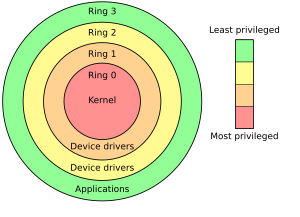
在x86 保护模式 可用的特权级别 在计算机科学 中, 分级保护域 (英語:hierarchical protection domains ),[ 1] [ 2] 保护环 (Protection Rings ),又称环型保护 (Rings Protection )、CPU环 (CPU Rings ),简称Rings 。这是一种用来在发生故障时保护数据和功能,提升容错度,避免恶意操作 ,提升计算机安全 的设计方式。这是一种与基於能力的安全 [來源請求]
电脑操作系统提供不同的资源访问级别。在计算机体系结构中,Rings是由两个或更多的特权态组成。在一些硬件或者微代码 级别上提供不同特权态 模式的CPU 架构 上,保护环通常都是硬件强制的。Rings是从最高特权级(通常被叫作0级)到最低特权级(通常对应最大的数字)排列的。在大多数操作系统中,Ring 0拥有最高特权,并且可以和最多的硬件直接交互(比如CPU,内存)。
Rings之间的特殊门是被提供用来允许外层Ring在预定义的方式内访问内层Ring的资源用的,内层Ring可以随便使用外层Ring的资源。正确使用Rings间的门可以阻止某个Ring或者特权级的程序故意滥用其他程序的资源,提升安全性。例如,某个间谍软件 作为一个在Ring 3运行的用户程序,它在不通知用户的时候打开摄像头 应该会被阻止,因为访问硬件需要使用被驱动程序 保留的Ring 1的方法。浏览器一类在高Ring级别运行的程序必须请求权限才能访问网络,也就是受低Ring级别限制的资源。
多Rings保护机制是Multics 操作系统提出的革命性概念之一,Multics 是今天的Unix 操作系统家族的一个高安全性的前任。 由于GE 645不支持硬件Rings, 所以Multics通过软件捕获Rings的转换[ 3] [ 4] Windows 7 和Windows Server 2008 R2 (还有之前版本的Windows )只用了2个Rings:Ring 0 对应内核模式,Ring 3对应用户模式 ,[ 5] [ 6]
大部分现代CPU架构(包括很流行的Intel x86 架构)中都有某种形式的保护环,但Windows NT 或者Unix 这类操作系统没有完整地利用到这个特性。相比之下OS/2 使用的更多,它用了3个Rings级别[ 7] DOS 下,内核、驱动和应用程序都运行在Ring 3(然而。这也是保护模式驱动和DOS扩展专用的级别;实模式的操作系统没有有效的保护措施),而像EMM386 这样的386内存管理程序运行在Ring 0。特别的,DR-DOS 的EMM386 3.xx可以可选地在Ring 1运行某些模块。OpenVMS 使用内核模式、管理模式、监督模式和用户模式四种模式(为了递减特权)。
计算机术语中,监控模式是一个可以通过运行在系统级的软件代码变更的硬件标志。系统级任务或线程会在它们运行时设置这个标志,而用户空间应用程序不会。这个标志决定程序是否能否执行一些诸如修改关于各种描述符表的寄存器,或禁止中断一类的机器码。监控模式下的程序应该永远不会挂掉,因为他们一挂掉整个系统就崩溃了。
在某些处理器上监控模式能够执行的所有指令,包括特权指令,也能访问到不同的地址空间,存储器管理硬件和其他外围设备,操作系统通常运行在该模式。[ 8]
Intel和AMD的CPU都提供了能使hypervisor 存取Ring 0硬件的x86虚拟化 指令集。x86虛擬化创建了一个叫Ring -1的Ring,所以虛擬機操作系统可以直接运行在Ring 0上而不影响其他虛擬機或者宿主系统。[ 9]
^ Paul A. Karger, Andrew J. Herbert, An Augmented Capability Architecture to Support Lattice Security and Traceability of Access [失效連結
^ Walter Binder, Design and Implementation of the J-SEAL2 Mobile Agent Kernel [失效連結
^ A Hardware Architecture for Implementing Protection Rings . [September 27, 2012] . (原始内容存档 于2019-12-28). ^ Multics Glossary - ring . [September 27, 2012] . (原始内容存档 于2020-11-08). ^ Russinovich, Mark E.; David A. Solomon. Microsoft Windows Internals 4. Microsoft Press. 2005: 16 . ISBN 978-0-7356-1917-3 ^ Russinovich, Mark. Windows Internals Part 1. 6th Ed. Redmond, Washington: Microsoft Press. 2012: 17. ISBN 978-0-7356-4873-9The reason Windows uses only two levels is that some hardware architectures that were supported in the past (such as Compaq Alpha and Silicon Graphics MIPS ) implemented only two privilege levels. ^ Presentation Device Driver Reference for OS/2 - 5. Introduction to OS/2 Presentation Drivers . [2017-11-25 ] . (原始内容存档 于2013-06-16). ^ FOLDOC supervisor mode
^ Dornan, Andy. Intel VT vs. AMD Pacifica . CMP. 1 November 2005 [11 November 2012] . (原始内容 存档于2013-05-30).
David T. Rogers: A FRAMEWORK FOR DYNAMIC SUBVERSION [永久失效連結
Glossary of Multics acronyms and terms: Ring 页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 )
William J. Caelli: Relearning "Trusted Systems" in an Age of NIIP: Lessons from the Past for the Future. [永久失效連結
Haruna R. Isa, William R. Shockley, Cynthia E. Irvine: A Multi-threading Architecture for Multilevel Secure Transaction Processing
Ivan Kelly: Report Porting MINIX to Xen 页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 ) 2006
Paul Barham, Boris Dragovic, Keir Fraser, Steven Hand, Tim Harris, Alex Ho, Rolf Neugebauer, Ian Pratt, Andrew Warfield: Xen and the Art of Virtualization 页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 ) 2003 (pdf)
Marcus Peinado, Yuqun Chen, Paul England, and John Manferdelli: NGSCB: A Trusted Open System 页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 ) (pdf)
Michael D. Schroeder , Jerome H. Saltzer : A Hardware Architecture for Implementing Protection Rings 页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 ) 1972Intel Architecture Software Developer's Manual Volume 3: System Programming 页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 ) (Order Number 243192) Chapter 4 Protection; section 4.5 Privilege levels. (pdf)Tzi-cker Chiueh, Ganesh Venkitachalam, Prashant Pradhan: Integrating segmentation and paging protection for safe, efficient and transparent software extensions
Takahiro Shinagawa, Kenji Kono, Takashi Masuda: Exploiting Segmentation Mechanism for Protecting Against Malicious Mobile Code
Boebert, William Earl and R. Kain. A Practical Alternative to Hierarchical Integrity Policies . Proceedings of the 8th National Computer Security Conference, 1985.
Gorine, Andrei and Krivolapov, Alexander. Kernel Mode Databases: A DBMS technology for high-performance applications (页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 ), Dr. Dobb's Journal , May, 2008.