Vrishni
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Cherokee (disambigua). Cherokee ᏣᎳᎩ ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢLuogo d'origine Stati Uniti Popolazione316.049 in totale, di cui Almeno 13.000 della Banda Orientale 288.749 della Nazione Cherokee 14.300 della Banda Unita Keetoowah[1] LinguaInglese, Cherokee ReligioneCristianesimo, Peyotismo[2] Distribuzione Carolina del Nord16.158[3]Oklahoma102.580[3] Manuale Bandiera della 'Cherokee Nation of Okla…

The SpireVista da O'Connel StreetLocalizzazioneStato Irlanda LocalitàDublino IndirizzoO'Connell Street Coordinate53°20′58.99″N 6°15′37.01″W / 53.34972°N 6.26028°W53.34972; -6.26028Coordinate: 53°20′58.99″N 6°15′37.01″W / 53.34972°N 6.26028°W53.34972; -6.26028 Informazioni generaliCondizioniIn uso Costruzione2002-2003 Inaugurazione2003 Stiletorre in acciaio Usoturistico Altezza120 m (394 piedi) RealizzazioneCosto€ 4.000.000 Architett…

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat TCL. TCL TechnologyNama asliTCL科技JenisPublikIndustriElektronik konsumenDidirikan1981 (Pendirian)1985 (Penubuhan)PendiriTomson Li DongshengKantorpusatHuizhou, Guangdong, TiongkokWilayah operasiSeluruh belahan duniaTokohkunciTomson Dongsheng Li (CEO)ProdukTelevisi, kamera video, telepon selulerPendapatanUS$16,44 miliar (2014)[1]KaryawanSekitar 75.000[1]Situs webtcl.com TCL Technology (Hanzi: TCL科技, TCL kējì), biasa disebut TCL saja, adalah p…

Artikel ini merupakan bagian dari sebuah seri padaPengobatan alternatif Informasi umum Pengobatan alternatif Sejarah Terminologi Pengobatan alternatif untuk hewan Perdukunan Kemajuan pengobatan modern Ilmu semu Antisains Skeptisisme Gerakan skeptis Nihilisme terapeutik Kedokteran dan ilmu pengetahuan Akupresur Akupuntur Diet alkali Kedokteran antroposofi Terapi lebah Kinesiologi terapan Aromaterapi Asosiasi untuk penelitian dan pengetahuan Terapi aurikula Metode bates Salep hitam Terapi pijat Pe…

German lawyer and forester Albrecht von BoeselagerGrand Chancellor of the Sovereign Military Order of MaltaIn office28 January 2017 – 4 September 2022MonarchsLudwig von Rumerstein (Acting)Giacomo dalla TorreRuy Gonçalo do Valle Peixoto de Villas Boas (Acting)Marco Luzzago (Acting)Ruy Gonçalo do Valle Peixoto de Villas Boas (Acting)John T. DunlapPreceded byJohn Edward CritienSucceeded byRiccardo Paternò di MontecupoIn office31 May 2014 – 8 December 2016MonarchMatthew Fest…

Method of assisted reproduction Embryo transfer 1238-cell embryo for transfer 3 days after fertilizationMeSHD004624[edit on Wikidata] Embryo transfer refers to a step in the process of assisted reproduction in which embryos are placed into the uterus of a female with the intent to establish a pregnancy. This technique - which is often used in connection with in vitro fertilization (IVF) - may be used in humans or in other animals, in which situations and goals may vary. Embryo transfer can b…

Medical conditionNeonatal jaundiceOther namesNeonatal hyperbilirubinemia, neonatal icterus, jaundice in newbornsJaundice in a newbornSpecialtyPediatricsSymptomsYellowish discoloration of the skin and white part of the eyes[1]ComplicationsSeizures, cerebral palsy, kernicterus[1]Usual onsetNewborns[1]TypesPhysiologic, pathologic[1]CausesRed blood cell breakdown, liver disease, infection, hypothyroidism, metabolic disorders[2][1]Diagnostic methodBased…

