CYCLADES
|

Prophet in the Book of Mormon Not to be confused with Michael Avenatti or Aminadi. This article uses texts from within a religion or faith system without referring to secondary sources that critically analyze them. Please help improve this article. (October 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Depiction of the death of Abinadi According to the Book of Mormon, Abinadi (/əˈbɪnədaɪ/)[1] was a prophet who lived on the American continent about 150 BC. In the Book of…

2019 song by Vishal–Shekhar For the musical anklet worn by classical Indian dancers, see Ghungroo. GhungrooOfficial song coverSingle by Vishal–Shekharfrom the album War LanguageHindiReleased5 September 2019Recorded2018–2019Studio YRF Studios, Mumbai Purple Haze Studio, New Delhi Mastering World, Wales GenreDancepopFunkLength5:02LabelYRF MusicComposer(s)Vishal–ShekharLyricist(s)KumaarProducer(s)Yash Raj FilmsWar track listing Ghungroo Jai Jai Shivshankar War Theme Kabir's Theme Khalid's T…

Class of 17 diesel-electric locomotives that was used by Portuguese Railways This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: CP Class 1930 – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Class 1930Locomotive 1943 heading an Inter City passenger train at Évora station…

Buaya irian Kepala buaya irian Status konservasi Risiko Rendah (IUCN 3.1) Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Sauropsida Ordo: Crocodilia Famili: Crocodylidae Genus: Crocodylus Spesies: C. novaeguineae Nama binomial Crocodylus novaeguineae Buaya irian (Crocodylus novaeguineae) adalah salah satu spesies buaya yang ditemukan menyebar di perairan tawar pedalaman Pulau Papua. Bentuk umum jenis ini mirip dengan buaya muara (C. porosus), tetapi lebih kecil dan warna …

B-25 Mitchell Sebuah B-25 Mitchell TNI AU di Museum Dirgantara Mandala Jenis Pembom menengah Negara asal Amerika Serikat Pembuat North American Aviation Penerbangan perdana 19 Agustus 1940 Pengenalan 1941 Dipensiunkan 1979 (Indonesia) Pengguna utama Angkatan Udara Amerika SerikatRoyal Air Force Soviet Air ForceUnited States Marine Corps Jumlah 9,816[1] Dikembangkan dari North American NA-40 Dikembangkan menjadi North American XB-28 North American B-25 Mitchell adalah sebuah pesawat …

Città metropolitana di Cataniacittà metropolitana Città metropolitana di Catania – VedutaPalazzo Minoriti, sede istituzionale LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Sicilia AmministrazioneCapoluogo Catania Sindaco metropolitanoEnrico Trantino (FdI) dal 6-6-2023[1] Data di istituzione4 agosto 2015 TerritorioCoordinatedel capoluogo37°31′N 15°04′E / 37.516667°N 15.066667°E37.516667; 15.066667 (Città metropolitana di Catania)Coordinate: 37°3…

For the song by Christine and the Queens, see Chris (album). 2013 single by Fitz and the TantrumsThe WalkerSingle by Fitz and the Tantrumsfrom the album More Than Just a Dream ReleasedDecember 10, 2013[1]GenreIndie popneo soulelectropopLength3:53LabelElektraSongwriter(s)Fitz and the TantrumsProducer(s)Tony HofferFitz and the Tantrums singles chronology Out of My League (2013) The Walker (2013) Fools Gold (2014) Music videoThe Walker” on YouTube The Walker is a song by the American neo …

Square matrix used to represent a graph or network In graph theory and computer science, an adjacency matrix is a square matrix used to represent a finite graph. The elements of the matrix indicate whether pairs of vertices are adjacent or not in the graph. In the special case of a finite simple graph, the adjacency matrix is a (0,1)-matrix with zeros on its diagonal. If the graph is undirected (i.e. all of its edges are bidirectional), the adjacency matrix is symmetric. The relationship between…

NBC Studios adalah dua fasilitas studio televisi yang dimiliki oleh National Broadcasting Company, dengan salah satunya berada di dalam GE Building di Rockefeller Center, New York City, dan satunya lagi di Burbank, California, di luar Los Angeles. Fasilitas produksi NBC ketiga, NBC Tower, terletak di Chicago, Illinois. Juga terdapat studio cadangan untuk kawasan New York di Marblehead, Massachusetts. NBC Studios juga dulunya merupakan nama bagi divisi produksi jaringan ini (sebelumnya NBC Produc…

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando il sito archeologico italiano situato a Viterbo (Lazio), vedi Acquarossa (sito archeologico). Questa voce sull'argomento centri abitati del Canton Ticino è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Acquarossacomune Acquarossa – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Svizzera Cantone Ticino DistrettoBlenio AmministrazioneSindacoOdis Barbara De Leoni dal 2016 Lingue ufficialiItaliano Data di istituzione2004 Te…

Monster FamilyPoster perilisan bioskopSutradaraHolger TappeProduserHolger TappeSkenarioDavid SafierCatharina JunkBerdasarkanHappy Familyoleh David SafierPemeran Emily Watson Nick Frost Jessica Brown Findlay Celia Imrie Catherine Tate Jason Isaacs Penata musikHendrik SchwarzerPenyuntingBjörn TeubnerPerusahaanproduksiAmbient Entertainment GmbHUnited EntertainmentMack MediaAgirTimeless FilmsRothkirch Cartoon FilmSky Cinema Original FilmsVideoBackDistributorWarner Bros. Pictures (Jerman)Altit…

