National Armed Forces
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Citt├Ā metropolitana di Cataniacitt├Ā metropolitana Citt├Ā metropolitana di Catania ŌĆō VedutaPalazzo Minoriti, sede istituzionale LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Sicilia AmministrazioneCapoluogo Catania Sindaco metropolitanoEnrico Trantino (FdI) dal 6-6-2023[1] Data di istituzione4 agosto 2015 TerritorioCoordinatedel capoluogo37┬░31ŌĆ▓N 15┬░04ŌĆ▓E / 37.516667┬░N 15.066667┬░E37.516667; 15.066667’╗┐ (Citt├Ā metropolitana di Catania)Coordinate: 37┬░3…

Serindit paruh-merah Status konservasi Hampir Terancam (IUCN 3.1)[1] Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Aves Ordo: Psittaciformes Superfamili: Psittacoidea Famili: Psittaculidae Subfamili: Agapornithinae Genus: Loriculus Spesies: L. exilis Nama binomial Loriculus exilisSchlegel, 1866 Serindit paruh-merah (Loriculus exilis) adalah spesies burung serindit dalam famili Psittaculidae. Burung ini endemik di Pulau Sulawesi.[2] Referensi ^ BirdLife In…

Not to be confused with Block├żltester or Blockleiter. Report Leader Campe with six Block Leaders during a roll call in Sachsenhausen concentration camp, 1936. Blockf├╝hrer (Block Leader; female rank name: Blockf├╝hrerin) was a paramilitary title specific to the SS-Death's Head Units in Concentration Camp Service. An SS-Block Leader was typically in charge of a prisoner barracks ranging from two hundred to three hundred concentration camp prisoners; in larger camps, the number of prisoners could…

Imperial AirwaysLogo Speedbird, dipakai Imperial Airways yang jarang menggunakannya pada pesawatnya sendiri sebelum 1939JenisSwastaIndustriTransportasi udaraNasibBergabung dengan British Airways Ltd.PendahuluBritish Marine Air Navigation Co LtdDaimler AirwayHandley Page TransportInstone Air LinePenerusBritish Overseas Airways CorporationDidirikan31 Maret 1924Ditutup24 November 1939KantorpusatCroydon, UK Imperial Airways adalah perusahaan transportasi udara jarak jauh komersial pertama Britania R…

Daniel Edward BarbeyJulukanPaman DanLahir(1889-12-23)23 Desember 1889Portland, OregonMeninggal11 Maret 1969(1969-03-11) (umur 79)Bremerton, WashingtonPengabdian Amerika SerikatDinas/cabang Angkatan Laut Amerika SerikatLama dinas1912ŌĆō1951Pangkat Wakil LaksamanaNRPO-7930KomandanFrontier Laut CaribbeanArmada KeempatArmada KetujuhPasukan Amfibi VIIUSS New YorkUSS RamapoUSS LeaUSS LawrencePerang/pertempuranPendudukan Amerika Serikat di NicaraguaRevolusi MeksikoPerang D…

Eucalyptus umbra Eucalyptus umbra Taman Nasional Ku-ring-gai Chase, Australia Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae (tanpa takson): Angiosperms (tanpa takson): Eudicots (tanpa takson): Rosids Ordo: Myrtales Famili: Myrtaceae Genus: Eucalyptus Spesies: E. umbra Nama binomial Eucalyptus umbraR.T.Baker Eucalyptus umbra adalah sebuah pohon eukaliptus dari wilayah pesisir bercurah hujan tinggi di New South Wales dan wilayah sekitar tenggara Queensland. Sebagai pohon berukuran kecil dan menengah, …

