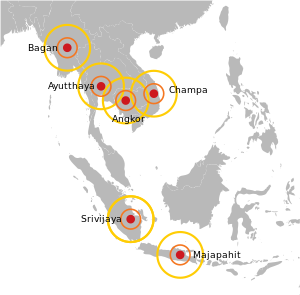
Mandala (political model)
|

SekarGenre Drama Roman PembuatSinemArtDitulis olehFairy AnselmoSkenarioFairy AnselmoSutradaraIndrayanto KurniawanPemeran Naysilla Mirdad Kevin Andrean Asmirandah Giovanni L. Tobing Ashraf Sinclair Rionaldo Stockhorst Fanny Ghassani Meriam Bellina Sigit Hardadi Ninok Wiryono Penggubah lagu temad'MasivLagu pembukaMerindukanmu oleh d'MasivLagu penutupMerindukanmu oleh d'MasivNegara asalIndonesiaBahasa asliBahasa IndonesiaJmlh. musim2Jmlh. episode150ProduksiProduserLeo SutantoPengaturan kameraMulti-…

Bagian dari seri mengenai Sejarah Indonesia Prasejarah Manusia Jawa 1.000.000 BP Manusia Flores 94.000–12.000 BP Bencana alam Toba 75.000 BP Kebudayaan Buni 400 SM Kerajaan Hindu-Buddha Kerajaan Kutai 400–1635 Kerajaan Tarumanagara 450–900 Kerajaan Kalingga 594–782 Kerajaan Melayu 671–1347 Kerajaan Sriwijaya 671–1028 Kerajaan Sunda 662–1579 Kerajaan Galuh 669–1482 Kerajaan Mataram 716–1016 Kerajaan Bali 914–1908 Kerajaan Kahuripan 1019̵…

AperamJenisSociété anonyme (Euronext: APAM)IndustriIndustri bajaDidirikan2011KantorpusatLuksemburgTokohkunciTimoteo Di Maulo, CEOKaryawan10,700Situs webwww.aperam.com Aperam adalah perusahaan yang memproduksi dan memasarkan baja tahan karat, baja elektrik dan baja khusus. Perusahaan, yang dipisahkan dari ArcelorMittal pada awal 2011, terdaftar di bursa saham di Amsterdam, Paris, Brussels dan Luksemburg.[1] Pabrik utama Aperam di Eropa berlokasi di Belgia dan Prancis.[2] Ca…

Alpay Özalan Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Alpay ÖzalanTanggal lahir 29 Mei 1973 (umur 50)Tempat lahir İzmir, TurkiPosisi bermain BekKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1992-1993 Altay 1993-1999 Beşiktaş 1999-2000 Fenerbahçe 2000-2003 Aston Villa 2004 Incheon United 2004-2005 Urawa Reds 2005-2007 Köln Tim nasional1995-2005 Turki 90 (4) * Penampilan dan gol di klub senior hanya dihitung dari liga domestik Alpay Özalan (lahir 29 Mei 1973) adalah pemain sepak bola asal Turki. Statistik…

Bernard Jeffrey McCullogh (5 Oktober 1957 – 9 Agustus 2008), atau lebih dikenal dengan Bernie Mac, merupakan seorang aktor berkebangsaan Amerika Serikat yang menjadi terkenal saat bermain di film utamanya seperti The Original Kings of Comedy. Dia dilahirkan di Chicago. Dia berkarier di dunia film sejak tahun 1977 hingga 2008. Dia meninggal dunia pada 9 Agustus 2008 akibat penyakit pneumonia yang dideritanya. Filmografi Tahun Judul Sebagai Catatan 1992 Mo' Money Club doorman 1993 …

Presiden Republik SingapuraBerkas:Singapore Presidental Crest.gifLambang Kepresidenan SingapuraBendera Kepresidenan SingapuraKepala NegaraKediamanThe IstanaDitunjuk olehParlemen (1965–1991)Pemilihan Langsung (1991-present)Masa jabatan6 Tahun; (bisa Periode ke-2)Dasar hukumKonstitusi Singapura, Pasal 17Situs webistana.gov.sgKekuasaan Presiden Singapura bersifat ke arah seremonial dalam menjalankan diskresi kebijakan dan dalam menjalankan kekuasaanya, Presiden harus berkolaborasi atas masukan da…

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut). …

Lokasi kota Aten yang ditemukan pada 2020-2021 dihamparkan pada peta modern rinci pertama di daerah tersebut. Aten adalah sisa-sisa kota di tepi barat Sungai Nil di Nekropolis Thebes dekat Luxor yang tampaknya relatif tetap utuh selama lebih dari dua milenium.[1] Sejak penggalian yang bermula pada akhir tahun 2020, kota ini muncul menjadi kota terbesar dari kota sejenis di Mesir Kuno, dengan tingkat kelestarian yang luar biasa, yang menyebabkan kota ini dibandingkan dengan Pompei.[2&…

John St. PolisSt. Polis dalam Party Girl (1930)Lahir(1873-11-24)24 November 1873New Orleans, Louisiana, Amerika SerikatMeninggal8 Oktober 1946(1946-10-08) (umur 72)Los Angeles, California, Amerika SerikatPekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1909–1943 John M. St. Polis (nama lahir John Marie Sainpolis; 24 November 1873 – 8 Oktober 1946) adalah seorang pemeran asal Amerika Serikat.[1] Ia tampil dalam 126 film antara 1914 dan 1943. Filmografi pilihan Soldiers of Fortune (1…

