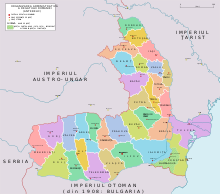
United Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

State-owned company that manages rail infrastructure in Great Britain Not to be confused with National Rail. Network Rail LimitedCompany typeGovernment-owned company/non-departmental public body[1](incorporated as a private company limited by guarantee without share capital)IndustryRail infrastructure and asset managementPredecessorRailtrackFoundedOctober 2002; 21 years ago (2002-10)SuccessorGreat British Railways (from 2024)Headquarters1 Eversholt Street London NW…

Jaime RibeiroJaime Ribeiro menerima Ordem de Timor-Leste dari Presiden Francisco Guterres pada tahun 2018 Informasi pribadiLahir(1959-04-15)15 April 1959Liquiçá, Timor PortugisMeninggal30 Juni 2019(2019-06-30) (umur 60)Dili, Timor LestePartai politikPartidu Libertasaun PopularKarier militerPihak Timor LesteDinas/cabang FalintilMasa dinas1975—2001Pertempuran/perangPendudukan Indonesia di Timor TimurSunting kotak info • L • B Perdana Menteri Taur Matan Ruak pada pemakam…

BMW Seri 3 (G20/G21)InformasiMasa produksi2019–sekarangPerakitanJerman: RegensburgTiongkok: ShenyangMeksiko: San Luis PotosíThailand: RayongPerancangMarc Michael MarkefkaBodi & rangkaKelasMobil eksekutif kompak (D)Bentuk kerangka4-pintu sedan (G20) 5-pintu station wagon (G21)Tata letakMesin Depan, Penggerak Roda BelakangMesin Depan, Penggerak Semua Roda (xDrive)PlatformBMW CLARPenyalur dayaMesinBensin:2.0 L turbocharged B48 I43.0 L turbocharged B58 I6 Hibrida Plug-in:2.0 L turbo…

Haemopis sanguisuga Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Annelida Kelas: Clitellata Subkelas: Hirudinea Ordo: Arhynchobdellida Famili: Haemopidae Genus: Haemopis Spesies: H. sanguisuga Nama binomial Haemopis sanguisuga(Linnaeus, 1758) Sinonim Hirudo sanguisuga Linnaeus, 1758 Haemopis sanguisuga dalam sebuah laboratorium Haemopis sanguisuga, dengan nama umum lintah kuda, adalah spesies lintah anggota genus Haemopis. Walaupun dinamai lintah kuda, hewan ini tidak dapat menggigit kulit …

Astro SuperSportSloganSaluran Juara!Negara Malaysia IndonesiaBahasaBahasa MelayuBahasa InggrisBahasa IndonesiaTanggal siaran perdana1 Juni 1996 (di Malaysia)28 Februari 2006 (di Indonesia)Tanggal peluncuran1 Juni 1996 (di Malaysia)28 Februari 2006 (di Indonesia)Kantor pusatBukit Jalil, Kuala Lumpur, MalaysiaKuningan Timur, Setiabudi, Jakarta Selatan, IndonesiaPemilikAstro Malaysia Berhad (Malaysia)First Media (Indonesia)Multipolar (Indonesia)PT Adhi Karya Visi (Indonesia)Satelit#Jaring…

République de Turquie(tr) Türkiye Cumhuriyeti Drapeau de la Turquie Armoiries de la Turquie Devise en turc : Yurtta sulh, cihanda sulh (« Paix dans le pays, paix dans le monde »), non officielle Hymne en turc : İstiklâl Marşı (« Hymne de l’indépendance ») Fête nationale 29 octobre · Événement commémoré Proclamation de la République (1923) Administration Forme de l'État République unitaire présidentielle[1] Président d…

Politics of Rwanda Constitution Human rights International Criminal Tribunal Government President Paul Kagame Prime Minister Édouard Ngirente Cabinet Parliament Senate President: Bernard Makuza Chamber of Deputies Speaker: Donatille Mukabalisa Judiciary Supreme Court Administrative divisions Provinces Districts Elections Recent elections President: 20172024 Assembly: 20182024 Senate: 20112019 Political parties Foreign relations Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Cooperation Ministry: Richard Sezib…

GantarKecamatanPeta lokasi Kecamatan GantarNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa BaratKabupatenIndramayuPemerintahan • CamatDrs. Asep MahmudPopulasi • Total91,622 jiwa (L: 34,428 P: 57,194) jiwaKode Kemendagri32.12.25 Kode BPS3212011 Luas125,56 km²Desa/kelurahan6 desa Gantar adalah sebuah kecamatan yang berada di Kabupaten Indramayu, Provinsi Jawa Barat, Indonesia. Kecamatan Gantar merupakan kecamatan yang di kelilingi oleh pemandangan indah. Di sebelah selatan terlihat deng…

Edmond JabèsLahir(1912-04-16)16 April 1912 Kairo, MesirMeninggal2 Januari 1991(1991-01-02) (umur 78) Paris, PerancisPekerjaanPenulis Edmond Jabès (16 April 1912 – 2 Januari 1991) Jabès adalah seorang penulis dan penyair Prancis yang berasal dari Mesir, dan salah satu tokoh sastra paling terkenal untuk menulis dalam bahasa Prancis setelah Perang Dunia II. Karya Beberapa buku Edmond Jabès antara lain: The book of questions. The book of margins. From the book to the book. Lihat pula Daft…

