Musselburgh
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

GolkondaBenteng GolkondaInformasi umumKotaHyderabadNegara IndiaRampung1600s Golkonda (Telugu గోల్కొండ) adalah reruntuhan kota di India selatan yang merupakan ibu kota dari Kerajaan Golkonda (c. 1364–1512). Kota ini terletak di sebelah barat Hyderabad, negara bagian Telangana, India. Pranala luar Photos of Golkonda Fort on HyderabadPlanet.com Diarsipkan 2013-03-27 di Wayback Machine. Golkonda among 7 Wonders Of Hyderabad[pranala nonaktif permanen] Golkonda at the Islamic…

عميل البريد الإلكتروني موزيلا ثندربرد عميل البريد الإلكتروني (بالإنجليزية: E-mail client) هو البرنامج أو الوسيط الذي يقوم بقراءة وإدارة محتوي البريد الإلكتروني.[1][2][3] هناك العديد من البرامج التي تقوم بذلك مثل برنامج الآوت لوك إكسبريس كبرنامج يعمل داخل بيئة ويندوز و�…

English footballer Matt Bulman Bulman with Forest Green Rovers.Personal informationFull name Matthew Kenneth BulmanDate of birth (1986-10-14) 14 October 1986 (age 37)Place of birth Bristol, EnglandPosition(s) GoalkeeperTeam informationCurrent team Oxford CityYouth career2004–2005 Swindon TownSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2005–2006 Swindon Town 0 (0)2006–2007 Salisbury City ? (0)2007–2008 Cirencester Town 40 (0)2008–2010 Swindon Supermarine 81 (0)2010–2011 Cirencester Town 3…

Berburu babi hutan. Perburuan atau berburu adalah praktik mengejar, menangkap, atau membunuh satwa liar untuk dimakan, rekreasi, perdagangan, atau memanfaatkan hasil produknya (seperti kulit, susu, gading dan lain-lain). Dalam penggunaannya, kata ini merujuk pada pemburuan yang sah dan sesuai dengan hukum, sedangkan yang bertentangan dengan hukum disebut dengan perburuan liar. Hewan yang disebut sebagai hewan buruan biasanya berupa mamalia berukuran sedang atau besar, atau burung. Artikel bertop…

Архангельский собор. Перспектива торцов надгробий царя Алексея Михайловича (1629—1676), царевича Алексея Алексеевича (1654—1670), царя Михаила Федоровича (1596—1645), царевичей-младенцев Василия и Ивана Михайловичей. Фотография К. А. Фишера. 1905 г. Из коллекций Музея архитекту�…

French supersonic fighter/interceptor aircraft Mirage III A Mirage IIIEA of the Argentinian Air Force Role Interceptor aircraftType of aircraft National origin France Manufacturer Dassault Aviation First flight 17 November 1956 Introduction 1961 Status In service with the Pakistan Air Force Primary users French Air Force (historical)Royal Australian Air Force (historical) Pakistan Air Force Israeli Air Force (historical) Number built 1422 Variants Dassault Mirage IIIV Dassault Mirage 5 Atla…

Danish finance minister Peder Oxe Peder Oxe (Peder Oxe til Nielstrup; 7 January 1520 – 24 October 1575) was a Danish finance minister and Steward of the Realm. Background At the age of twelve he was sent abroad to complete his education, and resided at the principal universities of Germany, the Netherlands, France, Italy, and Switzerland for seventeen years. On his return he found both his parents dead, and was appointed the guardian of his eleven young brothers and sisters, in which capacity,…

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Птиц�…
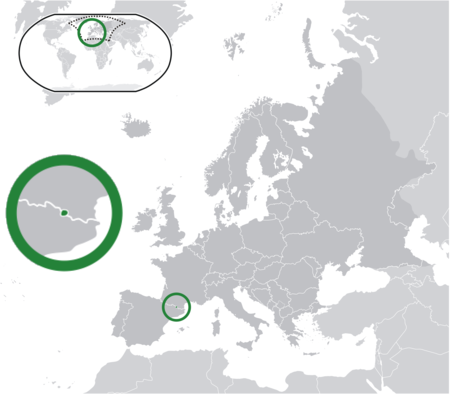
Telephone numbers in AndorraLocation of AndorraLocationCountryAndorraContinentEuropeNSN length6Access codesCountry code+376International access00Long-distancenone Telephone numbers in Andorra are six digits, with fixed line numbers beginning with the digits 8 and 7 and mobile telephone numbers with the digits 3 and 6. Toll-free numbers are eight digits, beginning with 1800 (if they are accessible only within Andorra) or 1802 (if they also can be reached internationally). Three-digit numbers star…

Toby RegboRegbo at the 2009 Venice Film FestivalLahirToby Finn RegboPekerjaanAktorTahun aktif2006 Toby Finn Regbo (lahir 18 Oktober 1991) adalah aktor asal Inggris. Ia mulai berkarier di teater pada tahun 2009 dalam pertunjukan berjudul Tusk Tusk, ia bermain sebagai Polly Stenham. Ia berperan dalam beberapa film seperti Mr. Nobody (sebagai Nemo Nobody umur 16), Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows (sebagai Dumbledore muda) dan sebagai Michael Walton dalam film Glorious 39. Filmografi Film T…

