Despotiko
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Raise the Red LanternSampul depan DVD yang dirilisSutradaraZhang YimouProduserHou Hsiao-hsienChiu Fu-shengZhang WenzeDitulis olehNi ZhenBerdasarkanWives and Concubinesoleh Su TongPemeranGong LiPenata musikZhao JipingSinematograferZhao FeiPenyuntingDu YuanDistributorOrion ClassicsTanggal rilis September 1991 (1991-09) (Venice) Durasi125 menitNegaraChinaHong KongTaiwanBahasaMandarinPendapatankotor$2,603,061 (Amerika Serikat)[1] Raise the Red Lantern (Hanzi sederhana:…

Gil BellowsBellows pada Genie Awards ke-32 tahun 2012Lahir28 Juni 1967 (umur 56)Vancouver, British Columbia, KanadaPekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1988–sekarangSuami/istriRya Kihlstedt (m. 1994)Anak2 Gil Bellows (lahir 28 Juni 1967) adalah pemeran, penulis naskah, dan sutradara Kanada. Ia dikenal untuk perannya sebagai Tommy Williams dalam film tahun 1994, The Shawshank Redemption, sebagai Billy Thomas dalam seri televisi Fox berjudul Ally McBeal (1997–200…

30th Governor of Wyoming Jim Geringer30th Governor of WyomingIn officeJanuary 2, 1995 – January 6, 2003Preceded byMike SullivanSucceeded byDave FreudenthalMember of the Wyoming Senatefrom the 3rd districtIn office1989–1995Succeeded byCurt Meier Personal detailsBorn (1944-04-24) April 24, 1944 (age 79)Wheatland, Wyoming, U.S.Political partyRepublicanSpouse Sharyn Geringer (m. 1967)Children5EducationKansas State University (BS)Military serviceAllegi…

Susno Duadji Kepala Badan Reserse Kriminal PolriMasa jabatan24 Oktober 2008 – 30 November 2009PresidenSusilo Bambang Yudhoyono PendahuluBambang Hendarso DanuriPenggantiIto SumardiKepala Kepolisian Daerah Jawa BaratMasa jabatan15 Januari 2008 – 24 Oktober 2008 PendahuluSoenarko Danu ArdantoPenggantiTimur Pradopo Informasi pribadiLahir1 Juli 1954 (umur 69)Kota Pagar Alam, Sumatera Selatan, IndonesiaSuami/istriHerawatiOrang tuaDuadji (ayah)Siti Amah (ibu)Alma materAkademi…

Political party in Mexico Coalition for the Good of All Coalición por el Bien de TodosLeaderAndrés Manuel López ObradorFounded2005 (2005)Dissolved2006 (2006)Preceded byProgressive MovementIdeologyCardenismSocial democracyLeft-wing nationalismProgressivismPolitical positionLeft-wingPolitics of MexicoPolitical partiesElections Politics of Mexico Federal government Constitution of Mexico(history) Human rights LGBT rights Law Abortion Labor Nationality Capital punishment L…
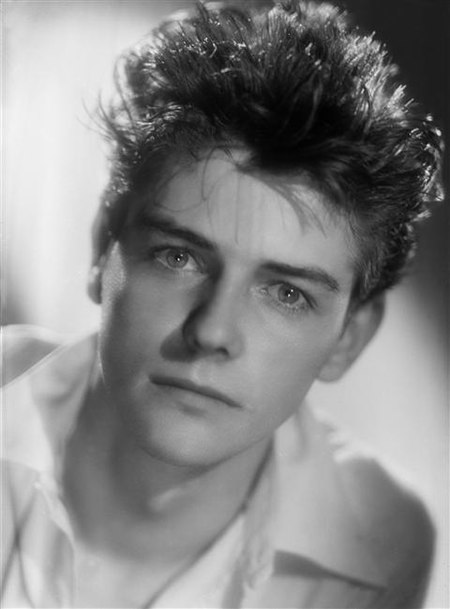

Vous lisez un « bon article » labellisé en 2012. Pour les articles homonymes, voir Mokiejewski. Pour le musicien, voir Mocky. Jean-Pierre MockyJean-Pierre Mocky en 1995.BiographieNaissance 6 juillet 1929Nice (France)Décès 8 août 2019 (à 90 ans)7e arrondissement de Paris (France)Sépulture Cimetière du prieuré noir (d)Nom de naissance Jean Paul Adam MokiejewskiPseudonyme Jean-Pierre MockyNationalité françaiseFormation Conservatoire national supérieur d'art dramatiqueAct…

Professional ice hockey team based in Virginia Roanoke Rail Yard DawgsCityRoanoke, VirginiaLeagueSPHLFounded2009; 15 years ago (2009)Home arenaBerglund CenterColorsRoyal blue, gold, white Owner(s)McGinn family[a]Head coachDan BremnerCaptainMac JansenMediaThe Roanoke TimesFranchise history2009–2014Mississippi Surge2016–presentRoanoke Rail Yard DawgsChampionshipsPlayoff championships1 (2022–23) The Roanoke Rail Yard Dawgs are a professional ice ho…

Questa voce sull'argomento stagioni delle società calcistiche italiane è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Voce principale: Associazione Calcio Fanfulla 1874. Associazione Sportiva FanfullaStagione 1962-1963Sport calcio Squadra Fanfulla Allenatore Fausto Braga Presidente Ennio Paleari Serie C7° Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Vaglia (34) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Spelta (11) 1961-1962 19…

