|
Syntactic movementSyntactic movement is the means by which some theories of syntax address discontinuities. Movement was first postulated by structuralist linguists who expressed it in terms of discontinuous constituents or displacement.[1] Some constituents appear to have been displaced from the position in which they receive important features of interpretation.[2] The concept of movement is controversial and is associated with so-called transformational or derivational theories of syntax (such as transformational grammar, government and binding theory, minimalist program). Representational theories (such as head-driven phrase structure grammar, lexical functional grammar, construction grammar, and most dependency grammars), in contrast, reject the notion of movement and often instead address discontinuities with other mechanisms including graph reentrancies, feature passing, and type shifters. IllustrationMovement is the traditional means of explaining discontinuities such as wh-fronting, topicalization, extraposition, scrambling, inversion, and shifting:[3]
The a-sentences show canonical word order, and the b-sentences illustrate the discontinuities that movement seeks to explain. Bold script marks the expression that is moved, and underscores mark the positions from which movement is assumed to have occurred. In the first a-sentence, the constituent the first story serves as the object of the verb likes and appears in its canonical position immediately following that verb. In the first b-sentence, the constituent which story likewise serves as the object of the verb, but appears at the beginning of the sentence rather than in its canonical position following the verb. Movement-based analyses explain this fact by positing that the constituent is base-generated in its canonical position but is moved to the beginning of the sentence, in this case because of a question-forming operation. Representation of movementThe examples above use an underscore to mark the position from which movement is assumed to have occurred. In formal theories of movement, these underscores correspond to actual syntactic objects, either traces or copies depending on one's particular theory.[4] e.g.
Subscripts help indicate the constituent that is assumed to have left a trace in its former position, the position marked by t.[5] The other means of indicating movement is in terms of copies. Movement is actually taken to be a process of copying the same constituent in different positions and deleting the phonological features in all but one case.[6] Italics are used in the following example to indicate a copy that lacks phonological representation:
There are various nuances associated with each of the means of indicating movement (blanks, traces, copies), but for the most part, each convention has the same goal of indicating the presence of a discontinuity. Types of movementWithin generative grammar, various types of movement have been distinguished. An important distinction is the one between head movement and phrasal movement, with the latter type being further subdivided into A-movement and A-bar movement. Copy movement is another more general type of movement. A-movement vs. A-bar movementArgument movement (A-movement) displaces a phrase into a position in which a fixed grammatical function is assigned, such as in movement of the object to the subject position in passives:[7]
Non-argument movement (A-bar movement or A'-movement), in contrast, displaces a phrase into a position where a fixed grammatical function is not assigned, such as the movement of a subject or object NP to a pre-verbal position in interrogatives:
The A- vs. A-bar distinction is a reference to the theoretical status of syntax with respect to the lexicon. The distinction elevates the role of syntax by locating the theory of voice (active vs. passive) almost entirely in syntax (as opposed to in the lexicon). A theory of syntax that locates the active-passive distinction in the lexicon (the passive is not derived via transformations from the active) rejects the distinction entirely. Phrasal movement vs. head movementA different partition among types of movement is phrasal vs. head movement.[8] Phrasal movement occurs when the head of a phrase moves together with all its dependents in such a manner that the entire phrase moves. Most of the examples above involve phrasal movement. Head movement, in contrast, occurs when just the head of a phrase moves, and the head leaves behind its dependents. Subject-auxiliary inversion is a canonical instance of head movement:
On the assumption that the auxiliaries has and will are the heads of phrases, such as of IPs (inflection phrases), the b-sentences are the result of head movement, and the auxiliary verbs has and will move leftward without taking with them the rest of the phrase that they head. The distinction between phrasal movement and head movement relies crucially on the assumption that movement is occurring leftward. An analysis of subject-auxiliary inversion that acknowledges rightward movement can dispense with head movement entirely:
The analysis shown in those sentences views the subject pronouns someone and she as moving rightward, instead of the auxiliary verbs moving leftward. Since the pronouns lack dependents (they alone qualify as complete phrases), there would be no reason to assume head movement. Islands and barriers to movementSince it was first proposed, the theory of syntactic movement has yielded a new field of research aiming at providing the filters that block certain types of movement. Called locality theory,[9] it is interested in discerning the islands and barriers to movement. It strives to identify the categories and constellations that block movement from occurring. In other words, it strives to explain the failure of certain attempts at movement:
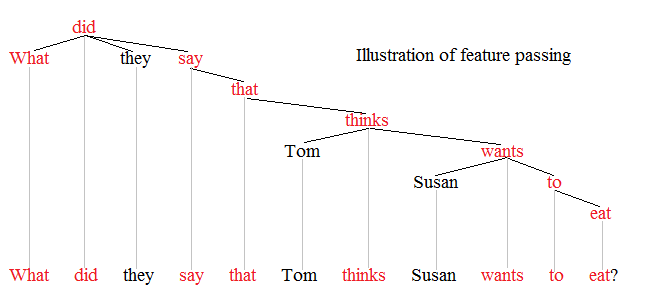
All of the b-sentences are now disallowed because of locality constraints on movement. Adjuncts and subjects are islands that block movement, and left branches in NPs are barriers that prevent pre-noun modifiers from being extracted out of NPS. Feature passingSyntactic movement is controversial, especially in light of movement paradoxes. Theories of syntax that posit feature passing reject syntactic movement outright, that is, they reject the notion that a given "moved" constituent ever appears in its "base" position below the surface: the positions marked by blanks, traces, or copies. Instead, they assume that there is but one level of syntax, and all constituents appear only in their surface positions, with no underlying level or derivation. To address discontinuities, they posit that the features of a displaced constituent are passed up and/or down the syntactic hierarchy between that constituent and its governor.[10] The following tree illustrates the feature passing analysis of a wh-discontinuity in a dependency grammar.[11] The words in red mark the catena (chain of words) that connects the displaced wh-constituent what to its governor eat, the word that licenses its appearance.[12] The assumption is that features (=information) associated with what (e.g. noun, direct object) are passed up and down along the catena marked in red. In that manner, the ability of eat to subcategorize for a direct object NP is acknowledged. By examining the nature of catenae like the one in red, the locality constraints on discontinuities can be identified. TracesIn government and binding theory and some of its descendant theories, movement leaves behind an empty category called a trace.
In such theories, traces are considered real parts of syntactic structure, detectable in secondary effects they have on the syntax. For instance, one empirical argument for their existence comes from the English phenomenon of wanna contraction, in which want to contracts into wanna. This phenomenon has been argued to be impossible when a trace would intervene between "want" and "to", as in the b-sentence below.[13]
Evidence of this sort has not led to a full consensus in favor of traces, since other kinds of contraction permit an intervening putative trace.[14]
Proponents of the trace theory have responded to these counterarguments in various ways. For instance, Bresnan (1971) argued that contractions of "to" are enclitic while contractions of tensed auxiliaries are proclitic, meaning that only the former would be affected by a preceding trace.[15] See alsoReferences
Sources
|