Tawfiq al-Hakim
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Questa voce sull'argomento contee del Wisconsin è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Contea di MarathonconteaLocalizzazioneStato Stati Uniti Stato federato Wisconsin AmministrazioneCapoluogoWausau Data di istituzione1850 TerritorioCoordinatedel capoluogo44°57′33″N 89°37′48″W / 44.959167°N 89.63°W44.959167; -89.63 (Contea di Marathon)Coordinate: 44°57′33″N 89°37′48″W / 44.959167°…

Pemilihan umum Presiden dan Wakil Presiden serta anggota DPR, DPRD, dan DPDTAHUN 2019 Presiden dan Wakil Presiden Kampanye Joko Widodo-Ma'ruf Amin Koalisi Indonesia Kerja Kampanye Prabowo Subianto-Sandiaga Uno Koalisi Indonesia Adil Makmur Dukungan bagi para paslon Hasil survei sementara Debat Anggota legislatif Daftar anggota DPR RI Berdasarkan provinsi Sumatera • Aceh • Sumatera Utara • Sumatera Barat • Riau • Kepulauan Riau • …

Bambang HaryadiS.E. Anggota Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Republik IndonesiaPetahanaMulai menjabat 1 Oktober 2014PresidenSusilo Bambang Yudhoyono Joko WidodoDaerah pemilihanJawa Timur IV Informasi pribadiLahir20 Agustus 1979 (umur 44)Bangsalsari, JemberPartai politikGerindraSuami/istriRetno Eka DewiAnak3Alma materSTIE Manajemen Industri dan Jasa IndonesiaPekerjaanPolitikusSunting kotak info • L • B Bambang Haryadi, S.E. (lahir 20 Agustus 1979) adalah politikus Indonesia yang men…

Kristen Michal Menteri KeadilanMasa jabatan6 April 2011 – 10 Desember 2012Perdana MenteriAndrus Ansip PendahuluRein LangPenggantiHanno Pevkur Informasi pribadiLahir2 Juli 1975 (umur 48)Tallinn, EstoniaKebangsaanEstoniaPartai politikPartai Reformasi EstoniaAlma materAkademi NordSunting kotak info • L • B Kristen Michal (2021) Kristen Michal (kelahiran 2 Juli 1975) adalah seorang politikus Estonia dan anggota Partai Reformasi Estonia. Ia menjadi menteri keadilan Eston…

Siklon SidrBadai siklon ekstrem (skala MD)Siklon tropis kategori 4 (SSHWS)Sidr di teluk BenggalaTerbentuk pada11 November 2007Mereda pada16 November 2007 Kecepatan anginmaksimal3 menit: 215 km/jam 1 menit: 250 km/jam Tekanan minimal944 hPa (mbar) Korban jiwa2,388Area terdampakBangladesh, India timurBagian dari Musim siklon Samudera Hindia Utara 2007 Siklon Sidr adalah nama keempat badai dari musim siklon Samudera Hindia Utara 2007. Pada pagi hari tanggal 15 November, angin bertiup dengan ke…

L. S. CousinsLance Selwyn Cousins, 2012.Lahir7 April 1942Hitchin, Britania RayaMeninggal14 Maret 2015 (usia 72) Lance Selwyn Cousins (7 April 1942 – 14 Maret 2015) adalah seorang cendekiawan utama dalam bidang kajian Buddha. Lahir di Hitchin, Hertfordshire, ia belajar sejarah dan kajian oriental di Universitas Cambridge[1] Referensi ^ oxford.academia.edu/LSCousins Pengawasan otoritas Umum Integrated Authority File (Jerman) ISNI 1 VIAF 1 WorldCat Perpustakaan nasional Norw…
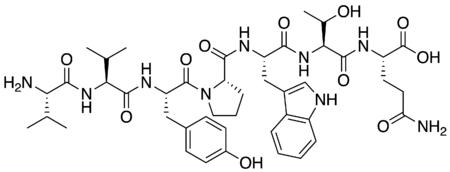
Valorphin Names IUPAC name L-Valyl-L-valyl-L-tyrosyl-L-prolyl-L-tryptophyl-L-threonyl-L-glutamine Identifiers CAS Number 144313-54-2 N[ChemSpider] 3D model (JSmol) Interactive image ChemSpider 27470960 PubChem CID 90470048 InChI InChI=1S/C44H60N8O12/c1-22(2)35(45)40(59)50-36(23(3)4)41(60)49-32(19-25-12-14-27(54)15-13-25)43(62)52-18-8-11-33(52)39(58)48-31(20-26-21-46-29-10-7-6-9-28(26)29)38(57)51-37(24(5)53)42(61)47-30(44(63)64)16-17-34(55)56/h6-7,9-10,12-15,21-24,30-33,35-37,46,53-5…