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2018年3月17日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:羅生門 (電影) — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 此�…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Kaulitz. Tom Kaulitz Tom Kaulitz en 2010.Informations générales Nom de naissance Tom Kaulitz-Trümper Naissance 1er septembre 1989 (34 ans)Leipzig, RDA Activité principale multi-instrumentiste, compositeur, producteur de musique, arrangeur Activités annexes mannequin Genre musical pop, teen pop, pop rock, pop punk, rock alternatif, électro-rock, dance-rock, synthpop, synthwave Instruments Guitare électrique, guitare, piano, synthétiseur Années activ…

This article's factual accuracy is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help to ensure that disputed statements are reliably sourced. (September 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message)The Lion's Back The Lion's Back is a sandstone ridge in Moab, Utah that used to be popular among drivers of four-wheel drive (4x4) vehicles. It has been closed to the public since 2004. It features a 65º incline and is 350 feet tall.[1] Crash The hill was t…

Sultan Sallehuddin ShahSultan SelangorBerkuasa1742 - 1778Penobatan1756Raja MudaIbrahim ShahKelahiran1705Kematian1778Nama lengkapAlmarhum Sultan Sallehuddin Shah ibni Almarhum Daeng ChelakAyahAlmarhum Daeng ChelakIbu—AnakRaja Ibrahim Shah Raja Muda Nala Raja Punuh Raja Sharifah Raja Lumu (Sultan Sallehuddin Shah ibni Almarhum Yamtuan Muda Riau ll Opu Daeng Chelak); 1705–1778) adalah Sultan Selangor yang pertama. Ia merupakan putra dari pangeran pejuang asal Bugis yang terkenal Opu Daeng Chela…

Serie A 1930-1931 Competizione Serie A Sport Calcio Edizione 31ª (2ª di Serie A) Organizzatore Direttorio Divisioni Superiori Date dal 28 settembre 1930al 28 giugno 1931 Luogo Italia Partecipanti 18 Formula girone unico Risultati Vincitore Juventus(3º titolo) Retrocessioni LivornoLegnano Statistiche Miglior marcatore Rodolfo Volk (28) Incontri disputati 306 Gol segnati 952 (3,11 per incontro) La Juventus vincitrice del campionato Cronologia della competizione 1929-1930…

2007 studio album by Still RemainsThe SerpentStudio album by Still RemainsReleasedAugust 7, 2007RecordedThe Omen Room studios, Sonikwire studios, StudiotteGenreMetalcoreLength41:52LabelRoadrunnerProducerSteve EvettsStill Remains chronology Of Love and Lunacy(2005) The Serpent(2007) Ceasing to Breathe(2013) Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingAllmusic[1]DecoyMusic.com[2]Alternative Press[3] The Serpent is the fourth release and second studio album by Still…

Franz BoppFranz BoppLahir(1791-09-14)14 September 1791Mainz, Elektorat MainzMeninggal23 Oktober 1867(1867-10-23) (umur 76)Berlin, Provinsi BrandenburgAliranLinguistik romantis[1]Minat utamaLinguistik Dipengaruhi Pāṇini, Friedrich Schlegel Memengaruhi Max MüllerMichel BréalAugust Schleicher[2] Franz Bopp (Jerman: [ˈfʁants ˈbɔp]; 14 Juni 1791 – 23 Oktober 1867)[a] adalah seorang linguis asal Jerman. Ia dikenal karena berkarya dalam…

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Harun Al-Rasyid Sutan Bandaro. Artikel ini bukan mengenai Soetan Haroen Al-Rasjid. Prof. Dr. (H.C.) Drs. H. SutanHarun Al-Rasjid ZainDatuak SinaroFoto sebagai Anggota MPR, 1982 Anggota Majelis Permusyawaratan RakyatMasa jabatan1 Oktober 1972 – 1 Oktober 1992Grup parlemenUtusan Daerah (1972–1982)Golongan Karya (1982–1992)Anggota Dewan Pertimbangan AgungMasa jabatan1983–1988Menteri Tenaga Kerja dan Transmigrasi Republik Indonesia ke-15Masa jabatan29 …

2013 video game EU4 redirects here. For other uses, see EU4 (disambiguation). 2013 video gameEuropa Universalis IVDeveloper(s)Paradox Development StudioPublisher(s)Paradox InteractiveDirector(s)Johan AnderssonProducer(s)Linda KibyDesigner(s)Johan AnderssonProgrammer(s)Niklas StridArtist(s)Fredrik TollComposer(s)Andreas WaldetoftEngineClausewitz EnginePlatform(s)Windows, macOS, LinuxRelease13 August 2013Genre(s)Grand strategyMode(s)Single-player, multiplayer Europa Universalis IV is a 2013 grand …

Rancho Rincón del Sanjón was granted to José Eusebio Boronda, a Californio ranchero. The present day community of Boronda is named for him and located on the former grounds of the rancho. Rancho Rincón del Sanjón was a 2,230-acre (9.0 km2) Mexican land grant in present-day Monterey County, California given in 1840 by Governor Juan B. Alvarado to José Eusebio Boronda.[1][2] The name means corner of Sanjo del Alisal. The grant was located on the north side of the Sanjo d…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Abelin. Pierre Abelin Pierre Abelin en 1952. Fonctions Député français 20 octobre 1975 – 20 novembre 1975(1 mois) Élection 19 octobre 1975 Circonscription 2e de la Vienne Législature Ve (Cinquième République) Groupe politique RDS Prédécesseur Robert Gourault (décès) Successeur Jean-Jacques Fouqueteau 25 novembre 1962 – 27 juin 1974(11 ans, 7 mois et 2 jours) Élection 25 novembre 1962 Réélection 12 mars 196730 juin 196811 mar…