(Tanggal dalam tulisan miring menandakan kelanjutan pemerintahan secara de facto) Periode Jabatan Pejabat Afiliasi Catatan 29 Mei 1991-24 Mei 1993 Isaias Afewerki, Sekretaris Jenderal Pemerintah Provisional EPLF Menjadi Presiden Negara Eritrea(Hagere Ertra) Merdeka dari Ethiopia 24 Mei 1993-sekarang Isaias Afewerki, Presiden, Ketua Parlemen Nasional PFDJ Sekretaris Jenderal Pemerintah Provinsi Hitherto; terpilih pada 22 Mei 1993 Afiliasi PFDJ: People's Front for Democracy and Justice authoritari…
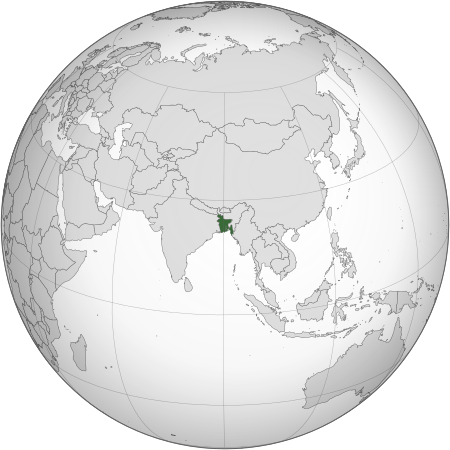
Country in South Asia This article is about the country. For other uses, see Bangladesh (disambiguation). People's Republic of Bangladeshগণপ্রজাতন্ত্রী বাংলাদেশ (Bengali)Gôṇôprôjātôntrī Bāṅlādeś Flag Emblem Anthem: আমার সোনার বাংলাAmar Shonar BanglaMy Golden BengalMarch: নতুনের গানNotuner GaanThe Song of Youth[1]Slogan: জয় বাংলাJoy BanglaVictory to Bengal[…

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Guerra finlandese. Guerra di Finlandiaparte delle Guerre russo-svedesi e delle Guerre napoleonicheLa battaglia di Ratan e Sävar, l'ultimo scontro del conflittoData21 febbraio 1808 - 17 settembre 1809 LuogoFinlandia EsitoVittoria russa, firma del Trattato di Fredrikshamn Modifiche territorialiseparazione della Finlandia dalla Svezia, e formazione del Granducato di Finlandia sotto controllo russo Schieramenti Impero russoSupporto estern…

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Goa. Goa adalah munisipalitas kelas 2 di provinsi Camarines Sur, Region Bicol, Filipina. Menurut sensus tahun 2015, Goa berpenduduk 63.308 jiwa. Wali kotanya sekarang adalah Antero Siros Lim. Pembagian wilayah Goa terbagi atas 34 barangay: Abucayan Bagumbayan Grande (Pob.) Bagumbayan Pequeño (Pob.) Balaynan Belen (Pob.) Buyo Cagaycay Catagbacan Digdigon Gimaga Halawig-Gogon Hiwacloy La Purisima (Pob.) Lamon Matacla Maymatan Maysalay Napawon (Napunuon) Panday (Pob.) Pa…

CenterportboroughBorough of Centerport Centerport – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Stati Uniti Stato federato Pennsylvania ConteaBerks TerritorioCoordinate40°29′12″N 76°00′26″W / 40.486667°N 76.007222°W40.486667; -76.007222 (Centerport)Coordinate: 40°29′12″N 76°00′26″W / 40.486667°N 76.007222°W40.486667; -76.007222 (Centerport) Altitudine106 m s.l.m. Superficie0,5 km² Abitanti387[1] (1-7-2010) Densità774…

Suhasini Mani Ratnam LahirSuhasini Charuhasan15 Agustus 1961 (umur 62)Paramakudi, Tamil Nadu, IndiaTempat tinggalAlwarpet, Chennai, IndiaPekerjaanActress, director, producer, writerTahun aktif1980–presentSuami/istriMani Ratnam (m. 1988–present)AnakNandan (b.1992) Suhasini Maniratnam (lahir pada 15 Agustus 1961), juga dikenal sebagai Suhasini, adalah seorang aktris India yang dikenal karena karyanya dalam film Kannada, Malayalam, Tamil, Telugu, dan Hindi. Ia membuat debut filmnya pa…

Laing O'RourkeJenisSwastaIndustriKonstruksi, Teknik SipilDidirikan1978KantorpusatDartford, Britania RayaTokohkunciRay O'Rourke KBE(Chairman dan CEO)Pendapatan£2.928,9 juta (2017/2018)[1][2]Laba operasi£(18,3) juta (2017/2018)[1]Laba bersih£(46,5) juta (2017/2018)[1]Karyawan12.796 (2017/2018)[1]Situs webwww.laingorourke.com Laing O'Rourke adalah sebuah perusahaan konstruksi multinasional yang berkantor pusat di Dartford, Inggris. Perusahaan ini didirikan…

Part of a series on theCulture of Qatar History People Languages Cuisine Festivals Public holidays Religion Art Collecting practices of the Al-Thani Family Public art in Qatar Literature Qatari folklore Music and Performing arts Media Radio Television Cinema Sport Monuments World Heritage Sites Symbols Flag Coat of arms National anthem vte Sport in Qatar is primarily centred on football in terms of participation and spectators. Additionally, athletics, basketball, handball, volleyball, camel rac…

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut). …