KingsmeadowNama lengkapKingsmeadowLokasiJack Goodchild Way, Kingston upon Thames, London, InggrisOperatorChelseaKapasitas4.850 (2.265 kursi)Ukuran lapangan110 x 75 kakiPermukaanRumputKonstruksiDidirikan1989Dibuka1989PemakaiKingstonian F.C. (1989–2017)AFC Wimbledon (2002–2020) Chelsea Wanita (2017–) Akademi Chelsea (2020–) Kingsmeadow adalah stadion sepak bola di Norbiton, Kingston upon Thames, London, yang merupakan kandang dari Chelsea Wanita dan Chelsea U-23. Sebelumnya digunakan Kings…

Asosiasi Sepak Bola BahamaCONCACAFDidirikan1967Bergabung dengan FIFA1968Bergabung dengan CONCACAF1981PresidenAnton SealeyWebsitewww.bahamasfa.com Asosiasi Sepak Bola Bahama adalah badan pengendali sepak bola di Bahama. Kompetisi Badan ini menyelenggarakan beberapa kompetisi di Bahama, yakni: Liga Sepak Bola Utama Bahama Liga Divisi Satu Bahama Liga Divisi Dua Bahama Piala Super Bahama Piala Utama Asosiasi Sepak Bola Bahama Piala Asosiasi Sepak Bola New Providence Tim nasional Badan ini juga meru…

Rugby teamMilwaukee BarbariansFull nameMilwaukee Barbarians RugbyFounded1975; 49 years ago (1975)Ground(s)Brown Deer ParkPresidentTy AshLeague(s)USA Rugby Division 2 & 3 Team kit Official websitemilwaukeerugby.org The Milwaukee Barbarians are an American rugby team based in Milwaukee. The first team plays in Division 2 with an additional team playing in Division 3. History The club was founded in 1975 as Derry's Rugby Club but rebranded as the Milwaukee Barbarians in 2012 a…

Museum and nature centre in England Bracken Hall Countryside Centre and MuseumBracken Hall MuseumEstablishedEarly 1980s; 1989 at Bracken Hall.LocationGlen Road, Baildon, Shipley, West Yorkshire, England BD17 5EATypeChildren's museum, Natural history museum, Local archaeology museum, Interpretation centrePublic transit accessShipley Glen Tramway or bus from Bradford InterchangeWebsiteThe Friends of Bracken Hall Bracken Hall Countryside Centre and Museum is a children's museum, natural history edu…

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento Messico non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Bassa California del Sudstato federatoEstado Libre y Soberano de Baja California Sur Bassa California del Sud – VedutaCabo San Lucas, uno dei principali centri della regione LocalizzazioneStato Messico AmministrazioneCapoluogoLa Paz GovernatoreVíctor Manuel C…

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang Kejuaraan Bola Voli Eropa kategori putri. Untuk kotegori putra, lihat Kejuaraan Bola Voli Eropa – putra. Kejuaraan Bola Voli Putri EropaMusim atau kompetisi terkini: Kejuaraan Bola Voli Eropa 2015 – putriOlahragaBola voliDidirikan1949Jumlah tim16 (putaran final)BenuaEropa (CEV)Juaraterkini Rusia (gelar ke-19)Juara terbanyak Rusia (19 gelar) Kejuaraan Bola Voli Eropa – putri (bahasa Inggris: European Volleyball Championship – Women) adalah komp…

