History of the Jews in Indonesia
|
Read other articles:

Bares mulut-besar Sander vitreus Status konservasiRisiko rendahIUCN202605 TaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumChordataKelasActinopteriOrdoPerciformesFamiliPercidaeGenusSanderSpesiesSander vitreus Mitchill, 1818 Tata namaSinonim takson Perca vitrea Mitchill, 1818 Stizostedion vitreum (Mitchill, 1818) Lucioperca americana Cuvier, 1828 Lucioperca grisea DeKay, 1842 Stizostedion glaucum Hubbs, 1926[1] Subspecieslbs Bares mulut-besar ( Sander vitreus, sinonim Stizostedion vitreum ), juga disebut ik…

PelacuranPekerjaanNamaPelacurPekerja seks komersialWanita tunasusilaLonteSundalPramuriaKupu-kupu malamJenis pekerjaanProfesiSektor kegiatanHiburanPenggambaranKompetensiLibidoKecantikanSeksologiBidang pekerjaanBordilBarDiskotekPekerjaan terkaitPemeran pornografi Pelacuran atau prostitusi adalah pertukaran hubungan seksual dengan uang atau hadiah sebagai suatu transaksi perdagangan.[1] Pelacuran merupakan cabang dari industri seks yang sejajar dengan pornografi, tari telanjang, bahkan sega…

Artour BabaevArteezy, 2018StatusActiveTanggal lahir1 Juli 1996 (umur 27)Tempat tinggalVancouver, British ColumbiaKebangsaan KanadaTim saat iniEvil GeniusesPermainanDota 2Riwayat karir2013Speed Gaming2014–2015Evil Geniuses2015Team Secret2015–2016Evil Geniuses2016Team Secret2016–kiniEvil Geniuses Artour Babaev (lahir 1 Juli 1996) dikenal juga dengan nama Arteezy, adalah seorang pemain profesional Dota 2 yang saat ini bermain untuk Evil Geniuses.[1] Selain keahliannya yang l…
Huruf Kiril Tse Penggunaan Fonetis:[ts]Nama:циNomor Kiril:900Sampel suaranoicon sumber · bantuan Alfabet KirilHuruf SlaviaАА́А̀А̂А̄ӒБВГҐДЂЃЕЕ́ÈЕ̂ЁЄЖЗЗ́ЅИИ́ЍИ̂ЙІЇЈКЛЉМНЊОŌПРСС́ТЋЌУУ́ У̀У̂ӮЎФХЦЧЏШЩЪЫЬЭЮЯHuruf non-SlaviaӐА̊А̃Ӓ̄ӔӘӘ́Ә̃ӚВ̌ҒГ̑Г̣Г̌ҔӺҒ̌ӶД̌Д̣Д̆ӖЕ̄Е̃Ё̄Є̈ӁҖӜҘӞЗ̌З̱З̣ԐԐ̈ӠӢИ̃ҊӤҚӃҠҞҜК̣ԚӅԮԒӍӉҢԨӇҤО́О̀О̆О̂О̃ӦӦ̄Ө…

Provinsi Son La merupakan sebuah provinsi di Vietnam. Provinsi ini terletak di bagian utara di negara itu. Provinsi ini memiliki luas wilayah 14.055 km² dengan memiliki jumlah penduduk 972.800 jiwa (2004). Provinsi ini memiliki angka kepadatan penduduk 69 jiwa/km². Ibu kotanya ialah Son La. lbsPembagian administratif Vietnam Wilayah di Vietnam Tay Bac · Dong Bac · Delta Sungai Merah · Bac Trung Bo · Nam Trung Bo · Tay Nguyen ·&#…

Bingöl province Bingöl iliProvince of TurkeyLocation of Bingöl Province in TurkeyCountryTurkeyRegionEastern AnatoliaLuas • Total8,125 km2 (3,137 sq mi)Populasi (2010-12-31)[1] • Total255.170 • Kepadatan31,000/km2 (81,000/sq mi)Kode area telepon0426Pelat kendaraan12Situs webbingöl.gov.tr Bingöl (Turki: Bingöl ili) adalah sebuah provinsi Turki. lbsDaftar provinsi Turki Adana · Adıyaman · Afyonkara…

