Religion in Zimbabwe
|

Rendra WijayaRendra Wijaya (kanan) bersama Fran KurniawanInformasi pribadiKebangsaan IndonesiaLahir1 November 1984 (umur 39)Cirebon, IndonesiaPeganganKananGanda PutraPeringkat tertinggi51 Meiliana Jauhari, 54 Fran Kurniawan (9 Oktober 2009)Peringkat saat ini70 Rian Sukmawan (24 Juni 2012) Rendra Wijaya (lahir 1 November 1984) adalah salah satu pemain bulu tangkis Ganda Putra & Ganda Putri Indonesia berpasangan dengan Rian Sukmawan. Rendra Wijaya besar dan tumbuh dalam kel…

Ilustasi diet Asupan Referensi Diet (Dietary Reference Intake, DRI) adalah sistem rekomendasi gizi dari Institute of Medicine (IOM), National Academies (United States).[1] Ini diperkenalkan pada tahun 1997 untuk memperluas pedoman yang ada yang dikenal sebagai Angka Kecukupan Gizi (AKG) atau Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA, lihat di bawah). Nilai DRI berbeda dari yang digunakan dalam pelabelan gizi pada produk makanan dan suplemen makanan di AS dan Kanada, yang menggunakan Asupan Har…

Injil Yohanes 3:16 dalam bahasa Georgia Alkitab bahasa Georgia pertama kali dibuat dengan menerjemahkan ke dalam bahasa Georgia pada awal abad ke-5.[1] Naskah Injil Vani (Vani Gospels; Vani Four Gospels; Vanis otkhtavi, bahasa Georgia: бғ•бғҗбғңбғҳбғЎ бғқбғ—бғ®бғ—бғҗбғ•бғҳ) adalah sebuah manuskrip bergambar yang memuat teks Injil dengan tulisan Nuskhuri Georgia bertarikh akhir abad ke-12 hingga awal abad ke-13. Baru-baru ini sebuah terjemahan baru telah diselesaikan oleh Institute fo…

1991 novel by Poul Anderson This article is about the 1991 science fiction novel. For the artistically described twinkle of stars, see twinkling stars. For the scientifically described variability of stars, see variable star. Inconstant Star Cover of first editionAuthorPoul AndersonCover artistLarry ElmoreCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishSeriesMan-Kzin WarsGenreScience fictionPublisherBaen BooksPublication date1 January 1991 (1st edition)Media typePrint (Paperback)Pages314 (paperback…

Ice hockey award Lady Byng Memorial TrophySportIce hockeyAwarded forplayer adjudged to have exhibited the best type of sportsmanship and gentlemanly conduct combined with a high standard of playing ability[1]HistoryFirst award1924вҖ“25 NHL seasonMost winsFrank Boucher (7)Most recentAnze KopitarLos Angeles Kings The Lady Byng Memorial Trophy, formerly known as the Lady Byng Trophy, is presented each year to the National Hockey League player adjudged to have exhibited the best type of spor…

Strada statale 313di Passo CoreseLocalizzazioneStato Italia Regioni Lazio Umbria Province Terni Rieti DatiClassificazioneStrada statale InizioPasso Corese FineTerni Lunghezza58,250[1][2] km Provvedimento di istituzioneD.M. 1/02/1962 - G.U. 97 del 13/04/1962[3] Gestore Lazio: ASTRAL (dal 2007)[4] Umbria: provincia di Terni (dal 2001) Manuale La ex strada statale 313 di Passo Corese (SS 313), ora strada regionale 313 di Passo Cores…

IdahoNegara bagian BenderaLambangPeta Amerika Serikat dengan ditandaiNegaraAmerika SerikatSebelum menjadi negara bagianIdaho TerritoryBergabung ke Serikat3 Juli 1890 (43)Kota terbesarBoiseMetropolitan terbesarKawasan metropolitan BoisePemerintahan вҖў GubernurC.L. Butch Otter (R) вҖў Wakil GubernurBrad Little (R) вҖў Majelis tinggi{{{Upperhouse}}} вҖў Majelis rendah{{{Lowerhouse}}}Senator ASMike Crapo (R)Jim Risch (R)Delegasi DPR AS1-Walt Minnick (D)2-Mike…

