Siege of Lleida (1149)
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang a vehicle manufacturing company. Untuk other uses, lihat Freightliner. Freightliner TrucksJenisDivisiIndustriOtomotifDidirikan1942; 82 tahun lalu (1942)(as Freightliner Inc)KantorpusatPortland, Oregon, A.S.TokohkunciJohn O'Leary, CEOProdukkendaraan niaga, kendaraan mewahsPemilikDaimler TruckIndukDaimler Truck North AmericaSitus webfreightliner.comFreightliner Trucks adalah produsen truk Amerika.[1] Didirikan pada tahun 1929 sebagai divisi manufaktu…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Maret 2023. Gunung Tua dapat mengacu pada beberapa hal berikut: Gunung Tua, Sosa, Padang Lawas Gunung Tua, Tanah Pinem, Dairi Gunung Tua, Tugala Oyo, Nias Utara Gunung Tua Baru, Padang Bolak, Padang Lawas Utara Gunung Tua Jae, Panyabungan, Mandailing Natal Gunung Tua J…

Voce principale: Kieler Sportvereinigung Holstein von 1900. Kieler Sportvereinigung Holstein von 1900Stagione 2001-2002Sport calcio Squadra Holstein Kiel Allenatore Gerd-Volker Schock Regionalliga nord13° posto Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Schiersand, Greil, Guščinas, Rose (34)Totale: Schiersand, Greil, Guščinas, Rose (34) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Guščinas (11)Totale: Guščinas (11) StadioHolstein-Stadion Maggior numero di spettatori7 197 vs. Lubecca Minor numero di spettat…

X Games of the Small States of EuropeCountry MaltaNations8Events105 in 10 sportsOpeningJune 2ClosingJune 7Opened byGuido de MarcoWebsitewww.nocmalta.org/gsse.htm← 20012005 → The 2003 Games of the Small States of Europe, or the Xth Games of the Small States of Europe, were held in Valletta, Malta from June 2 to June 7, 2003. Valletta previously hosted the games in 1993. Malta was not due to host the Games again until 2009, but a strong bid helped them to gain the games …

Alan MacDiarmidAlan MacDiarmid, dibawa saat berkunjung ke Beijing, Cina, Mei 2005.Lahir14 April 1927Masterton, Selandia BaruMeninggal7 Februari 2007Drexel Hill, Pennsylvania, Amerika SerikatAlmamaterVictoria University of WellingtonPenghargaanPenghargaan Nobel untuk bidang Kimia pada tahun 2000 Alan Graham MacDiarmid (14 April 1927 – 7 Februari 2007) adalah seorang kimiawan kelahiran Selandia Baru. Bersama dengan Alan Heeger dan Hideki Shirakawa pada 2000 ia dianugerahi Hadiah No…

Questa voce è parte della serieStoria della musica Categoria:Storia della musica Categoria:Musica per anno Musica nel mondo antico · medievale · rinascimentale · barocca · classica · romantica · moderna · contemporanea Preistoria e antichità Musica preistorica - ante XXXV sec. a.C. Musica nel mondo antico - ca. XXXV sec. a.C. - V sec. d.C. Musica mesopotamica - ca. XXXIII-V sec. a.C. Musica egizia - ca. XXVII-XVI sec. a.C. Musica greca - ca. X sec. - 1…

Lokasi An Gang di Vietnam. Provinsi An Giang merupakan sebuah provinsi di Vietnam. Provinsi ini terletak di bagian selatan. Tepatnya di dekat perbatasan Kamboja. Provinsi ini memiliki luas wilayah 3.406 km² dengan memiliki jumlah penduduk 2.170.100 jiwa (2004). Provinsi ini beribu kota di Long Xuyen. Terletak di region Mekong Delta. Demografi Etnis Ibadah di Kuil Van Linh Provinsi An Giang sebagian besar dihuni oleh etnis Kinh atau Vietnam. Data pada sensus penduduk Vietnam 2009, dari 2.14…

Second formation of Nigeria 1979–1983 Federal Republic of Nigeria1979–1983 Flag Coat of arms Motto: Unity and Faith, Peace and Progress[1]Anthem: Arise, O Compatriots[1]CapitalLagosCommon languagesEnglish · Hausa · Igbo · Yoruba · and other regional languagesReligion Christianity · Islam · Traditional beliefsGovernmentFederal presidential republicPresident • 1979–…

Air-pollution episode in New York City 1966 New York City smogOn November 25, 1966, the front page of The New York Times featured this photograph by Neal Boenzi. Taken the morning before, the photo shows a view facing south from the Empire State Building.[1] Roy Popkin of the EPA said the surrealistic image made Lower Manhattan look like a science-fiction Cloud City.[2]DateNovember 23–26, 1966LocationAcute smog in New York City; lesser smog throughout the New York metropolitan …
Petrokemiskt raffinaderi i Grangemouth, Skottland. Petrokemi är en avdelning inom den industriella kemin, som sysslar med raffineringen av petroleum och naturgas[1] samt deras sidoprodukter. Se även Kemiteknik Referenser ^ ”petrokemi - Uppslagsverk”. www.ne.se. https://www.ne.se/uppslagsverk/encyklopedi/l%C3%A5ng/petrokemi. Läst 27 juni 2020. Externa länkar Läroresurs för petrokemi Tekniskt Magasin, med Erik Bergsten, från 1964, om den petrokemiska industrin i Stenungsun…