United States historic placeSpring Valley Public LibraryU.S. National Register of Historic Places Spring Valley Public LibraryShow map of MinnesotaShow map of the United StatesLocation121 E. Jefferson St. Spring Valley MN 55975Coordinates43°41′19.5″N 92°23′22.5″W / 43.688750°N 92.389583°W / 43.688750; -92.389583Built1904ArchitectH. J. AmlicArchitectural styleBeaux-ArtsMPSFillmore County MRANRHP reference No.82002951 [1]Added to NRHPApril…

Sporting event delegationMadagascar at the2008 Summer OlympicsIOC codeMADNOCComité Olympique Malgachein BeijingCompetitors6 in 4 sportsFlag bearer Jean de Dieu SoloniainaMedals Gold 0 Silver 0 Bronze 0 Total 0 Summer Olympics appearances (overview)1964196819721976198019841988199219962000200420082012201620202024 Madagascar competed at the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing, People's Republic of China. The country sent six representatives to compete in four sports.[1] Athletics Main art…

Hosted Payload Box installed on Hodoyoshi-3 & Hodooyshi-4 satellites Hodoyoshi-4 adalah mikro-satelit Jepang diluncurkan pada 2014. Satelit itu dibangun di bus 0.5x0.6x0.7m kotak-bentuk, dioptimalkan untuk peluncuran piggy-back. Semua instrumen yang didukung oleh sel surya yang dipasang di tubuh pesawat ruang angkasa dan dua sayap rintisan, dengan perkiraan daya listrik dari 50W. Referensi Lihat juga Hodoyoshi 3 Pranala luar Hodoyoshi 4 di Facebook Nano-Satellite Center, University of Tokyo …

1938 annexation of Austria into Nazi Germany Austrian citizens gather on the Heldenplatz to hear Hitler's declaration of annexation. Territory of the German Reich and Austria before the Anschluss Territorial evolution of Germanyin the 20th century Pre-World War II Act of 5th November proclaiming Kingdom of Poland (1916) Treaty of Brest-Litovsk with Ukraine (1918) Treaty of Brest-Litovsk with Soviet Russia (1918) Treaty of Versailles (1919) German–Polish Convention regarding Upper Silesia (1922…

Simple, loose over-garment wore by women, especially Muslim women For other uses, see Abaya (disambiguation). A modern abaya. Part of a series onIslamic female dress Types Abaya Battoulah Boshiya Burkini Burqa Çarşaf Chador Haik Hijab Jilbaab Kerudung Kimeshek Kurhars Mukena Niqaab Paranja Safseri Selendang Shayla Tudong Yashmak Practice and law by country Australia Britain Canada Egypt France Indonesia Iran Pakistan Saudi Arabia Taliban Afghanistan Turkey Concepts Andaruni Awrah Fahisha Gende…

NASA satellite of the Explorer program Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic ImagerRHESSI spacecraft observing the SunNamesExplorer 81HESSIHigh Energy Solar Spectroscopic ImagerRHESSISMEX-6Mission typeSolar observatoryOperatorNASA / Space Sciences LaboratoryCOSPAR ID2002-004A SATCAT no.27370WebsiteRHESSIMission duration2 years (planned) [1]16 years, 6 months, 10 days (achieved) Spacecraft propertiesSpacecraftExplorer LXXXISpacecraft typeReuven Ramaty High Energy So…