BBC SportJenisDepartment of the BBCIndustriMediaGenreOlahragaDidirikan1988KantorpusatMediaCityUK,Salford, Manchester, Britania RayaWilayah operasiLayanan tertentu di Britania Raya dan seluruh duniaTokohkunciBarbara Slater (Direktur)JasaRadio Televisi OnlinePemilikBBCSitus webwww.bbc.co.uk/sport BBC Sport adalah departemen dari divisi BBC North yang menyediakan cakupan olahraga nasional untuk BBC Television, radio dan online. BBC memegang hak siar televisi dan radio Inggris untuk beberapa olahrag…

Dominique Voynet Dominique Voynet en 2006. Fonctions Directrice de l'Agence rГ©gionale de santГ© de Mayotte 1er septembre 2019 вҖ“ 1er fГ©vrier 2021(1 an et 5 mois) PrГ©dГ©cesseur Poste créé Successeur StГ©phanie FrГ©chet (intГ©rim) Olivier Brahic Maire de Montreuil 22 mars 2008 вҖ“ 4 avril 2014(6 ans et 13 jours) PrГ©dГ©cesseur Jean-Pierre Brard Successeur Patrice Bessac SГ©natrice franГ§aise 26 septembre 2004 вҖ“ 30 septembre 2011(7 ans et 4 jours) Гүlection 26 …

Part of a series onBritish law Acts of Parliament of the United Kingdom Year 1801 1802 1803 1804 1805 1806 1807 1808 1809 1810 1811 1812 1813 1814 1815 1816 1817 1818 1819 1820 1821 1822 1823 1824 1825 1826 1827 1828 1829 1830 1831 1832 1833 1834 1835 1836 1837 1838 1839 1840 1841 1842 1843 1844 1845 1846 1847 1848 1849 1850 1851 1852 1853 1854 1855 1856 1857 1858 1859 1860 1861 1862 1863 1864 1865 1866 1867 1868 1869 1870 1871 1872 1873 1874 1875 1876 1877 1878 1879…

Former association football club in Scotland Football clubBlythswoodFull nameBlythswood Football ClubFounded1873Dissolved1882GroundWestburn ParkSecretaryGeorge Armstrong Home colours Blythswood Football Club was a 19th-century football club based in Glasgow. History The club was founded on 14 August 1873 as an offshoot of the Blythswood Cricket Club,[1] which had changed its name from the Bellegrove club in 1866, and which played at Queen's Park until 1869. Announcement of the foundation…

BBC New Year Special This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: BBC New Year's Eve specials вҖ“ news В· newspapers В· books В· scholar В· JSTOR (January 2020) …

FC LuzernNama lengkapFussball Club LuzernJulukanFCLBerdiri1901StadionSwissporarena(Kapasitas: 17,800)KetuaMike HauserManajerCarlos BerneggerLigaSwiss Super League2022вҖ“23ke-4 Kostum kandang Kostum tandang Berkas:Allmend.jpgStadion Allmend, markas FC Luzern. FC Luzern (atau FC Lucerne) adalah sebuah klub sepak bola di Swiss yang didirikan pada tahun 1901. Warna resmi klub adalah biru dan putih yang diambil dari warna dasar lambang Kanton Luzern dan Kota Luzern. Markas mereka adalah Stadion Allme…