Fathul Mu'in Daeng MaggadingLahir(1919-12-17)17 Desember 1919Pakalli, Maros, Hindia BelandaMeninggal18 September 1985(1985-09-18) (umur 65)Kuri, Kabupaten Maros, Sulawesi Selatan, IndonesiaMakamPemakaman Umum MarosKebangsaanIndonesiaAlmamaterMULO (SMP zaman Hindia Belanda)PekerjaanPemuka AgamaDikenal atasPejuang KemerdekaanTokoh Muhammadiyah Sulawesi SelatanSuami/istriHj. Badate (Istri Pertama)Hj. Rahmah Masbah (Istri Kedua)Anak8Orang tuaH. Malawi (Ayah)Hj. Husna (Ibu) Mayor K.H. Fathul Mu'…
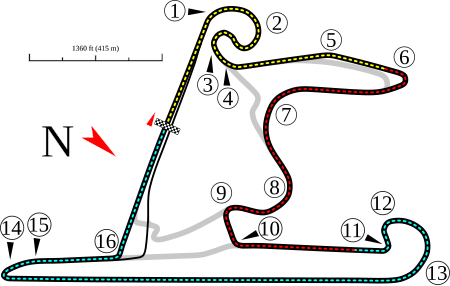
Grand Prix Tiongkok 2011 Lomba ke-3 dari 19 dalam Formula Satu musim 2011 Detail perlombaanTanggal 17 April 2011Nama resmi 2011 Formula 1 UBS Grand Prix TiongkokLokasi Shanghai International CircuitShanghai, TiongkokSirkuit Permanent racing facilityPanjang sirkuit 5.451 km (3.387 mi)Jarak tempuh 56 putaran, 305.066 km (189.559 mi)Posisi polePembalap Sebastian Vettel Red Bull-RenaultWaktu 1:33.706Putaran tercepatPembalap Mark Webber Red Bull-RenaultWaktu 1:38.993 putaran ke-42PodiumPertama Lewis …

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Potsdam (disambigua). Potsdamcittà extracircondariale Potsdam – VedutaVeduta di Potsdam dal parco Babelsberg LocalizzazioneStato Germania Land Brandeburgo DistrettoNon presente CircondarioNon presente AmministrazioneSindacoMike Schubert (SPD) TerritorioCoordinate52°24′N 13°04′E / 52.4°N 13.066667°E52.4; 13.066667Coordinate: 52°24′N 13°04′E / 52.4°N 13.066667°E52.4; 13.0666…

Voce principale: A' Katīgoria (calcio). A' Katīgoria 2000-2001 Competizione A' Katīgoria Sport Calcio Edizione 62ª Organizzatore CFA Date dal 16 settembre 2000al 6 maggio 2001 Luogo Cipro Partecipanti 14 Risultati Vincitore Omonia(18º titolo) Retrocessioni Nea Salamis Digenīs Morphou Arīs Limassol Statistiche Miglior marcatore Rainer Rauffmann (30 gol) Incontri disputati 182 Gol segnati 646 (3,55 per incontro) Cronologia della competizione 199…

Engelberto IIarcivescovo della Chiesa cattolicaStatua di Engelberto nel castello di Burg TitoloArcivescovo di Colonia (1218-1225) Nato1185 o 1186 a Solingen Nominato arcivescovo26 febbraio 1216 Consacrato arcivescovo24 settembre 1217 Deceduto7 novembre 1225 a Gevelsberg Manuale Engelberto IIConte di BergStemma In carica1218 –1225 PredecessoreAdolfo III SuccessoreErmengarda di Berg col marito Enrico NascitaSolingen, 1185 o 1186 MorteGevelsberg, 7 novembre 1225 Luogo…