Berkik kayu Gallinago nemoricola Status konservasiRentanIUCN22693082 TaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumChordataKelasAvesOrdoCharadriiformesFamiliScolopacidaeGenusGallinagoSpesiesGallinago nemoricola Hodgson, 1836 Tata namaSinonim taksonCapella nemoricola (en) DistribusiEndemikNamdapha National Park (en) dan Tso Lhamo Cold Desert Conservation Area (en) lbs Berkik kayu ( Gallinago nemoricola ) adalah spesies berkik yang berkembang biak di Himalaya di India utara, Nepal, Bhutan, dan Cina selatan. Di mu…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada September 2016. Alen Stevanovi─ć Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Alen Stevanovi─ćTanggal lahir 7 Januari 1991 (umur 33)Tempat lahir Z├╝rich, SwissTinggi 1,80 m (5 ft 11 in)Posisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini Spezia(pinjaman dari Torino…

KepercayaanBangsa Romawi KunoMarcus Aurelius (berkudung toga)mempersembahkan kurban di Kuil Yupiter Amalan dan Akidah Persembahan curahan Votum Kuil Hari raya Ludi Perkabungan Seni rupa Pemujaan kaisar Agama-agama Misteri Ver Sacrum Pemuka Agama Pontifices Augures Vestales Flamines Fetiales Epulones Fratres arvales Dewa-Dewi Dua belas dewa-dewi utama Tridewata Kapitolin Tridewata Aventin Pratala indigitamenta Pertanian Persalinan Kaisar yang dipertuhan: Divus Iulius Divus Augustus Topik Terkait …

PathURLwww.path.comTipesitus web Registration (en)YaLangueInggris, Arab, Norwegia, Belanda, Prancis, Jerman, Yunani, Indonesia, Italia, Jepang, Korea, Mandarin Sederhana, Mandarin Tradisional, Melayu, Portugis, Rusia, Spanyol, Swedia, ThaiPemilikIndependen (2010-2015)KAKAO Inc.PembuatDave Morin dan Shawn Fanning (en) Service entry (en)November 2010Service retirement (en)September 2018 KeadaanDitutup Path adalah sebuah aplikasi jejaring sosial pada telepon pintar yang memungkinkan penggunanya unt…

St. Gallen Bendera Kanton St. Gallen Lambang Kanton St. Gallen Peta Swiss menunjukkan Kanton St. Gallen Ibu kota St. Gallen Wilayah 2026 km┬▓ (Peringkat ke-6) Titik tertinggi Ringelspitz 3248 m Jumlah penduduk (2006) 461.810 (Peringkat ke-5)223 /km┬▓ Bergabung 1803 Singkatan SG Bahasa Jerman Eksekutif [[Daftar pejabat Swiss pada 2005#{{{short name}}}|Regierungsrat (7)]] Legislatif Kantonsrat (180) Kotamadya 90 buah Distrik [[Distrik di Swiss#Kanton{{{short name}}}|8…

Brickyard 400NASCAR Cup SeriesTempatIndianapolis Motor SpeedwayLokasiSpeedway, Indiana, United StatesPerusahaan sponsorBig Machine RecordsLomba pertama1994 (1994)Lomba terakhir2020 (2020)Jarak tempuh4.025 mi (6.477,610 km)Jumlah putaran160Stage 1: 50Stage 2: 50Final stage: 60Nama sebelumnyaBrickyard 400 (1994ŌĆō2004, 2010)Allstate 400 at the Brickyard (2005ŌĆō2009)Brickyard 400 presented by BigMachineRecords.com (2011)Crown Royal presents the Your Hero's Name Here 400 at the …

Kimi wa MelodyLagu oleh AKB48Sisi-AKimi wa MelodySisi-BLALALA MessageShigamitsuita Seishun (Tipe A)Gonna Jump (Tipe B)Make Noise (Tipe C)Max toki 315-go (Tipe D)Mazari au mono (Tipe E)M.T. ni Sasagu (Teater)Dirilis09 Maret 2016 (2016-03-09)Format Singel maxi (CD) unduhan digital Direkam2015-16GenreJ-popDurasi4:43LabelYou, Be Cool! / KingPenciptaTrack UtamaLirik: Yasushi AkimotoMusik: you-meAransemen: Yuuichi NonakaProduserYasushi AkimotoVideo musik di YouTubeKimi wa Melody (Short ver.)MV ve…