Kimagure PrincessLagu oleh Morning Musumedari album 10 My MeDirilis28 Oktober 2009 (CD)4 November 2009 (DVD)FormatCD, DVDDirekam2009GenreJ-popLabelZetimaProduserTsunkuVideo musikKimagure Princess di YouTube Kimagure Princess (ж°—гҒҫгҒҗгӮҢгғ—гғӘгғігӮ»гӮ№code: ja is deprecated , Putri Plin-plan) Adalah singel ke-41 Unit Hello! Project Morning Musume. Singel ini dirilis pada tanggal 28 Oktober 2009[1] dan menjadi lagu penutup untuk acara TV Tokyo, The GyakuryЕ« Researchers. Ini juga menjadi…

TaГ§a Brasil 1966 Competizione TaГ§a Brasil Sport Calcio Edizione 8ВӘ Organizzatore CBD Date dal 10 luglioal 7 dicembre 1966 Luogo Brasile Partecipanti 22 Risultati Vincitore Cruzeiro(1Вә titolo) Secondo Santos Statistiche Miglior marcatore Bita (NГЎutico) e Toninho Guerreiro (Santos), 10 gol Incontri disputati 47 Gol segnati 149 (3,17 per incontro) Cronologia della competizione 1965 1967 Manuale La TaГ§a Brasil 1966 (in italiano Coppa Brasile 1966) ГЁ stata la 8ВӘ edizio…

L'histoire de l'AlgГ©rie s'insГЁre dans l'histoire plus large du Maghreb et remonte Г des millГ©naires. Dans l'AntiquitГ©, le territoire algГ©rien connaГ®t la formation du royaume de Numidie considГ©rГ© comme le premier Г©tat algГ©rien de lвҖҷhistoire[1], avant de passer sous la domination partielle des Romains, des Vandales, des Byzantins et des principautГ©s berbГЁres indГ©pendantes (notamment le royaume d'Altava et le royaume des Maures et des Romains)[2]. Le VIIe siГЁcle marque le dГ©b…

вҖ Р§РөР»РҫРІРөРә РҝСҖСҸРјРҫС…РҫРҙСҸСүРёР№ РқР°СғСҮРҪР°СҸ РәлаСҒСҒифиРәР°СҶРёСҸ Р”РҫРјРөРҪ:РӯСғРәР°СҖРёРҫСӮСӢРҰР°СҖСҒСӮРІРҫ:Р–РёРІРҫСӮРҪСӢРөРҹРҫРҙСҶР°СҖСҒСӮРІРҫ:РӯСғРјРөСӮазРҫРёР‘РөР· СҖР°РҪРіР°:ДвСғСҒСӮРҫСҖРҫРҪРҪРө-СҒРёРјРјРөСӮСҖРёСҮРҪСӢРөР‘РөР· СҖР°РҪРіР°:Р’СӮРҫСҖРёСҮРҪРҫСҖРҫСӮСӢРөРўРёРҝ:РҘРҫСҖРҙРҫРІСӢРөРҹРҫРҙСӮРёРҝ:РҹРҫР·РІРҫРҪРҫСҮРҪСӢРөРҳРҪС„СҖР°СӮРёРҝ:Р§РөР»СҺСҒСӮРҪРҫСҖРҫСӮСӢРөРқР°РҙРәлаСҒСҒ:Р§РөСӮРІРөСҖРҫРҪРҫРіРёРөРҡлаРҙР°:РҗРјРҪРёРҫСӮСӢРҡлаРҙР°:РЎРёРҪР°РҝСҒРёРҙСӢРҡлЅ
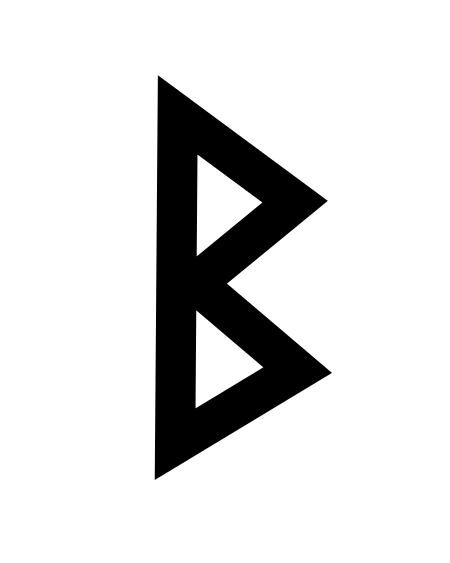
жӯӨжўқзӣ®д»Ӣзҙ№зҡ„жҳҜжӢүдёҒеӯ—жҜҚдёӯзҡ„第2дёӘеӯ—жҜҚгҖӮе…ідәҺе…¶д»–з”Ёжі•пјҢиҜ·и§ҒгҖҢB (ж¶Ҳжӯ§д№ү)гҖҚгҖӮ жҸҗзӨәпјҡжӯӨжқЎзӣ®йЎөзҡ„дё»йўҳдёҚжҳҜеёҢи…Ҡеӯ—жҜҚО’гҖҒиҘҝйҮҢе°”еӯ—жҜҚР’гҖҒР‘гҖҒРӘгҖҒР¬жҲ–еҫ·иҜӯеӯ—жҜҚбәһгҖҒГҹгҖӮ BB b(и§ҒдёӢ)з”Ёжі•жӣёеҜ«зі»зөұжӢүдёҒеӯ—жҜҚиӢұж–Үеӯ—жҜҚISOеҹәжң¬жӢүдёҒеӯ—жҜҚпјҲиӢұиҜӯпјҡISO basic Latin alphabetпјүзұ»еһӢе…Ёйҹізҙ ж–Үеӯ—зӣёе…іжүҖеұһиӘһиЁҖжӢүдёҒиҜӯиҜ»йҹіж–№жі• [b][p][Й“](йҖӮеә”еҸҳдҪ“)Unicodeзј–з ҒU+0042, U+0062еӯ—жҜҚйЎәдҪҚ2ж•°еҖј 2жӯ·еҸІзҷјеұ•…