Art and practice of creating images by recording light For other uses, see Photography (disambiguation). Photographers at the Chicago Old Town Art Fair in 1968 Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employed in many fields of science, manufacturing (e.g., photolithography), and business, as well as its more dire…
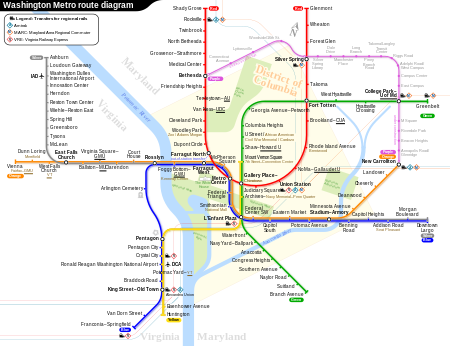
Washington MetroInfoWilayahWashington, D.C.JenisAngkutan cepatJumlah jalur6Jumlah stasiun91Penumpang harian758.489 (Juni 2013)[1]Penumpang tahunan209 juta (2013, perkiraan)[2]Pimpinan utamaRichard M. SarlesKantor pusat600 5th St NWWashington, D.C. 20001Situs webwww.wmata.comOperasiDimulai27 Maret 1976; 48 tahun lalu (1976-03-27)OperatorWashington Metropolitan Area Transit Authority (WMATA)Jumlah gerbong1.126 rangkaianPanjang kereta6 atau 8 keretaWaktu antara6 menit puncak; 1…

Pandemi COVID-19 di EtiopiaPeta wilayah dengan kasus koronavirus terkonfirmasi (merah) (pada 3 Juli 2020)PenyakitCOVID-19Galur virusSARS-CoV-2LokasiEtiopiaKasus pertamaAddis AbabaTanggal kemunculan13 Maret 2020(4 tahun, 1 bulan dan 1 hari)AsalWuhan, Hubei, TiongkokKasus terkonfirmasi85.136 (pada 12 Oktober)[1]Kasus sembuh38.904 (pada 12 Oktober)Kematian1.301 (pada 12 Oktober)Tingkat kematian1.53%Situs web resmid19.et Pandemi COVID-19 terkonfirmasi mencapai Etiopia pada 13 …
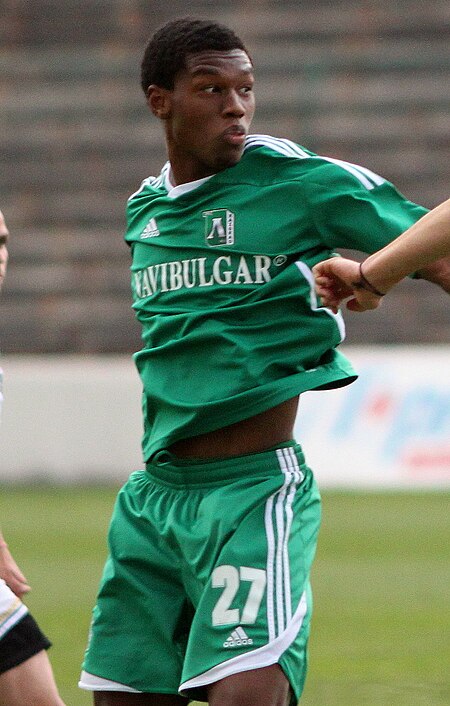

Christian Kabasele Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Christian Kabasele[1]Tanggal lahir 24 Februari 1991 (umur 33)Tempat lahir Lubumbashi, ZaireTinggi 187 cm (6 ft 2 in)Posisi bermain Bek tengahInformasi klubKlub saat ini UdineseNomor 27Karier junior–2008 EupenKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2008–2011 Eupen 9 (0)2011 → Mechelen (pinjaman) 4 (1)2011–2012 Ludogorets Razgrad 11 (3)2012–2014 Eupen 41 (6)2014–2016 Genk 76 (6)2016–2023 Watford 153 (6)2023– U…

