / 36.39611°N 59.30917°E / 36.39611; 59.30917[1]CountryIranProvinceRazavi KhorasanCountyTorqabeh and ShandizDistrictShandizPopulation (2016)[2] • Total13,987Time zoneUTC+3:30 (…

For other places with the same name, see Gniewkowo (disambiguation). Place in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, PolandGniewkowoTown hall in Gniewkowo Coat of armsGniewkowoShow map of PolandGniewkowoShow map of Kuyavian-Pomeranian VoivodeshipCoordinates: 52°54′N 18°25′E / 52.900°N 18.417°E / 52.900; 18.417Country PolandVoivodeshipKuyavian-PomeranianCountyInowrocławGminaGniewkowoFirst mentioned1185Town rights1268Government • MayorAdam StraszyńskiAr…

French explorer of Canada (c.1592 - c.1633) Étienne BrûléBornc. 1592Paris, FranceDiedc. 1633 (aged 40–41)Toanche, New FranceNationalityFrenchOccupation(s)Fur trader, explorer Étienne Brûlé (French pronunciation: [etjɛn bʁyle]; c. 1592 – c. June 1633)[1][2][3] was the first European explorer to journey beyond the St. Lawrence River into what is now known as Canada. He spent much of his early adult life among the Hurons, and mastered…

Austrian myriapodologist and invertebrate zoologist Carl AttemsBorn(1868-10-13)13 October 1868Graz, AustriaDied19 April 1952(1952-04-19) (aged 83)ViennaNationalityAustrianAlma materUniversity of ViennaSpouseEmma von MontbachScientific careerFieldsMyriapodology, Invertebrate zoologyInstitutionsNaturhistorisches Museum (Vienna) Carl August Graf Attems-Petzenstein (13 October 1868 in Graz, Austria – 19 April 1952 in Vienna) was an Austrian myriapodologist and invertebrate zoologist.…

1930 play by William Somerset Maugham First US editionpubl. Doubleday, Doran & Co.) The Bread-Winner (1930) is William Somerset Maugham's third-last play. It is a comedy in one continuous act, lasting about 2 hours, but with the curtain lowered twice to rest the audience. Charles Battle has been 'hammered' in the London Stock Exchange, to the point where he may be bankrupted. Maugham keeps his audience ignorant of the disaster facing Charles for much of the play, at which point we learn what…

American film company Cosmopolitan Productions, also often referred to as Cosmopolitan Pictures, was an American film company based in New York City from 1918 to 1923 and Hollywood until 1938. History Marion Davies in Yolanda (1924) Newspaper tycoon William Randolph Hearst formed Cosmopolitan in conjunction with Adolph Zukor of Paramount after Hearst's bid for entry into the motion picture business was rebuffed by United Artists.[1] The advantage of Paramount having a production deal wit…

Country in Southeast Europe This article is about the modern country. For other uses, see Macedonia (disambiguation). Republic of North MacedoniaРепублика Северна Македонија (Macedonian)Republika e Maqedonisë së Veriut (Albanian) Flag National emblem Anthem: Денес над Македонија (Macedonian)Today over MacedoniaLocation of North Macedonia (green)in Europe (dark grey) – [Legend]Capitaland largest…

Prussian politician (1805–1882) Otto Theodor von Manteuffel6th Minister President of PrussiaIn office9 December 1850 – 6 November 1858MonarchFrederick William IVPreceded byFriedrich Wilhelm, Count BrandenburgSucceeded byKarl Anton, Prince of HohenzollernForeign Minister of PrussiaIn office2 November 1850 – 6 November 1858MonarchFrederick William IVPreceded byJoseph von RadowitzSucceeded byAlexander von Schleinitz Personal detailsBorn(1805-02-03)3 February 1805Lübben (Spr…

Державний комітет телебачення і радіомовлення України (Держкомтелерадіо) Приміщення комітетуЗагальна інформаціяКраїна УкраїнаДата створення 2003Керівне відомство Кабінет Міністрів УкраїниРічний бюджет 1 964 898 500 ₴[1]Голова Олег НаливайкоПідвідомчі орг�…

Odet de Coligny de Châtilloncardinale di Santa Romana ChiesaJean Clouet, Ritratto del cardinale de Coligny (1555 circa); disegno su carta, Musée Condé, Chantilly. Incarichi ricoperti Cardinale diacono dei Santi Sergio e Bacco (1533-1549) Amministratore apostolico di Tolosa (1534-1550) Amministratore apostolico di Beauvais (1535-1563) Abate commendatario di Saint-Lucien de Beauvais (1537-1563) Abate commendatario di Froidmont (1547-1563) Abate commendatario di Sainte-Trinité de la Lucer…

This is a list of awards and nominations received by American singer Cyndi Lauper. Among her numerous accolades, Lauper has won two Grammys (1985, 2014) an Emmy (1995) and a Tony (2013), which are three of the four major annual American entertainment awards (EGOT). Cyndi Lauper awards and nominationsCyndi Lauper (2017)Awards and nominationsAward Wins NominationsGrammy Awards 2 15Billboard Awards 4 25MTV Video Music Award 3 16American Music Awards 2 3Emmy Award 1 2BMI Awards 10 10Tony Award 1 1To…

Canada-related events during the year of 1882 This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: 1882 in Canada – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) ← 1881 1880 1879 1882 in Canada → 1883 1884 1885 Decades: 1860s 1870s 1880s 1890s 1900…

French television channel Television channel 13ème RueCountryFranceBroadcast areaFrance Belgium Switzerland Luxembourg MonacoHeadquartersSaint-Cloud, FranceProgrammingLanguage(s)FrenchPicture format16:9 576i (SDTV)16:9 1080i (HDTV)OwnershipOwnerUniversal Networks International (NBCUniversal)Sister channelsSyfy E!HistoryLaunched13 November 1997; 26 years ago (1997-11-13)Former names13ème Rue Universal (2010-2012)LinksWebsitewww.13emerue.fr 13ème Rue is a television channel sp…

Georges ContenauTepe Sialk in 1934: seated from right to left: Roman Ghirshman, Tania Ghirshman, Georges Contenau.Born9 April 1877LaonDied22 March 1964(1964-03-22) (aged 86)ParisOccupation(s)PhysicianArchaeologistHistorian Georges Contenau (April 9, 1877 – March 22, 1964) was a French archeologist, curator, orientalist and religious historian who was an expert in the field of culture and religion of the ancient civilizations of the Near and Middle East.[1] Life Contenau was profes…

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's notability guidelines for companies and organizations. Please help to demonstrate the notability of the topic by citing reliable secondary sources that are independent of the topic and provide significant coverage of it beyond a mere trivial mention. If notability cannot be shown, the article i…

Bagian dari seri tentangBudaya Indonesia Sejarah Sejarah menurut provinsi Bangsa Daftar suku bangsa Daftar suku bangsa menurut provinsi Bahasa Bahasa Indonesia Tradisi Etiket di Indonesia Busana nasional Indonesia Mitologi dan cerita rakyat Mitologi Cerita rakyat Hidangan Hari raya Festival Hari libur nasional Agama Islam Kekristenan Katolik Protestan Hindu Buddhisme Konghucu Yahudi Kepercayaan Seni Arsitektur Tarian Sastra Musik dan seni pertunjukan Musik Media Televisi Perfilman Olahraga Bola …