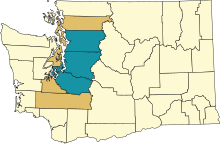
Puget Sound region
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Keuskupan Yaroslavl and RostovOrtodoks Katedral TransfigurasiLokasiKantor pusatYaroslavlInformasiDenominasiOrtodoks TimurGereja sui iurisGereja Ortodoks RusiaPendirian991 (resminya 1788)Kepemimpinan kiniBentukEparkiSitus webwww.yareparhia.ru Keuskupan Yaroslavl dan Rostov (Rusia: –Į—Ä–ĺ—Ā–Ľ–į–≤—Ā–ļ–į—Ź –ł –†–ĺ—Ā—ā–ĺ–≤—Ā–ļ–į—Ź –Ķ–Ņ–į—Ä—Ö–ł—Źcode: ru is deprecated ) adalah sebuah eparki Gereja Ortodoks Rusia di kawasan Oblast Yaroslavl.[1] Riwayat Keuskupan Rostov dan Suzdal didirikan…

artikel ini perlu dirapikan agar memenuhi standar Wikipedia. Tidak ada alasan yang diberikan. Silakan kembangkan artikel ini semampu Anda. Merapikan artikel dapat dilakukan dengan wikifikasi atau membagi artikel ke paragraf-paragraf. Jika sudah dirapikan, silakan hapus templat ini. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Sutradara Dan Produser Henry Lincoln Duarte alias Hendro Sudarto lahir di (Agana, Guam, Amerika Serikat, 2 September 1909)adalah seorang penulis dan …

Bagian dari seri tentangHukum KanonikGereja Katolik Hukum Mutakhir Kitab Hukum Kanonik 1983 Omnium in mentem Kitab Hukum Kanon Gereja-Gereja Timur Ad tuendam fidem Ex Corde Ecclesiae Indulgentiarum Doctrina Pastor Bonus Pontificalis Domus Universi Dominici Gregis Consuetudo Sejarah Hukum Kitab Hukum Kanonik 1917 Corpus Iuris Canonici Dekretis Regul√¶ Iuris Decretales Gregorii IX Dekretalis Decretum Gratiani Extravagantes Liber Septimus Tata Tertib Gereja Purba Didakhe Konstitusi Apostolik Kanon …

Letnan Jenderal TNI (Purn.)Hasnan Habib Duta Besar Indonesia untuk Amerika Serikat ke-10Masa jabatan1982‚Äď1985PresidenSoeharto PendahuluAshari DanudirdjoPenggantiSoesilo SoedarmanDuta Besar Indonesia untuk Thailand ke-10Masa jabatan1978‚Äď1982PresidenSoeharto PendahuluKharis SuhudPenggantiSubambang Informasi pribadiLahir(1927-12-03)3 Desember 1927 Maninjau, Agam, Sumatera Barat, Hindia BelandaMeninggal16 Februari 2006(2006-02-16) (umur 78) JakartaKebangsaanIndonesiaPekerjaanMiliter…

Group of nine deities in Egyptian mythology worshipped at Heliopolis Not to be confused with Enneads or Aeneid. For other uses, see Ennead (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Ennead ‚Äď news ¬∑ newspapers ¬∑ books ¬∑ scholar ¬∑ JSTOR (January 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this temp…

