|
Anencephaly
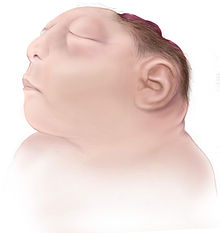
Anencephaly is the absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp that occurs during embryonic development.[1] It is a cephalic disorder that results from a neural tube defect that occurs when the rostral (head) end of the neural tube fails to close, usually between the 23rd and 26th day following conception.[2] Strictly speaking, the Greek term translates as "without a brain" (or totally lacking the inside part of the head), but it is accepted that children born with this disorder usually only lack a telencephalon,[3] the largest part of the brain consisting mainly of the cerebral hemispheres, including the neocortex, which is responsible for cognition. The remaining structure is usually covered only by a thin layer of membrane—skin, bone, meninges, etc., are all lacking.[4] With very few exceptions,[5] infants with this disorder do not survive longer than a few hours or days after birth. Signs and symptomsThe National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) describes the presentation of this condition as follows: "A baby born with anencephaly is usually blind, deaf, unaware of its surroundings and unable to feel pain. Although some individuals with anencephaly may be born with a main brain stem, the lack of a functioning cerebrum permanently rules out the possibility of ever gaining awareness of their surroundings. Reflex actions such as breathing and responses to sound or touch may occur."[4]
A side view of an anencephalic fetus A front view of an anencephalic fetus X-ray of an anencephalic stillborn baby CausesFolic acid has been shown to be important in neural tube formation since at least 1991,[6][7] and as a subtype of neural tube defect, folic acid may play a role in anencephaly. Studies have shown that the addition of folic acid to the diet of women of child-bearing age may significantly reduce, although not eliminate, the incidence of neural tube defects. Therefore, it is recommended that all women of child-bearing age consume 0.4 mg of folic acid daily,[4] especially those attempting to conceive or who may possibly conceive, as this can reduce the risk to 0.03%.[8] It is not advisable to wait until pregnancy has begun, since, by the time a woman knows she is pregnant, the critical time for the formation of a neural tube defect has usually already passed. A physician may prescribe even higher dosages of folic acid (5 mg/day) for women having had a previous pregnancy with a neural tube defect.[8] Neural tube defects can follow patterns of heredity, with direct evidence of autosomal recessive inheritance.[9] As reported by Bruno Reversade and colleagues, the homozygous inactivation of the NUAK2 kinase leads to anencephaly in humans.[10] Animal models indicate a possible association with deficiencies of the transcription factor TEAD2.[11] A woman who has had one child with a neural tube defect such as anencephaly has about a 3% risk of having another child with a neural tube defect,[12] as opposed to the background rate of 0.1% occurrence in the population at large.[13] Genetic counseling is usually offered to women at a higher risk of having a child with a neural tube defect to discuss available testing.[14]  It is known that people taking certain anticonvulsants and people with insulin-dependent diabetes have a higher risk of having a child with a neural tube defect.[15] Relation to genetic ciliopathyUntil recently, medical literature did not indicate a connection among many genetic disorders, both genetic syndromes and genetic diseases, that are now being found to be related. As a result of new genetic research, some of these are, in fact, highly related in their root cause despite the widely varying set of medical symptoms that are clinically visible in the disorders. Anencephaly is one such disease, part of an emerging class of diseases called ciliopathies. The underlying cause may be a dysfunctional molecular mechanism in the primary cilia structures of the cell, organelles present in many cellular types throughout the human body. The cilia defects adversely affect "numerous critical developmental signaling pathways" essential to cellular development and, thus, offer a plausible hypothesis for the often multi-symptom nature of a large set of syndromes and diseases. Known ciliopathies include primary ciliary dyskinesia, Bardet–Biedl syndrome, polycystic kidney and liver disease, nephronophthisis, Alström syndrome, Meckel–Gruber syndrome, and some forms of retinal degeneration.[16] Diagnosis Anencephaly can often be diagnosed before birth through an ultrasound examination. The maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP screening)[17] and detailed fetal ultrasound[18] can be useful for screening for neural tube defects such as spina bifida or anencephaly. MeroanencephalyMeroanencephaly is a rare form of anencephaly characterized by malformed cranial bones, a median cranial defect, and a cranial protrusion called area cerebrovasculosa. Area cerebrovasculosa is a section of abnormal, spongy, vascular tissue admixed with glial tissue ranging from simply a membrane to a large mass of connective tissue, hemorrhagic vascular channels, glial nodules, and disorganized choroid plexuses.[19] HoloanencephalyThe most common type of anencephaly, where the brain has entirely failed to form, except for the brain stem. Infants rarely survive more than one day after birth with holoanencephaly.[19] CraniorachischisisThe most severe type of anencephaly where area cerebrovasculosa and area medullovasculosa fill both cranial defects and the spinal column. Craniorachischisis is characterized by anencephaly accompanied by bony defects in the spine and the exposure of neural tissue as the vault of the skull fails to form.[19][20] Craniorachischisis occurs in about 1 of every 1000 live births, but various physical and chemical tests can detect neural tube closure during early pregnancy.[21] PrognosisThere is no cure or standard treatment for anencephaly. Prognosis is extremely poor, as many anencephalic fetuses do not survive birth and infants that are not stillborn will usually die within a few hours or days after birth from cardiorespiratory arrest.[4] EpidemiologyIn the United States, anencephaly occurs in about 1 out of every 4600 births.