Walla Walla people
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Cui-cui kardinal Burung Myzomela dengan warna scarlettnya Status konservasi Risiko Rendah (IUCN 3.1)[1] Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Aves Ordo: Passeriformes Famili: Maliphagidae Genus: Myzomela Spesies: M. cardinalis Nama binomial Myzomela cardinalis(Gmelin, 1788) Cui-cui kardinal (Myzomela cardinalis) adalah spesies burung pemakan madu yang termasuk famili Meliphagidae. Dinamakan demikian karena warna merah tua yang biasa ada pada jantannya. Bu…

TalangDanau Talang di Kaki Gunung TalangLetakKabupaten Solok, Sumatera Barat, Indonesia Koordinat1°0′45.71″S 100°42′3.59″E / 1.0126972°S 100.7009972°E / -1.0126972; 100.7009972Jenis perairanDanau vulkanikTerletak di negaraIndonesiaArea permukaan5.0 km²KepulauanSumatra Danau Talang adalah sebuah danau di kabupaten Solok, provinsi Sumatera Barat, Indonesia. Danau ini adalah danau vulkanik yang terbentuk dari salah satu dan merupakan danau vulkanik yang berbahay…
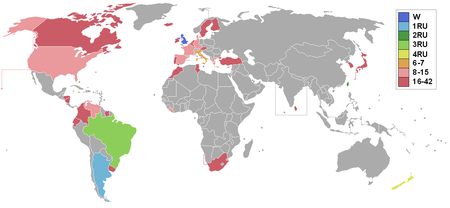
Miss World 1964Tanggal12 November 1964TempatLyceum Theatre, London, Britania RayaPembawa acaraMichael AspelPenyiaranBBCPeserta42DebutAruba dan MontserratTidak tampilBolivia, Siprus, Israel, Yordania, Nigeria, dan PeruTampil kembaliEkuador, Gibraltar, Honduras, Italia, Lebanon, Maroko, Nikaragua, Republik Tiongkok, dan UruguayPemenangAnn Sidney UKlbs Negara dan teritori yang mengirimkan delegasi Miss World 1964, merupakan edisi ke-14 dari ajang kontes kecantikan Miss World, di…

1940 film by Anatole Litvak This article is about the film. For the album by Andrew Gold, see All This and Heaven Too (album). All This, and Heaven TooTheatrical release posterDirected byAnatole LitvakScreenplay byCasey RobinsonBased onAll This, and Heaven Too (1938 novel)by Rachel FieldProduced byDavid LewisHal B. WallisStarringBette DavisCharles BoyerBarbara O'NeilCinematographyErnie HallerEdited byWarren LowMusic byMax SteinerDistributed byWarner Bros.Release date July 4, 1940 …

У списку об'єктів Світової спадщини ЮНЕСКО в Канаді налічується 20 найменувань (станом на 2022 рік). У цій таблиці об'єкти розташовано в порядку їх додавання до списку Світової спадщини ЮНЕСКО. № Зображення Назва Місцеположення Час створення Час внесення до списку № Критерії…

Voce principale: Modena Football Club 2018. Modena FC 2018Stagione 2020-2021Sport calcio Squadra Modena Allenatore Michele Mignani All. in seconda Simone Vergassola Presidente Romano Sghedoni Serie C4º nel girone B Play off Serie CPrimo turno Coppa ItaliaPrimo turno Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Gerli (37)Totale: Gerli (40) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Spagnoli, Muroni, Scappini (6)Totale: Spagnoli (7) StadioAlberto Braglia (21 092) Maggior numero di spettatori1000 Media spettatori1000…

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年10月13日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 国际调查记者同盟International Consortium of Investigative Journalists成立時間1997年總部华盛顿哥伦比亚特区 地址华�…

Державний комітет телебачення і радіомовлення України (Держкомтелерадіо) Приміщення комітетуЗагальна інформаціяКраїна УкраїнаДата створення 2003Керівне відомство Кабінет Міністрів УкраїниРічний бюджет 1 964 898 500 ₴[1]Голова Олег НаливайкоПідвідомчі орг�…

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府與�…

English musician MaximMaxim on tour in Washington, D.C., 2007Background informationBirth nameKeith Andrew PalmerAlso known asMaxim RealityBorn (1967-03-21) 21 March 1967 (age 57)Peterborough, EnglandGenresBig beatbreakbeattrip hopInstrument(s)VocalsMember ofThe ProdigyMusical artist Keith Andrew Palmer (born 21 March 1967),[1] better known by his stage name Maxim (previously Maxim Reality), is an English musician, known for being a vocalist of electronic music band the Prodigy. Pre-…