Tai WoÕż¬ÕÆīStasiun angkutan cepat MTRNama TionghoaTionghoa Õż¬ÕÆī Jyutpingtaai3wo4Hanyu PinyinT├Āih├® TranskripsiTionghoa StandarHanyu PinyinT├Āih├®Yue: KantonRomanisasi YaleTaaiw├▓IPA[t╩░ā╦Éiw╔ö̏╦É]Jyutpingtaai3wo4 Informasi umumLokasiPo Nga Road, Tai WoDistrik Tai Po, Hong KongKoordinat22┬░27ŌĆ▓04ŌĆ│N 114┬░09ŌĆ▓40ŌĆ│E / 22.4511┬░N 114.1611┬░E / 22.4511; 114.1611Koordinat: 22┬░27ŌĆ▓04ŌĆ│N 114┬░09ŌĆ▓40ŌĆ│E / 22.4511┬░N 114.1611┬░E / 22.…
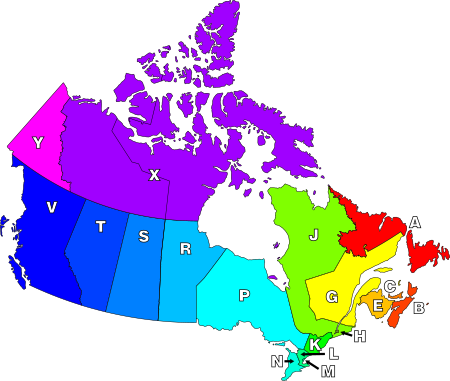
Kodepos Kanada NL NS PE NB QC ON MB SK AB BC NU/NT YT A B C E G H J K L M N P R S T V X Y Newfoundland dan Labrador - 35 FSA Catatan: Bulan Mei 2007, tidak ada kode pos yang berawalan A3*, A4*, A6* atau A7*. A0ASemenanjung Avalon Tenggara(Ferryland) A1ASt. John'sUtara A2AGrand Falls A5AClarenville A8ADeer Lake A9ABelum disetujui A0BSemenanjung Avalon Barat(Argentia) A1BSt. John'sBaratlautPemerintah Provinsi Newfoundland & Labrador A2BWindsor A5BBelum disetujui A8BBelum disetujui A9BBelum dis…

ž¦┘䞦ž¬žŁž¦ž» ž¦┘äž▒┘łž│┘Ŗ ┘ä┘āž▒ž® ž¦┘ä┘éž»┘ģ ž¦┘䞦ž│┘ģ ž¦┘ä┘ģž«ž¬žĄž▒ RFS ž¦┘äž▒┘Ŗž¦žČž® ┘āž▒ž® ž¦┘ä┘éž»┘ģ žŻž│ž│ ž╣ž¦┘ģ 1912 ž¦┘äž▒ž”┘Ŗž│ ┘å┘Ŗ┘ā┘ł┘䞦┘Ŗ ž¬┘ł┘äž│ž¬┘Ŗž« ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘éž▒ ┘ģ┘łž│┘ā┘ł[1] ž¦┘䞦┘垬ž│ž¦ž©ž¦ž¬ ž¦┘ä┘ü┘Ŗ┘üž¦ : 1912 ž¦┘䞦ž¬žŁž¦ž» ž¦┘䞯┘łž▒┘łž©┘Ŗ : 1992 ž▒┘ģž▓ ž¦┘ä┘ü┘Ŗ┘üž¦ RUS ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘ł┘éž╣ ž¦┘äž▒ž│┘ģ┘Ŗ www.rfs.ru ž¬ž╣ž»┘Ŗ┘ä ┘ģžĄž»ž▒┘Ŗ - ž¬ž╣ž»┘Ŗ┘ä ž¦┘äž┤ž╣ž¦ž▒ ž¦┘äž│ž¦ž©┘é ┘ä┘䞦ž¬žŁž¦ž» ž¦┘äž▒┘łž│┘Ŗ ž¬žŻž│ž│ ž¦┘䞦ž¬žŁž¦ž» ž¦┘äž▒┘łž│…
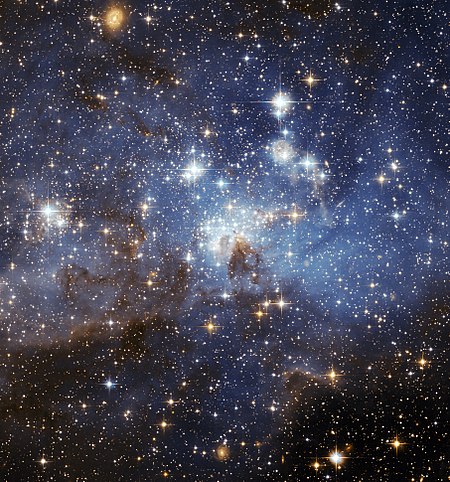