[22] Rates may be higher among Africans with rates in Nigeria estimated at 3 per 10,000 in 1990 while rates in Ghana estimated at 8 per 10,000 in 1992.[23] As of 2005, rates in China were estimated at 5 per 10,000.[23] A high anencephaly rate of 19.7 per 10,000 live births was found in 1990/1991 in Brownsville, Texas. A cluster of cases made national headlines[24] and prompted a public health investigation and the Texas Neural Tube Defect Project. It was found, that neural tube defects in general, including spina bifida, and encephalocele had been occurring in Mexican-American women undetected for years in the area.[25] Subsequently, multiple risk factors were found, foremost folic acid deficiency, low serum vitamin B12, high serum homocysteine levels, and obesity independently contributed to risk. Increasing dietary folate intake had a protective effect.[26] Research has suggested that, overall, female babies are more likely to be affected by the disorder.[27] Ethical issuesOrgan donationOne issue concerning anencephalic newborns is organ donation. Initial legal guidance came from the case of Baby Theresa in 1992, in which the boundaries of organ donation were tested for the first time.[28] Infant organs are scarce, and the high demand for pediatric organ transplants poses a major public health issue. In 1999, it was found that for American children under the age of two who are waiting for a transplant, 30–50% die before an organ becomes available.[28] Within the medical community, the main ethical issues with organ donation are a misdiagnosis of anencephaly, the slippery slope argument, that anencephalic neonates would rarely be a source of organs, and that it would undermine confidence in organ transplantation.[29] Slippery slope concerns are a major issue in personhood debates, across the board. In regards to anencephaly, those who oppose organ donation argue that it could open the door for involuntary organ donors such as an elderly person with severe dementia. Another point of contention is the number of children who would actually benefit. There are discrepancies in statistics; however, it is known that most anencephalic children are stillborn.[29] Proposals have been made to bypass the legal and ethical issues surrounding organ donation. These include waiting for death to occur before procuring organs, expanding the definition of death, creating a special legal category for anencephalic infants, and defining them as non-persons.[30] In the United Kingdom, a child born with anencephaly was reported as the country's youngest organ donor. Teddy Houlston was diagnosed as anencephalic at 12 weeks of gestation. His parents, Jess Evans and Mike Houlston, decided against abortion and instead proposed organ donation. Teddy was born on 22 April 2014, in Cardiff, Wales, and lived for 100 minutes, after which his heart and kidneys were removed. His kidneys were later transplanted into an adult in Leeds. Teddy's twin, Noah, was born healthy.[31] Brain deathThere are four different concepts used to determine brain death: failure of heart, failure of lungs, whole brain death, and neocortical death.[citation needed] Neocortical death, similar to a persistent vegetative state (PVS), involves loss of cognitive functioning of the brain. A proposal by law professor David Randolph Smith,[32] in an attempt to prove that neocortical death should legally be treated the same as brain death, involved PET scans to determine the similarities. However, this proposal has been criticized on the basis that confirming neocortical death by PET scan may risk indeterminacy.[33] Pregnancy terminationAnencephaly can be diagnosed before delivery with a high degree of accuracy. Although anencephaly is a fatal condition, the option of abortion is dependent on the abortion laws in the state.[34] According to a 2013 report, 26% of the world's population reside in a country where abortion is generally prohibited.[34][35] In 2012, Brazil extended the right of abortion to mothers with anencephalic fetuses. This decision is, however, receiving much disapproval by several religious groups.[36] Legal proceedingsThe case of baby Theresa was the beginning of the ethical debate over anencephalic infant organ donation.[28] The story of baby Theresa remains a focus of basic moral philosophy. Baby Theresa was born with anencephaly in 1992. Her parents, knowing that their child was going to die, requested that her organs be given for transplantation. Although her physicians agreed, Florida law prohibited the infant's organs from being removed while she was still alive. By the time she died nine days after birth, her organs had deteriorated past the point of being viable.[37] United States uniform actsThe Uniform Determination of Death Act (UDDA) is a model bill, adopted by many US states, stating that an individual who has sustained either 1) irreversible cessation of circulatory and respiratory functions or 2) irreversible cessation of all functions of the entire brain, including the brain stem, is dead. This bill was a result of much debate over the definition of death and is applicable to the debate over anencephaly. A related bill, the Uniform Anatomical Gift Act (UAGA), grants individuals and, after death, their family members the right to decide whether or not to donate organs. Because it is against the law for any person to pay money for an organ, the person in need of an organ transplant must rely on a volunteer.[34] There have been two state bills that proposed to change current laws regarding death and organ donation. California Senate Bill 2018 proposed to amend the UDDA to define anencephalic infants as already dead, while New Jersey Assembly Bill 3367 proposed to allow anencephalic infants to be organ sources even if they are not dead.[34][38] ResearchSome genetic research has been conducted to determine the causes of anencephaly. It has been found that cartilage homeoprotein (CART1) is selectively expressed in chondrocytes (cartilage cells). The CART1 gene to chromosome 12q21.3–q22 has been mapped. Also, it has been found that mice homozygous for deficiency in the Cart1 gene manifested acrania and meroanencephaly, and prenatal treatment with folic acid will suppress acrania and meroanencephaly in the Cart1-deficient mutants.[39][40] See alsoReferences
External linksWikimedia Commons has media related to Anencephaly. |
||||||||||||||||||