Ruta de la Seda: red viaria del corredor Chang'an-Tianshan Patrimonio de la Humanidad de la Unesco Rutas principales de la Ruta de la SedaLocalizaciónPaís China ChinaKirguistán Kirguistán TayikistánUzbekistán Uzbekistán TurkmenistánIrán IránIrak IrakSiria SiriaTurquía TurquíaJordania JordaniaPalestina PalestinaIsrael IsraelEgipto EgiptoDatos generalesTipo CulturalCriterios ii, iii, iv, viIdentificación 1442Región Asia y Pa…

Suburb of Sydney, New South Wales, AustraliaBalmainSydney, New South WalesDarling StreetBalmainBalmainCoordinates33°51′32″S 151°10′45″E / 33.85895°S 151.17906°E / -33.85895; 151.17906Population10,454 (SAL 2021)[1]Established1836Postcode(s)2041Elevation49 m (161 ft)Area1.5 km2 (0.6 sq mi)Location5 km (3 mi) west of Sydney CBDLGA(s)Inner West CouncilState electorate(s)BalmainFederal division(s)Grayndler Suburbs aro…
Schleswig-HolsteinNegara bagian BenderaLambang kebesaranKoordinat: 54°28′12″N 9°30′50″E / 54.47000°N 9.51389°E / 54.47000; 9.51389NegaraJermanIbu kotaKielPemerintahan • BadanLandtag of Schleswig-Holstein • Presiden MenteriDaniel Günther (CDU) • Governing partiesCDU / Hijau / FDP • Bundesrat4 (dari 69)Luas • Total15.763,18 km2 (608,620 sq mi)Populasi (31 Desember 2017)[1]&#…

هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (نوفمبر 2020) سيجونغ سيتي شعار الاسم الرسمي (بالكورية: 세종특별자치시) الإحداثيا�…

本表是動態列表,或許永遠不會完結。歡迎您參考可靠來源來查漏補缺。 潛伏於中華民國國軍中的中共間諜列表收錄根據公開資料來源,曾潛伏於中華民國國軍、被中國共產黨聲稱或承認,或者遭中華民國政府調查審判,為中華人民共和國和中國人民解放軍進行間諜行為的人物。以下列表以現今可查知時間為準,正確的間諜活動或洩漏機密時間可能早於或晚於以下所歸類�…
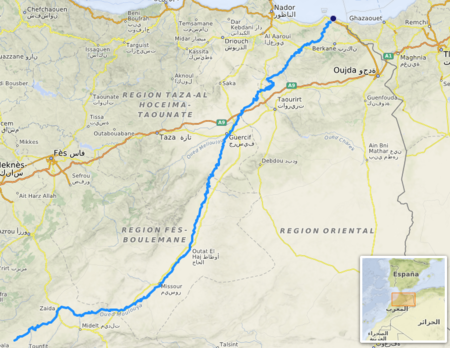
وادي ملوية صورة لمصب نهر ملوية المنطقة البلد المغرب الخصائص الطول 600 كم المجرى المنبع الرئيسي الأطلس المتوسط والكبير والريف المصب البحر الأبيض المتوسط مساحة الحوض 74.000 كم² الروافد وادي زا تعديل مصدري - تعديل ملوية (بالأمازيغية: ملویت؛ بالنطق الريفي: ملوشت) نهر ف…

McMillan Brothers Tac-50 Varian Tac-50 dengan nama C15 yang digunakan militer Kanada Jenis Senapan runduk, Senapan anti materiel Negara asal Amerika Serikat Sejarah pemakaian Masa penggunaan 2000-sekarang Digunakan oleh Turki Pada perang Perang Afganistan [1] Sejarah produksi Tahun 1980s Produsen McMillan Brothers Rifle Co. Diproduksi 1980s–sekarang Spesifikasi Berat 260 pon (117,9 kg) Panjang 570 in (14.478 mm) Panjang laras 290…

北賽普勒斯土耳其共和國Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti 国旗 国徽 国歌:《独立进行曲》首都暨最大城市北尼科西亚官方语言土耳其语族群土耳其裔塞浦路斯人宗教伊斯蘭教政府單一制 半总统制 共和国• 總統 埃尔辛·塔塔尔• 總理 于纳尔·于斯泰尔(英语:Ünal Üstel) 立法机构共和国议会成立• 土耳其占领 1974年• 独立 1983年11月15日 面积• 总计3,355平方公里�…

Epithelial hyperplasia redirects here. For epidermis in general, see Epidermal hyperplasia. Medical conditionHeck's diseaseOther namesMultifocal epithelial hyperplasiaSpecialtyOral and maxillofacial surgery Heck's disease, also known as Focal Epithelial Hyperplasia, is an asymptomatic, benign neoplastic condition characterized by multiple white to pinkish papules that occur diffusely in the oral cavity.[1][2]: 411 Can present with slightly pale, smooth …

Department of the University of Cambridge Department of Physiology, Development and Neuroscience (PDN)ChairmanSarah Bray and William Henry Colledge (joint Heads of Department)LocationCambridge, United KingdomAffiliationsUniversity of CambridgeWebsitewww.pdn.cam.ac.ukThe Department of Physiology, Development and Neuroscience, (PDN) is a part of the School of Biological Sciences at the University of Cambridge. Research in PDN focuses on three main areas: Cellular and Systems Physiology, Developmen…