Bacillaria Bacillaria paxillifer Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae Divisi: Bacillariophyta Kelas: Bacillariophyceae Ordo: Bacillariales Famili: Bacillariaceae Genus: BacillariaJ.F. Gmelin (1791) Bacillaria adalah genus diatom dalam keluarga Bacillariaceae.[1][2][3] Spesies Bacillaria paradoxa Gmelin 1788 Bacillaria paxillifer (O. F. M√ľller) Hendey (1951) Referensi ^ ITIS database ^ M.G. Kelly; H. Bennion; E.J. Cox; B. Goldsmith; J. Jamieson; S. Juggins D.G. Mann; R.J.…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Maret 2023. Nancy Witcher Astor, Viscountess. Astor Nancy Witcher Astor (lahir: Langhorne), Viscountess Astor dari Hever Castle (19 Mei 1879 - 2 Mai 1964), merupakan perempuan Amerika pertama yang duduk di parlemen dalam sejarah Inggris. Nancy Astor lahir di Danville, …
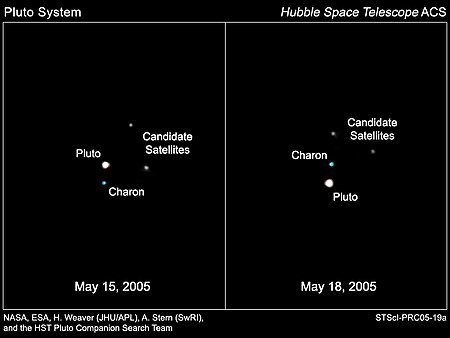
NixCitra Nix dengan resolusi terbesar yang diabadikan oleh New Horizons pada 14 Juli 2015. Citra ini diabadikan dalam warna abu-abu oleh LORRI, warna ditambahkan berdasarkan citra lainnya dari Ralph MVIC.PenemuanDitemukan olehTeleskop Luar Angkasa HubblePluto Companion Search TeamTanggal penemuan15 Juni 2005PenamaanPelafalan/ňąn…™ks/Asal namaNiksNama alternatifS/2005 P 2, P2, Pluto II[1]Kata sifat bahasa InggrisNictianCiri-ciri orbit[2]Sumbu semimayor48.694¬Ī3…

Koordinat: 41¬į17‚Ä≤N 48¬į37‚Ä≤E / 41.283¬įN 48.617¬įE / 41.283; 48.617 Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Kardash (disambiguasi). KardashKardashKoordinat: 41¬į17‚Ä≤N 48¬į37‚Ä≤E / 41.283¬įN 48.617¬įE / 41.283; 48.617Negara AzerbaijanRayonQubaZona waktuUTC+4 (AZT) ‚ÄĘ Musim panas (DST)UTC+5 (AZT) Kardash (juga Kyardash) adalah sebuah desa di Rayon Quba, Azerbaijan. Referensi Kardash pada GEOnet Names Server lbsRayon QubaIbu kota: Quba Adur Af…

ōßŔĄōĻŔĄōßŔāōßō™ ōßŔĄō•ŔÖōßōĪōßō™Ŕäō© ōßŔĄŔÉŔąŔĄŔąŔÖō®Ŕäō© ōßŔĄō•ŔÖōßōĪōßō™ ōßŔĄōĻōĪō®Ŕäō© ōßŔĄŔÖō™ō≠ōĮō© ŔÉŔąŔĄŔąŔÖō®Ŕäōß ōßŔĄō•ŔÖōßōĪōßō™ ōßŔĄōĻōĪō®Ŕäō© ōßŔĄŔÖō™ō≠ōĮō© ŔÉŔąŔĄŔąŔÖō®Ŕäōß ō™ōĻōĮŔäŔĄ ŔÖōĶōĮōĪŔä - ō™ōĻōĮŔäŔĄ ōßŔĄōĻŔĄōßŔāōßō™ ōßŔĄō•ŔÖōßōĪōßō™Ŕäō© ōßŔĄŔÉŔąŔĄŔąŔÖō®Ŕäō© ŔáŔä ōßŔĄōĻŔĄōßŔāōßō™ ōßŔĄōęŔÜōßō¶Ŕäō© ōßŔĄō™Ŕä ō™ō¨ŔÖōĻ ō®ŔäŔÜ ōßŔĄō•ŔÖōßōĪōßō™ ōßŔĄōĻōĪō®Ŕäō© ōßŔĄŔÖō™ō≠ōĮō© ŔąŔÉŔąŔĄŔąŔÖō®Ŕäōß.[1][2][3][4][5] ŔÖ…

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Liya Bahari Indah, Wangi-Wangi Selatan, Wakatobi ‚Äď berita ¬∑ surat kabar ¬∑ buku ¬∑ cendekiawan ¬∑ JSTOR Liya Bahari IndahDesaNegara IndonesiaProvinsiSulawesi TenggaraKabupatenWakatobiKecamatanWangi-Wangi …

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Saint L√©ger, Saint-L√©ger et L√©ger. L√©ger d'Autun Martyre de saint L√©ger, miniature (vers 1200). Saint, √©v√™que, martyr Naissance v. 616 D√©c√®s 678 ou 679 Nom de naissance L√©odegard Ordre religieux Ordre de Saint-Beno√ģt V√©n√©r√© √† Autun, Poitiers, Lucheux Canonisation 681 V√©n√©r√© par √Čglise catholique modifier L√©ger d'Autun ou L√©odegard (en latin Leodegarius) - francisation du germanique Leudgard, de ¬ę leud ¬Ľ (¬ę peupl…