Artikel ini mungkin terdampak dengan peristiwa terkini: Invasi Rusia ke Ukraina 2022. Informasi di halaman ini bisa berubah setiap saat. Pembagian administratif Moldova. Pembagian administratif Moldova pada tingkat pertama terdiri atas 32 distrik, 3 munisipalitas, dan 2 daerah otonom. lbsPembagian administratif EropaNegaraberdaulat Albania Andorra Armenia1 Austria Azerbaijan1 Belanda Belarus Belgia Bosnia dan Herzegovina Britania Raya Inggris Irlandia Utara Skotlandia Wales Bulgaria Ceko Denmark…

2013 studio album by Richard & AdamThe Impossible DreamStudio album by Richard & AdamReleased29 July 2013 (2013-07-29)RecordedJuly 2013GenreOperatic pop, gospelLength39:45LabelSonyProducerGraham Stack, Matt FurmidgeRichard & Adam chronology The Impossible Dream(2013) The Christmas Album(2013) The Impossible Dream is the debut studio album by Welsh operatic duo Richard & Adam, who first rose to fame on the seventh series of the ITV talent show Britain's Got …

Roofing bones of the skull The full complement of bones of the tetrapod skull roof, as seen in the temnospondyl Xenotosuchus The skull roof or the roofing bones of the skull are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes and all land-living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone and are part of the dermatocranium. In comparative anatomy, the term is applied to the whole dermatocranium.[1] In general anatomy, the roofing bones may refer specifically t…

Questa voce sull'argomento isole dell'Oceania è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Mappa delle Isole Samoa. Le Isole Samoa o Isole Samoane (in samoano: Samoa, in inglese: Samoan Islands o Samoa Islands), in passato note anche come Isole dei Navigatori da Louis-Antoine de Bougainville o Isole degli Amici da James Cook, sono un arcipelago di 3.030 km² situato nel Pacifico meridionale, facenti parte della regione della Polinesia. Registrano una p…

Voce principale: Virtus Entella. Virtus EntellaStagione 2013-2014Sport calcio Squadra Entella Allenatore Luca Prina All. in seconda Sergio Spalla Presidente Antonio Gozzi 1ª Divisione - Gir. A1º posto (in Serie B) Coppa ItaliaSecondo turno Coppa Italia Lega ProTerzo turno Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Paroni (30)Totale: Russo (36) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Marchi, Moreo (6)Totale: Marchi, Moreo (6) StadioComunale (capienza: 4.154) Abbonati472 Maggior numero di spettatori3.318 vs Pro Ver…

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Defri Juliant. Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Defry Palulu – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Defry PaluluStatistikNama panggilanThe Unseen HammerDinilai padaSuper BantamKebangsaan Indones…

David CameronRitratto ufficiale, 2023 Segretario di Stato per gli affari esteri, del Commonwealth e dello sviluppoIn caricaInizio mandato13 novembre 2023 MonarcaCarlo III Capo del governoRishi Sunak PredecessoreJames Cleverly Primo ministro del Regno UnitoDurata mandato11 maggio 2010 –13 luglio 2016 MonarcaElisabetta II ViceNick Clegg[1] PredecessoreGordon Brown SuccessoreTheresa May Leader dell'opposizioneDurata mandato6 dicembre 2005 –11 maggio 2010…

「俄亥俄」重定向至此。关于其他用法,请见「俄亥俄 (消歧义)」。 俄亥俄州 美國联邦州State of Ohio 州旗州徽綽號:七葉果之州地图中高亮部分为俄亥俄州坐标:38°27'N-41°58'N, 80°32'W-84°49'W国家 美國加入聯邦1803年3月1日,在1953年8月7日追溯頒定(第17个加入联邦)首府哥倫布(及最大城市)政府 • 州长(英语:List of Governors of {{{Name}}}]]) • …
周處除三害The Pig, The Snake and The Pigeon正式版海報基本资料导演黃精甫监制李烈黃江豐動作指導洪昰顥编剧黃精甫主演阮經天袁富華陳以文王淨李李仁謝瓊煖配乐盧律銘林孝親林思妤保卜摄影王金城剪辑黃精甫林雍益制片商一種態度電影股份有限公司片长134分鐘产地 臺灣语言國語粵語台語上映及发行上映日期 2023年10月6日 (2023-10-06)(台灣) 2023年11月2日 (2023-11-02)(香港、…

「アプリケーション」はこの項目へ転送されています。英語の意味については「wikt:応用」、「wikt:application」をご覧ください。 この記事には複数の問題があります。改善やノートページでの議論にご協力ください。 出典がまったく示されていないか不十分です。内容に関する文献や情報源が必要です。(2018年4月) 古い情報を更新する必要があります。(2021年3月)出典�…

أنتوني ماندريا معلومات شخصية الميلاد 25 ديسمبر 1996 (28 سنة) غراس الطول 1.86 م (6 قدم 1 بوصة) مركز اللعب حارس مرمى الجنسية الجزائر فرنسا معلومات النادي النادي الحالي ستاد ماليرب كان الرقم 1 مسيرة الشباب سنوات فريق 2002–2009 U.S. Pegomas 2009–2013 نيس المسيرة الاحترافية1 سنوات فر…

This article is about the house in Potsdam. For the buildings in Greece, see Dragon houses. For the novel, see The Dragon House. Historical building in Potsdam, GermanyDragon HouseDrachenhausThe Dragon House from the SouthGeneral informationTypeHistorical buildingArchitectural styleChinoiserieTown or cityPotsdamCountryGermanyConstruction started1770Completed1772Renovated1787 Dragon House (German Drachenhaus) is a historical building in Potsdam, Germany, built by King Frederick the Great of Pruss…