NBC affiliate in Pueblo, Colorado This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: KOAA-TV – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) KOAA-TVPueblo–Colorado Springs, ColoradoUnited StatesCityPueblo, ColoradoChannelsDigital: 25 (UHF)Virtual: 5BrandingK…

British car brand For the other companies with that name, see Rover Company and Rover Group.Not to be confused with Land Rover. RoverRover logo from 2003OwnerJaguar Land Rover (since 2013)[1]CountryUnited KingdomIntroduced1878; 146 years ago (1878)Discontinued15 April 2005; 19 years ago (2005-04-15)MarketsAutomotivePrevious ownersRover Company (1878–1967)Leyland Motors (1967–1968)British Leyland (1968–1986)Rover Group (1986–2000)BMW (2000–200…

Palais de Justice, Conciergerie dan Pont au Change sekitar 1900 Pont au Change - 2008 Pont au Change merupakan sebuah jembatan yang melintasi Sungai Seine di Paris, Prancis. Menghubungkan Île de la Cité dari Palais de Justice dan Conciergerie, ke Tepi Kanan, di Théâtre du Châtelet. Terletak di perbatasan antara arondisemen Ier dan IVe. Mengambil namanya dari pemilik emas dan penukar uang yang mendirikan tokonya di jembatan itu pada abad ke-12. Letak Letak jembatan di Seine: Letak jembatan H…

Parts of this article (those related to Luca Visentini) need to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (December 2022) Global trade union federation International Trade Union ConfederationAbbreviationITUCFormation1 November 2006; 17 years ago (2006-11-01)Merger ofInternational Confederation of Free Trade UnionsWorld Confederation of LabourTypeTrade union centreHeadquartersBrussels, BelgiumMembership (2018) 207 m…

Karachiکراچی— Thành phố — Theo chiều kim đồng hồ: [[Mazar-e-Quaid|nơi chôn cất Muhammad Ali Jinnah]], Frere Hall, một góc đường I. I. Chundrigar, Tòa nhà tín nhiệm cảng Karachi thời thuộc địa, cung điện Mohatta, cảng Karachi Tên hiệu: Thành phố Quaid,[1] Paris của châu Á,[2][3] Thành phố ánh sáng,[2] Cô dâu của các Thành phố[4] (عروس البل…

Университет Париж-Дофин(Université Paris-Dauphine)Université Paris-IX Год основания 1971 Тип Grand établissement Президент Laurent Batsch Студенты 9 630 Преподаватели 970 Расположение Париж Сайт www.dauphine.fr Медиафайлы на Викискладе Университет Париж-Дофин (фр. Université Paris-Dauphine) — экономический университет, �…

Jean Louis Rodolphe Agassiz Jean Louis Rodolphe Agassiz (Môtier, 28 maggio 1807 – Cambridge, 14 dicembre 1873) è stato un biologo, zoologo, paleontologo e ittiologo svizzero; fu anche un valente alpinista e glaciologo. Svolse gran parte della propria attività negli Stati Uniti. Sposato con l'educatrice Elizabeth Cabot Cary, fu uno dei maggiori scienziati statunitensi del suo tempo. Viene ricordato principalmente per il suo lavoro sulle ere glaciali e per essere stato uno dei maggiori zoolog…

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Parade – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message)This article is in list format but may read better as prose. You can help by converting this article, if appropriate. Editing help is available. (March 202…

Türkei (grün) und Irak (orange) Die Grenze zwischen der Türkei und dem Irak ist 367 Kilometer lang.[1] Insbesondere grenzt die irakische Autonome Region Kurdistan hier an die Türkei. Das Grenzgebiet ist sehr gebirgig und steigt in östlicher Richtung von 400 Meter bis zu über 3000 Meter an. Der einzige Grenzübergang ist der Grenzübergang Ibrahim Khalil im westlichen flacheren Teil der Grenze. Unweit davon befindet sich das Dreiländereck von Türkei, Irak und Syrien…

Museo di antropologia e etnologia Sala del Museo di Antropologia e Etnologia, con statua equestre dei Kalash, regione del Chitral, Pakistan UbicazioneStato Italia LocalitàFirenze IndirizzoVia del Proconsolo 12 Coordinate43°46′18.1″N 11°15′30.12″E43°46′18.1″N, 11°15′30.12″E CaratteristicheTipoAntropologia, Etnologia Istituzione1869 Visitatori14 405 (2022) Sito web Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Il Museo di antropologia e etnologia di Firenze conserva ed e…