Eric Maxim Choupo-Moting Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Jean-Eric Maxim Choupo-Moting[1]Tanggal lahir 23 Maret 1989 (umur 35)Tempat lahir Hamburg, Jerman Barat[2]Tinggi 191 cm (6 ft 3 in)[3][4]Posisi bermain PenyerangInformasi klubKlub saat ini Bayern M√ľnchenNomor 13Karier junior1995‚Äď2000 Teutonia 052000‚Äď2003 Altona 932003‚Äď2004 FC St. Pauli2004‚Äď2007 Hamburger SVKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2007‚Äď2011 Hamburger SV II 31 (1)2007‚Ä…

Witold BaŇĄka Presiden WADA ke-4PetahanaMulai menjabat 1 Januari 2020Wakil PresidenYang YangPendahuluCraig ReediePenggantiPetahanaMenteri Olahraga dan PariwisataMasa jabatan16 November 2015 ‚Äď 15 November 2019PresidenAndrzej DudaPerdana MenteriBeata SzydŇāoMateusz MorawieckiPendahuluAdam KorolPenggantiMateusz Morawiecki Informasi pribadiLahir3 Oktober 1984 (umur 39)Tychy, PolandiaPartai politikLaw and JusticeAlma materUniversitas Silesia di KatowiceProfesiAtlet lariIlmuwan pol…

„É≠„Éź„Éľ„Éą„ÉĽ„Éá„ÉĽ„Éč„Éľ„É≠Robert De Niro 2011ŚĻī„Āģ„Éá„ÉĽ„Éč„Éľ„É≠ÁĒüŚĻīśúąśó• (1943-08-17) 1943ŚĻī8śúą17śó•Ôľą80ś≠≥ԾȌáļÁĒüŚúį „āĘ„É°„É™„āꌟąŤ°ÜŚõĹ„ÉĽ„Éč„É•„Éľ„É®„Éľ„āĮŚ∑ě„Éč„É•„Éľ„É®„Éľ„āĮŚłāŤļęťē∑ 177 cmŤĀ∑ś•≠ šŅ≥ŚĄ™„ÄĀśė†ÁĒĽÁõ£ÁĚ£„ÄĀśė†ÁĒĽ„Éó„É≠„Éá„É•„Éľ„āĶ„Éľ„āł„É£„É≥„Éę śė†ÁĒĽ„ÄĀ„É܄ɨ„Éď„ÉČ„É©„ÉěśīĽŚčēśúüťĖď 1963ŚĻī -ťÖćŚĀ∂ŤÄÖ „ÉÄ„ā§„āĘ„É≥„ÉĽ„āĘ„Éú„ÉÉ„ÉąÔľą1976ŚĻī - 1988ŚĻīԾȄāį„ɨ„ā§„āĻ„ÉĽ„ÉŹ„ā§„āŅ„ÉĮ„ÉľÔľą1997ŚĻī - ԾȚłĽ„Ā™šĹúŚďĀ „Äé„Éü„Éľ„É≥„ÉĽ„āĻ„Éą„É™„Éľ„Éą„ÄŹÔľą1973ŚĻīԾȄÄé…

Philosophical system of Giovanni Gentile For the philosophical approach in analytic philosophy, see Actualism. Italian philosopher Giovanni Gentile, who developed actual idealism. It contrasted the transcendental idealism of Kant and the absolute idealism of Hegel Actual idealism is a form of idealism, developed by Giovanni Gentile, that grew into a grounded idealism, contrasting the transcendental idealism of Immanuel Kant, and the absolute idealism of G. W. F. Hegel. To Gentile, who considered…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Grandi. Dino GrandiDino GrandiFonctionsMinistre de la Justice12 juillet 1939 - 6 f√©vrier 1943Arrigo Solmi (en)Alfredo De Marsico (en)Conseiller √† la chambre des CorporationsXXXe l√©gislature du royaume d'Italie23 mars 1939 - 2 ao√Ľt 1943D√©put√©XXIXe l√©gislature du royaume d'Italie28 avril 1934 - 2 mars 1939Ministre des Affaires √©trang√®res du royaume d'Italie12 septembre 1929 - 19 juillet 1932Benito MussoliniBenito MussoliniD√©put√©XXVIIIe l√©gislature du r…

