Hungary–Soviet Union relations
| |||||||||||

Gaelic football trophy This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Sam Maguire Cup – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Original 1928 Sam Maguire Cup on display in the GAA Museum at Croke Park The Sam Maguire Cup (Irish: Chorn Sam Mh…

Pembukaan COP19 tanggal 11 November 2013 Konferensi Perubahan Iklim Perserikatan Bangsa-Bangsa 2013 akan diselenggarakan di Warsawa, Polandia, pada tanggal 11 sampai 22 November 2013. Ini adalah sidang tahunan ke-19 Konferensi Pihak (COP 19) Konvensi Kerangka Kerja Perubahan Iklim Perserikatan Bangsa-Bangsa (UNFCCC) dan sidang ke-9 Pertemuan Pihak (CMP 9) Protokol Kyoto 1997 (protokol ini disusun sesuai piagam UNFCCC).[1] Delegasi konferensi tahun 2013 akan melanjutkan negosiasi putaran …

Remis zebra (Dreissena polymorpha) salah satu jenis spesies invasif yang menyebar melalui air pemberat (ballast water) di dalam kapal. Ketersediaan jalur perkapalan barat-laut akibat pengaruh perubahan iklim memungkinkan penyeberan remis air tawar ini di lokasi-lokasi baru.Perubahan iklim diprediksi dapat mempengaruhi keanekaragaman hayati secara subtansial; menyebabkan perubahan fenologi, komposisi genetik, dan sebaran spesies; serta mempengaruhi interaksi antarspesies dan berbagai proses di ek…
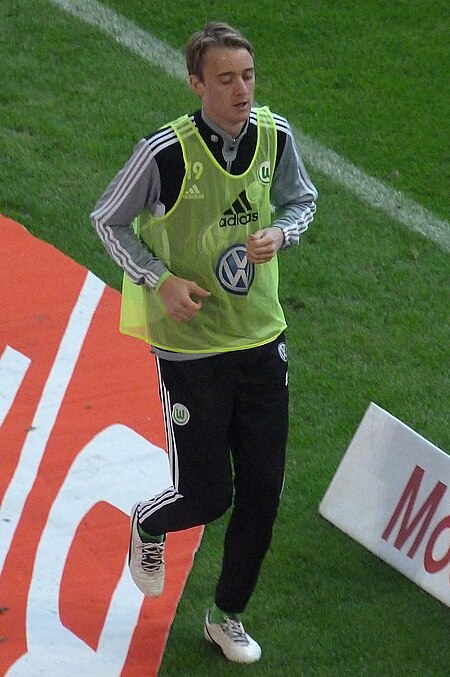

Rasmus Jönsson Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Rasmus JönssonTanggal lahir 27 Januari 1990 (umur 34)Tempat lahir Viken, SwediaTinggi 1,92 m (6 ft 3+1⁄2 in)Posisi bermain PenyerangInformasi klubKlub saat ini FSV Frankfurt(pinjaman dari VfL Wolfsburg)Nomor 10Karier junior0000–2007 Helsingborgs IFKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2007–2011 Helsingborgs IF 97 (27)2011– VfL Wolfsburg 17 (0)2013– → FSV Frankfurt (pinjaman) 2 (0)Tim nasional‡2007 Swedia U-17 3 (2…

Jeff GordonJeff Gordon pada tahun 2019.LahirJeffery Michael Gordon4 Agustus 1971 (umur 52)Vallejo, California, A.S.KebangsaanAmerika SerikatPekerjaanPembalap mobil (1990–2016)Pembawa acara (2015–2021)Pebisnis (2021–sekarang)Tempat kerjaHendrick MotorsportsTinggi5 ft 8 in (1,73 m)Berat150 pon (68 kg)Suami/istriBrooke Sealey (m. 1994; c. 2003)Ingrid Vandebosch (m. 2006)AnakElla So…
7-Zip Antarmuka grafis 7-Zip di Windows 11TipePengarsip berkas Versi pertama18 Juli 1999 (1999-07-18)[1]Versi stabilDaftarMicrosoft Windows, Linux, macOS: 23.01 (20 Juni 2023) GenrePengarsip berkasLisensiLGPL[2]BahasaDaftar bahasa 79 bahasa, termasuk Bahasa Indonesia Karakteristik teknisSistem operasiWindows Mobile, Linux, ReactOS, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows XP, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, Windows Server …