иҝҪжҷүйҷёи»ҚдәҢзҙҡдёҠе°Үи¶ҷ家й©Өе°Үи»ҚдёӘдәәиө„ж–ҷеҮәз”ҹ1910е№ҙ еӨ§жё…жІіеҚ—зңҒиЎӣијқеәңжұІзёЈйҖқдё–1958е№ҙ8жңҲ23ж—Ҙ(1958жӯІвҖ”08вҖ”23)пјҲ47вҖ”48жӯІпјү † дёӯиҸҜж°‘еңӢзҰҸе»әзңҒйҮ‘й–ҖзёЈеӣҪзұҚ дёӯиҸҜж°‘еңӢж”ҝе…ҡ дёӯеңӢеңӢж°‘й»ЁиҺ·еҘ– йқ’еӨ©зҷҪж—ҘеӢіз« пјҲиҝҪиҙҲпјүеҶӣдәӢиғҢжҷҜж•Ҳеҝ дёӯиҸҜж°‘еңӢжңҚеҪ№ еңӢж°‘йқ©е‘Ҫи»Қ дёӯиҸҜж°‘еңӢйҷёи»ҚжңҚеҪ№ж—¶й—ҙ1924е№ҙпјҚ1958е№ҙеҶӣиЎ” дәҢзҙҡдёҠе°Ү пјҲиҝҪжҷүпјүйғЁйҳҹеӣӣеҚҒдёғеё«жҢҮжҢҘжқұеҢ—еүҝеҢӘзёҪеҸёд»ӨйғЁеҸғи¬Җй•·йҷёи»ҚзёҪйғ…

Israeli psychologist and genocide scholar Israel CharnyBorn1931 (age 92–93)Brooklyn, New YorkOccupation(s)Psychologist, genocide scholar Israel W. Charny (born 1931) is an Israeli psychologist and genocide scholar.[1] He is the editor of two-volume Encyclopedia of Genocide,[2] and executive director of the Institute on the Holocaust and Genocide in Jerusalem.[3][4] Background Israel Charny received his A.B. in Psychology with Distinction from Temple Uni…