ś≠§śĘĚÁõģŚŹĮŚŹāÁÖߍčĪŤ™ěÁ∂≠ŚüļÁôĺÁßĎÁõłśáČśĘĚÁõģśĚ•śČ©ŚÖÖ„Äā (2021ŚĻī5śúą6śó•)Ťč•śā®ÁÜüśāȜ̕śļźŤĮ≠Ť®ÄŚíĆšłĽťĘėԾƍĮ∑ŚćŹŚä©ŚŹāŤÄÉŚ§ĖŤĮ≠ÁĽīŚüļÁôĺÁßϜȩŚÖ̰֜Áõģ„ÄāŤĮ∑ŚčŅÁõīśé•śŹźšļ§śúļśĘįÁŅĽŤĮĎԾƚĻüšłćŤ¶ĀÁŅĽŤĮĎšłćŚŹĮťĚ†„ÄĀšĹéŚďĀŤī®ŚÜÖŚģĻ„ÄāšĺĚÁČąśĚɌ揍ģģԾƍĮĎśĖáťúÄŚú®ÁľĖŤĺĎśĎėŤ¶Āś≥®śėéśĚ•śļźÔľĆśąĖšļéŤģ®Ťģļť°Ķť°∂ťÉ®ś†áŤģį{{Translated page}}ś†áÁ≠ĺ„Äā Áļ¶ÁŅįśĖĮť°ŅÁéĮÁ§ĀKalama Atoll ÁĺéŚúčśú¨ŚúüŚ§ĖŚįŹŚ≥∂Ś∂ľ Johnston Atoll śóóŚĻüťĘāś≠ĆÔľö„ÄäśėüśĘĚśóó„ÄčThe Star-Spangled BannerÁīĄÁŅįśĖĮť†ďÁíįÁ§ĀŚúįŚ…

Community college in Columbia, Maryland, U.S. For the school in Texas, see Howard College. This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (September 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Howard Community CollegeMottoYou can get there from hereTypePublic community collegeEstablished1966PresidentDaria WillisAcademic staff196 Full-Time and 454 Part-Time…

–Ē–Ķ—Ä–∂–į–≤–Ĺ–ł–Ļ –ļ–ĺ–ľ—Ė—ā–Ķ—ā —ā–Ķ–Ľ–Ķ–Ī–į—á–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ—Ź —Ė —Ä–į–ī—Ė–ĺ–ľ–ĺ–≤–Ľ–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ—Ź –£–ļ—Ä–į—ó–Ĺ–ł (–Ē–Ķ—Ä–∂–ļ–ĺ–ľ—ā–Ķ–Ľ–Ķ—Ä–į–ī—Ė–ĺ) –ü—Ä–ł–ľ—Ė—Č–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ—Ź –ļ–ĺ–ľ—Ė—ā–Ķ—ā—É–ó–į–≥–į–Ľ—Ć–Ĺ–į —Ė–Ĺ—Ą–ĺ—Ä–ľ–į—Ü—Ė—Ź–ö—Ä–į—ó–Ĺ–į –£–ļ—Ä–į—ó–Ĺ–į–Ē–į—ā–į —Ā—ā–≤–ĺ—Ä–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ—Ź 2003–ö–Ķ—Ä—Ė–≤–Ĺ–Ķ –≤—Ė–ī–ĺ–ľ—Ā—ā–≤–ĺ –ö–į–Ī—Ė–Ĺ–Ķ—ā –ú—Ė–Ĺ—Ė—Ā—ā—Ä—Ė–≤ –£–ļ—Ä–į—ó–Ĺ–ł–†—Ė—á–Ĺ–ł–Ļ –Ī—é–ī–∂–Ķ—ā 1 964 898 500 ‚āī[1]–ď–ĺ–Ľ–ĺ–≤–į –ě–Ľ–Ķ–≥ –Ě–į–Ľ–ł–≤–į–Ļ–ļ–ĺ–ü—Ė–ī–≤—Ė–ī–ĺ–ľ—á—Ė –ĺ—Ä–≥–…