John Stafford John Stafford (24 novembre 1427 – 8 maggio 1473) è stato un nobile inglese ed ebbe il titolo di conte di Wiltshire. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Note 3 Bibliografia 4 Voci correlate Biografia Era figlio di Humphrey Stafford, I duca di Buckingham e della consorte Anne Neville, figlia di Ralph Neville, I conte di Westmorland. Nel 1461 venne creato cavaliere dell'ordine del bagno. Combatté come Yorkista nella battaglia di Hexham nel 1464. Nel 1469 venne fatto Steward del ducato di Cornova…

This article is about a people of ancient South West Asia. For an African ethnic group sometimes known as the Tukri, see Toucouleur people. The Turukkaeans were a Bronze and Iron Age people of Zagros Mountains. Their endonym has sometimes been reconstructed as Tukri. History Middle Bronze Turukku was regarded by the Old Assyrian Empire as a constant threat, during the reign of Shamshi-Adad I (1813-1782 BCE) and his son and successor Ishme-Dagan (1781-1750 BCE). The Turukkaeans were allied to the…

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang penyanyi. Untuk album berjudul-diri, lihat Luis Miguel (album). Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Luis Miguel (disambiguasi). Luis MiguelInformasi latar belakangNama lahirLuis Miguel Gallego BasteriNama lainEl Sol de México, Luismi, MickyLahir19 April 1970 (umur 54)Santurce, San Juan, Puerto RikoAsalPuerto Riko, Spanyol & ItaliaGenrePop Latin, pop, bolero, mariachiPekerjaanPenyanyi, penulis lagu, produser rekamanInstrumenVokal, pianoTahun aktif1981–sekaran…

National Geographic WildDiluncurkan21 Agustus 2006 (internasional) 29 Maret 2010 (Amerika Serikat)PemilikAmerika Serikat:National Geographic PartnersWalt Disney TelevisionInternasional:Fox Networks GroupPangsa pemirsa0.1% Britania Raya (Februari 2008, [1])SloganThink again.Dare to ExploreNegara Amerika Serikat (sejak 2010) SingapuraSaluran seindukNational Geographic Channel, National Geographic MusicSitus webhttp://www.natgeowild.com National Geographic Wild, biasanya disebut sebagai …

ХристианствоБиблия Ветхий Завет Новый Завет Евангелие Десять заповедей Нагорная проповедь Апокрифы Бог, Троица Бог Отец Иисус Христос Святой Дух История христианства Апостолы Хронология христианства Раннее христианство Гностическое христианство Вселенские соборы Ни�…

Jalur Utama MuroranKiHa 183 seri DMU pada layanan ekspres terbatas Hokuto.IkhtisarJenisKereta api lokalLokasiHokkaidoTerminusOshamambeIwamizawaStasiun44 (jalur utama)5 (jalur cabang)OperasiDibuka1892Pemilik JR HokkaidoData teknisLebar sepur1.067 mm (3 ft 6 in)ElektrifikasiAC 20 KV 50 Hz dengan Listrik aliran atas (Higashi-Muroran ke Numanohata, dan Muroran ke cabang Higashi-Muroran) Peta rute Jalur Utama Muroran (室蘭本線code: ja is deprecated , Muroran Honsen) adalah jal…

1950 film MiquetteDanièle Delorme and BourvilDirected byHenri-Georges ClouzotScreenplay byJean FerryHenri-Georges ClouzotBased onMiquette et sa mere byRobert de Flers &Gaston Arman de CaillavetProduced byRaymond BorderieRobert DorfmannPaul-Edmond DecharmeStarringLouis JouvetBourvilSaturnin FabreDanièle DelormeCinematographyLouis NéeArmand ThirardEdited byMonique KirsanoffMusic byAlbert LasryProductioncompanyCompagnie Industrielle et Commerciale CinématographiqueDistributed byLes Films Co…

「俄亥俄」重定向至此。关于其他用法,请见「俄亥俄 (消歧义)」。 俄亥俄州 美國联邦州State of Ohio 州旗州徽綽號:七葉果之州地图中高亮部分为俄亥俄州坐标:38°27'N-41°58'N, 80°32'W-84°49'W国家 美國加入聯邦1803年3月1日,在1953年8月7日追溯頒定(第17个加入联邦)首府哥倫布(及最大城市)政府 • 州长(英语:List of Governors of {{{Name}}}]]) • …

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع أنقرة (توضيح). أنقرة Ankara صورة لبعض معالم المدينة خريطة الموقع تاريخ التأسيس 1330م تقسيم إداري البلد تركيا[1][2] عاصمة لـ تركيا (13 أكتوبر 1923–)أنقرة المنطقة وسط الأناضول المحافظة أنقرة المسؤولون رئيس البلدية منصور يافاش (CHP) خصائص جغرافية …

非常尊敬的讓·克雷蒂安Jean ChrétienPC OM CC KC 加拿大第20任總理任期1993年11月4日—2003年12月12日君主伊利沙伯二世总督Ray HnatyshynRoméo LeBlancAdrienne Clarkson副职Sheila Copps赫布·格雷John Manley前任金·坎貝爾继任保羅·馬田加拿大自由黨黨魁任期1990年6月23日—2003年11月14日前任約翰·特納继任保羅·馬田 高級政治職位 加拿大官方反對黨領袖任期1990年12月21日—1993年11月4日…