تحتاج النصوص المترجمة في هذه المقالة إلى مراجعة لضمان معلوماتها وإسنادها وأسلوبها ومصطلحاتها ووضوحها للقارئ، لأنها تشمل ترجمة اقتراضية أو غير سليمة. فضلاً ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة بمراجعة النصوص وإعادة صياغتها بما يتناسب مع دليل الأسلوب في ويكيبيديا. (ديسمبر 2015) لي سي (بال…

Grand Prix MeadowlandsCART PPG IndyCar World SeriesLokasiMeadowlands Sports Complex, East Rutherford, New JerseyPerusahaan sponsorMarlboroLomba pertama1984Lomba terakhir1991Jarak tempuh18.255 mi (29.379 km)Terbanyak menang(pengemudi)Bobby Rahal (3)Terbanyak menang(tim)Newman-Haas Racing (2)Galles Racing (2)Terbanyak menang(pabrikan)Lola (6)Informasi sirkuitPermukaanAsphaltPanjang1.217 mi (1.959 km)Tikungan6Rekor putaran37.772 (Rick Mears, Penske PC19-Chevrolet, 1990, IndyCar)…

Puerto de San Vicente municipio de España Escudo Casa consistorial Puerto de San VicenteUbicación de Puerto de San Vicente en España Puerto de San VicenteUbicación de Puerto de San Vicente en la provincia de ToledoPaís España• Com. autónoma Castilla-La Mancha• Provincia Toledo• Comarca La Jara• Partido judicial Talavera de la ReinaUbicación 39°31′19″N 5°06′59″O / 39.521944444444, -5.11638888…

ヨハネス12世 第130代 ローマ教皇 教皇就任 955年12月16日教皇離任 964年5月14日先代 アガペトゥス2世次代 レオ8世個人情報出生 937年スポレート公国(中部イタリア)スポレート死去 964年5月14日 教皇領、ローマ原国籍 スポレート公国親 父アルベリーコ2世(スポレート公)、母アルダその他のヨハネステンプレートを表示 ヨハネス12世(Ioannes XII、937年 - 964年5月14日)は、ロー…

SMA Negeri 19 MedanInformasiDidirikan2004Jumlah kelas32 kelasRentang kelasX, XI,XIIKurikulumMerdekaJumlah siswa1000 SiswaAlamatLokasiJl. Seruwai, Medan, Sumatera UtaraMoto SMA Negeri (SMAN) 19 Medan, merupakan salah satu Sekolah Menengah Atas Negeri yang ada di Provinsi Sumatera Utara, Indonesia. Sama dengan SMA pada umumnya di Indonesia masa pendidikan sekolah di SMAN 19 Medan ditempuh dalam waktu tiga tahun pelajaran, mulai dari Kelas X sampai Kelas XII. Fasilitas Berbagai fasilitas …

Italian swimmer (born 1994) Gregorio PaltrinieriPaltrinieri in 2019Personal informationNickname(s)Greg, SuperGreg[2]National teamItalyBorn (1994-09-05) 5 September 1994 (age 29)Carpi, ItalyHeight1.91 m (6 ft 3 in)Weight72 kg (159 lb)SportSportSwimmingStrokesFreestyleClub Fiamme Oro[1] Coopernuoto CoachFabrizio Antonelli Medal record Men's swimming Representing Italy Event 1st 2nd 3rd Olympic Games 1 1 1 World Aquatics Championships 6 5 4 W…

BMW X3 (G01)Descrizione generaleCostruttore BMW Tipo principaleSUV Produzionedal 2017 Sostituisce laBMW F25 Euro NCAP (2019[1]) NHTSA (2019[2]) Altre caratteristicheAltroAssemblaggioSpartanburgPuneShenyang Stessa famigliaBMW X4 Auto similiMercedes-Benz GLCAudi Q5 La BMW G01 è la terza generazione della BMW X3, SUV di segmento D prodotto dalla casa automobilistica tedesca BMW a partire dal 2017 nello stabilimento di Spartanburg in Carolina del Sud. Indice 1 Produzione 2 Debu…