Continuous band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness For the racehorse, see Main Sequence (horse). A HertzsprungŌĆōRussell diagram plots the luminosity (or absolute magnitude) of a star against its color index (represented as BŌłÆV). The main sequence is visible as a prominent diagonal band from upper left to lower right. This plot shows 22,000 stars from the Hipparcos Catalog together with 1,000 low-luminosity stars (red and white dwarfs) from the Gliese Catalogue o…

American politician For other people with the same name, see John Murdock (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: John R. Murdock politician ŌĆō news ┬Ę newspapers ┬Ę books ┬Ę scholar ┬Ę JSTOR (March 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) John R. MurdockMurdock in 19…

Dalam artikel ini, nama keluarganya adalah Ma. Ma JinInformasi pribadiKebangsaanChinaLahir7 Mei 1988 (umur 35)Nantong, Jiangsu, China[1]Tinggi165 m (541 ft 4 in)[1]Berat55 kg (121 pon)PeganganKanadaGanda putri & ganda campuranPeringkat tertinggi1 (WD 23 September 2010) 1 (XD 12 September 2013) Rekam medali Putri bulu tangkis Mewakili Tiongkok Olympic Games 2012 London Mixed doubles World Championships 2010 Paris Mixed doubles 2010 Paris Wom…

ž¦┘äž╣┘䞦┘鞦ž¬ ž¦┘äž©┘łž¬ž¦┘å┘Ŗž® ž¦┘ä┘垦┘ģ┘Ŗž©┘Ŗž® ž©┘łž¬ž¦┘å ┘垦┘ģ┘Ŗž©┘Ŗž¦ ž©┘łž¬ž¦┘å ┘垦┘ģ┘Ŗž©┘Ŗž¦ ž¬ž╣ž»┘Ŗ┘ä ┘ģžĄž»ž▒┘Ŗ - ž¬ž╣ž»┘Ŗ┘ä ž¦┘äž╣┘䞦┘鞦ž¬ ž¦┘äž©┘łž¬ž¦┘å┘Ŗž® ž¦┘ä┘垦┘ģ┘Ŗž©┘Ŗž® ┘ć┘Ŗ ž¦┘äž╣┘䞦┘鞦ž¬ ž¦┘äž½┘垦ž”┘Ŗž® ž¦┘䞬┘Ŗ ž¬ž¼┘ģž╣ ž©┘Ŗ┘å ž©┘łž¬ž¦┘å ┘ł┘垦┘ģ┘Ŗž©┘Ŗž¦.[1][2][3][4][5] ┘ģ┘鞦ž▒┘åž® ž©┘Ŗ┘å ž¦┘äž©┘äž»┘Ŗ┘å ┘ćž░┘ć ┘ģ┘鞦ž▒┘åž® ž╣ž¦┘ģž® ┘ł┘ģž▒ž¼ž╣┘Ŗž® ┘ä┘äž»┘ł┘䞬┘Ŗ┘å: ┘łž¼┘ć ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘鞦ž▒┘åž® ž©┘…