1957 film directed by Mark Robson This article is about the motion picture. For the TV show, see Peyton Place (TV series). For the book on which both of them were based, see Peyton Place (novel). Peyton PlaceTheatrical release posterDirected byMark RobsonScreenplay byJohn Michael HayesBased onPeyton Placeby Grace MetaliousProduced byJerry WaldStarring Lana Turner Hope Lange Lee Philips Lloyd Nolan Diane Varsi Arthur Kennedy Russ Tamblyn Terry Moore CinematographyWilliam C. MellorEdited byDavid B…

Chemical compound SergolexoleIdentifiers IUPAC name (4-methoxycyclohexyl) (6aR,9R,10aR)-7-methyl-4-propan-2-yl-6,6a,8,9,10,10a-hexahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxylate CAS Number108674-86-8 YPubChem CID60262UNIIJ6TGA89COPCompTox Dashboard (EPA)DTXSID10148700 Chemical and physical dataFormulaC26H36N2O3Molar mass424.585 g·mol−13D model (JSmol)Interactive image SMILES CC(C)N1C=C2C[C@@H]3[C@H](C[C@H](CN3C)C(=O)OC4CCC(CC4)OC)C5=C2C1=CC=C5 InChI InChI=1S/C26H36N2O3/c1-16(2)28-15-17-…

1968 single by Joe South For other uses of the same title, see Games People Play (disambiguation). Games People PlaySingle by Joe Southfrom the album Introspect B-sideMirror of Your MindReleasedAugust 1968GenreFolk rock, country rock, psychedelic rock, raga rockLength3:34LabelCapitolSongwriter(s)Joe SouthProducer(s)Joe SouthJoe South singles chronology Birds of a Feather (1968) Games People Play (1968) Don't It Make You Want to Go Home (1969) Official audioGames People Play (Remastered 2002) on …

Style of Kung-Fu jacket wrestling Not to be confused with Shui jiao. Shuai jiao摔跤Two shuai jiao wrestlers testing each other in Tianjin, China.Also known asKung Fu Wrestling, Chinese WrestlingFocusJacket wrestling, Grappling, Joint locksCountry of originAncient ChinaCreatorUnknown (said to have existed for over 6,000 years)Olympic sportNo A modern shuai jiao match. One fighter is trying to sweep his rival with a leg hook. Shuai jiao (Chinese: 摔跤 or 摔角; pinyin: Shuāijiāo; Wa…
![Silver coin of a "King Vrishni" (of the Audumbaras according to Cunningham).[1][2] Obv Pillar with half-lion and half-elephant, surmounted by a Triratna symbol and surrounded by Buddhist railing. Brahmi legend Vṛishṇi Raja jnâgaṇyasya blubharasya Rev Large Dharmachakra symbol. Kharosthi legend Vrishni Raja jnâganyasya blubharasya.[1] of](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/9f/Vrishni_coin.png/300px-Vrishni_coin.png)


!["Vrishni heroes" on the coinage of Agathocles of Bactria, circa 190-180 BCE: Samkarshana-Balarama, with Gada mace and plow, and Vāsudeva-Krishna, with Shankha (a pear-shaped case or conch) and Chakra wheel.[12][16][17] This is "the earliest unambiguous image" of the two deities.[18] Another variation [1].[19]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/cd/Coin_of_the_Bactrian_King_Agathokles.jpg/350px-Coin_of_the_Bactrian_King_Agathokles.jpg)
![Vrishni triad shown in a rock painting at Tikla, Madhya Pradesh, 3rd-2nd century BCE. These would be Saṃkarṣaṇa (with plough and mace), Vāsudeva (with mace and wheel) and a female deity, probably Ekanamsha.[20]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4a/Vrishni_triad_shown_in_a_rock_painting_at_Tikla%2C_M.P._3rd-2nd_century_BCE.jpg/244px-Vrishni_triad_shown_in_a_rock_painting_at_Tikla%2C_M.P._3rd-2nd_century_BCE.jpg)