Reform synagogue in Manhattan, New York For similarly named synagogues, see Shaare Tefila. Temple Shaaray TefilaHebrew: שערי תפילהThe synagogue from the north-eastern corner of East 79th Street and 2nd AvenueReligionAffiliationReform JudaismEcclesiastical or organisational statusSynagogueLeadershipRabbi Joel MosbacherRabbi Jill Rubin (Associate)StatusActiveLocationLocation250 East 79th Street, Upper East Side, Manhattan, New York City, New York 10075CountryUnited StatesLocation in Manha…
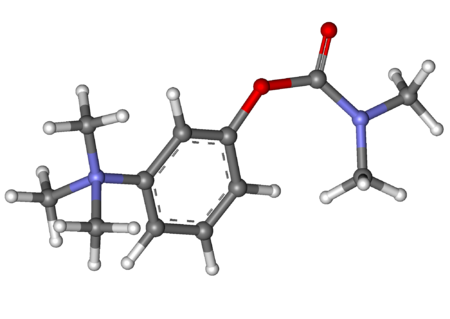
Anti-full body paralysis drug treatment NeostigmineClinical dataTrade namesBloxiverz, Prostigmin, Vagostigmin, othersAHFS/Drugs.comMonographLicense data US DailyMed: Neostigmine Pregnancycategory AU: B2[1] Routes ofadministrationIntramuscular, intravenous, subcutaneous, by mouthDrug classCholinesterase inhibitorATC codeN07AA01 (WHO) S01EB06 (WHO) QA03AB93 (WHO)Legal statusLegal status AU: S4 (Prescription only) UK: POM (Prescription only) US:&…

Au début du Moyen Âge, Arles, profitant de l'affaiblissement du pouvoir comtal et de ses chevaliers urbains, essaye de s'émanciper d'abord par le consulat en 1130 puis par la République d'Arles à partir de la fin du XIIe siècle. La ville avec la Provence, passe toutefois en 1251 sous la domination complète de la première dynastie Angevine et la cité, bien qu'ayant réalisé son unité, perd de son importance politique. En revanche Arles et son territoire se développent par l'agric…

Voce principale: Campionato mondiale di Formula 1 1981. Gran Premio del Canada 1981 356º GP del Mondiale di Formula 1Gara 14 di 15 del Campionato 1981 Data 27 settembre 1981 Nome ufficiale XX Grand Prix Labatt du Canada Luogo Montreal Percorso 4,410 km Distanza 63 giri, 277,830[1] km Clima Piovoso Risultati Pole position Giro più veloce Nelson Piquet John Watson Brabham-Ford Cosworth in 1'29211 McLaren-Ford Cosworth in 1'49475 (nel giro 43) Podio 1. Jacques LaffiteLigier-Matra 2.…

土库曼斯坦总统土库曼斯坦国徽土库曼斯坦总统旗現任谢尔达尔·别尔德穆哈梅多夫自2022年3月19日官邸阿什哈巴德总统府(Oguzkhan Presidential Palace)機關所在地阿什哈巴德任命者直接选举任期7年,可连选连任首任萨帕尔穆拉特·尼亚佐夫设立1991年10月27日 土库曼斯坦土库曼斯坦政府与政治 国家政府 土库曼斯坦宪法 国旗 国徽 国歌 立法機關(英语:National Council of Turkmenistan) 土�…

此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2021年7月4日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:美国众议院 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 美國眾議院 United States House of Representatives第118届美国国会众议院徽章 众议院旗帜…

Cotton mill in Greater Manchester, England Royton Ring MillThe mill before 1951Location in Greater ManchesterCottonSpinning (ring & doubling mill)LocationRoyton, Greater Manchester, EnglandFurther ownershipLancashire Cotton Corporation (1935)Courtaulds (1964)Coordinates53°33′17″N 2°07′09″W / 53.5546°N 2.1191°W / 53.5546; -2.1191ConstructionCompleted1908Renovated 1:1912 (expanded) Design teamArchitecture FirmP.S.StottPowerEngine makerUrmson & ThompsonEn…

「アプリケーション」はこの項目へ転送されています。英語の意味については「wikt:応用」、「wikt:application」をご覧ください。 この記事には複数の問題があります。改善やノートページでの議論にご協力ください。 出典がまったく示されていないか不十分です。内容に関する文献や情報源が必要です。(2018年4月) 古い情報を更新する必要があります。(2021年3月)出典�…