Electro Velvet Informations générales Pays d'origine Royaume-Uni Genre musical Electro swing Années actives Depuis 2015 Composition du groupe Membres Alex LarkeBianca Nicholas modifier Electro Velvet est un groupe de musique britannique d'electro swing composé d'Alex Larke et Bianca Nicholas. Le 7 mars 2015, ils sont choisis en interne pour représenter le Royaume-Uni au Concours Eurovision de la chanson 2015 à Vienne, en Autriche avec la chanson Still in Love with You[1]. Ils sont qualifi�…

Barra KillaPosterGenre Drama Komedi Roman BerdasarkanBarra Killaoleh Nova AdhitaSkenarioNarendra ArtamusaSutradaraAbdullahPemeran Elina Joerg Alzio Faaz Lilis Suganda Khaedor Jonsen Perianti Almer Vicko Fajar Septyanto Dikky Carmelo Qerent Natasha Mayla Syakira Chelcy Clarissa Ayesha Guimara Khasmira Anjani Kireyna Eka Dhian MusikArya WibowoNegara asalIndonesiaBahasa asliBahasa IndonesiaJmlh. episode6ProduksiProduser eksekutif Haji Wilmon, S.T. Fitriyanti Dhian, S.E., S.H. ProduserHendra Suhendi…

Henry Charles Lea (19 September 1825 – 24 Oktober 1909) adalah seorang sejarawan asal Amerika Serikat. Ia merupakan penulis sebuah buku berjilid tentang kejahatan dari Inkuisisi Spanyol.[1] Karya tulis A History of the Inquisition of Spain A History of the Inquisition of Spain merupakan karya tulis dari Lea yang membahas tentang kejahatan dari Inkuisisi Spanyol. Buku ini terdiri dari empat jilid. Pembahasannya tentang bantahan kepada gereja bahwa gereja tidak dapat dipers…

Alis mata Alis mata pada sebagian besar mamalia berupa bagian yang sedikit menonjol sedikit di atas kedua belah kelopak mata dan mempunyai sedikit rambut halus. Alis mata berfungsi sebagai pelindung mata yang peka dari tetesan keringat yang jatuh dari bagian dahi, air hujan, atau sinar matahari yang berlebihan. Bentuk alis mata pada manusia biasanya bagaikan bulan sabit dengan lengkungan agak tajam di bagian pelipis. Tidak jarang juga dijumpai orang dengan alis mata bagian kiri dan bagian kanan …

Santo AbboSampul depan dari salah satu trakta yang dibuat Santo Abbo, yang menunjukkan kata ABBO. Dibuat antara tahun 962 dan 986 M.Lahirsekitar 945OrléansMeninggal13 November 1004GasconiDihormati diGereja Katolik RomaPesta13 November Abbo (meninggal tahun 1004) adalah seorang biarawan Benediktus yang menjadi martir.[1][2] Ia dilahirkan di dekat Orleans, dan menempuh studi di Paris dan Rheims.[1] Selain sebagai seorang biarawan, Abbo juga dikenal sebagai seorang akademis…

Branjangan-pingai Eremopterix Males and females of the sixspecies on the African mainlandTaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumChordataKelasAvesOrdoPasseriformesFamiliAlaudidaeGenusEremopterix Kaup, 1836 Tata namaSinonim takson Coraphites Megalotis Pyrrhulauda - A. Smith, 1839[1] SpeciesSee textRange of the genus lbs Eremopterix adalah genus branjangan-pingai, burung pengicau dalam keluarga Alaudidae . Branjangan-pingai ditemukan dari Afrika hingga anak benua India. Spesies yang masih ada Gambar…

Participation since 2003: Entered at least once Never entered, although eligible to do so Entry intended, but later withdrew Competed as a part of another country, but never as a sovereign state[a] Map showing each country's number of Junior Eurovision Song Contest wins Graph showing the number of countries in each contest from 2003 to 2022. A total of 42 countries have participated in the Junior Eurovision Song Contest since the first edit…

Bahan bakar penerbangan adalah bahan bakar dengan jenis khusus yang berasal dari minyak bumi yang digunakan sebagai bahan bakar pesawat udara. Bahan bakar penerbangan harus memenuhi persyaratan serta karakteristik yang ketat, seperti titik nyala dan titik beku yang harus sesuai dengan aturan yang ada. Ada beberapa jenis bahan bakar utama penerbangan, diantaranya yaitu avtur (Jet A-1) yang digunakan untuk pesawat udara dengan tipe mesin turbin, avgas yang digunakan untuk pesawat udara dengan tipe…

1926 film This article is about the film. For the musical, see Battling Buttler. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Battling Butler – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Battling ButlerLobby cardDirected byBuster KeatonWrit…

Artikel ini memberikan informasi dasar tentang topik kesehatan. Informasi dalam artikel ini hanya boleh digunakan untuk penjelasan ilmiah; bukan untuk diagnosis diri dan tidak dapat menggantikan diagnosis medis. Wikipedia tidak memberikan konsultasi medis. Jika Anda perlu bantuan atau hendak berobat, berkonsultasilah dengan tenaga kesehatan profesional. InsomniaGambar seseorang penderita insomnia dari abad ke-14Informasi umumNama lainSulit tidur, gangguan tidurPelafalan/ɪnˈsɒmniə/[1]…

Daftar keuskupan di Libya adalah sebuah daftar yang memuat dan menjabarkan pembagian terhadap wilayah administratif Gereja Katolik Roma yang dipimpin oleh seorang uskup ataupun ordinaris di Libya. Konferensi para uskup Libya bergabung dalam Konferensi Waligereja Libya. Saat ini terdapat 4 buah yurisdiksi, di mana 3 merupakan vikariat apostolik dan 1 lainnya merupakan prefektur apostolik. Daftar keuskupan Yurisdiksi Tahta Suci Vikariat Apostolik Benghazi: lowong, diisi oleh Administrator Apostoli…