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang film. Untuk lagu 1980, lihat Entre Nous (lagu Rush). Untuk lagu 2003, lihat Entre nous (lagu Chimène Badi). Entre NousPoster film Prancis untuk Entre NousSutradaraDiane KurysProduserAriel ZeitounDitulis olehOlivier Cohen (buku)Diane Kurys (buku)Alain Le HenryPemeranMiou-MiouIsabelle HuppertGuy MarchandPenata musikLuis Enríquez BacalovSinematograferBernard LuticPenyuntingJoële Van EffenterreDistributorGaumontTanggal rilis 6 April 1983 (1983-04-06) …

Coordinate: 55°00′N 64°00′W / 55°N 64°W55; -64 Il territorio della regione Nunavik Il territorio denominato Nunavik è collocato nel terzo settentrionale della provincia del Québec, in Canada. Copre una porzione di terreno vasta 443.684,71 km² situata a nord del 55º parallelo, ed è la patria degli Inuit del Québec. Gran parte degli abitanti della Regione (erano 11.627 al Censimento canadese del 2006 dei quali il 90% sono Inuit[1]) vive nei quattordici ce…

2009 single by Arashi Ashita no Kioku redirects here. For the 2006 movie starring Ken Watanabe, see Memories of Tomorrow. Ashita no Kioku/Crazy Moon (Kimi wa Muteki)Single by Arashifrom the album All the Best! 1999–2009 ReleasedMay 27, 2009 (2009-05-27)Recorded2009GenrePopLabelJ StormSongwriter(s)Ashita no Kioku: Yoshitaka TairaCrazy Moon (Kimi wa Muteki): Soluna · Hyper SlipperArashi singles chronology Believe / Kumorinochi, Kaisei (2009) Ashita no Kioku/Crazy Moon (Kimi wa Mu…

45°55′17″N 59°58′13″W / 45.92138889°N 59.97027778°W / 45.92138889; -59.97027778 ميّز عن حصار لويسبورغ (1758). حصار لويسبورغ جزء من حرب الخلافة النمساوية التاريخ وسيط property غير متوفر. بداية 11 مايو 1745 نهاية 28 يونيو 1745 الموقع 45°55′17″N 59°58′13″W / 45.92138889°N 59.97027778°W / 45…

Letak San Antonio di Texas Untuk munisipalitas di Filipina, lihat San Antonio, Quezon. San Antonio merupakan nama kota di Amerika Serikat. Letaknya di bagian selatan. Tepatnya di negara bagian Texas. Pada tahun 2005, kota ini memiliki jumlah penduduk sebanyak 1.256.509 jiwa. Di daerah metropolitan, berjumlah 1.889.797 jiwa. Kota ini memiliki luas wilayah 1.067 km². Kota kembar Guadalajara, Meksiko Kaohsiung, Republik Tiongkok Kumamoto, Jepang Gwangju, Korea Selatan Las Palmas de Gran Canar…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. 2MASX J00482185-2507365Pasangan galaksi sebagaimana difoto Teleskop Luar Angkasa HubbleData pengamatan (J2000 epos)Rasi bintangPemahatAsensio rekta 00j 48m 21.859d [1]Deklinasi -25° 07′ 36.53″[1]Pergesera…

Universitas Yordaniaالجامعة الأردنيةMotoTahun KeunggulanJenisUniversitas negeriDidirikan1962; 62 tahun lalu (1962)Dana abadi4,800,000 JOD ($6.77 million USD) (2015)[1]KetuaAdnan Badran[2]PresidenAbdul Karim Al-Qudah[3]Staf akademik1485 (2019/2020)[4]Staf administrasi2415 (2019/2020)[5]Jumlah mahasiswa46951 (2020/2021)[6]Sarjana40142 (2020/2021)[7]Magister6765 (2020/2021)[8]LokasiAmman, YordaniaKampusperkotaan12 k…

Adrian Jopie Paruntu Anggota Dewan Perwakilan RakyatPetahanaMulai menjabat 1 November 2019Daerah pemilihanSulawesi Utara Informasi pribadiLahir10 Maret 1994 (umur 30)Jakarta, IndonesiaKebangsaanIndonesiaPartai politikGolkarSuami/istriHanna Enah Supit (m. 2020)[1]Anak1Orang tuaChristiany Eugenia Paruntu (ibu)PekerjaanPolitikusSunting kotak info • L • B Adrian Jopie Paruntu (lahir 10 Maret 1994) adalah seorang politikus Indonesia. Saat …

Orang VietCewek Viet memakai gaun áo dài dengan topi nón láJumlah populasi±89 jutaDaerah dengan populasi signifikan Vietnam82.085.826 (2019)[1] Amerika Serikat2.067.527 (2016)[2] Kamboja400.000-1.000.000[3][4][5] Jepang420.415 (2020)[6] Prancis~400.000[7][8] Taiwan320.000 (2019)[9] Australia>300.000 (2018)[10][11] Kanada240.514[12] Korea Selatan224.…
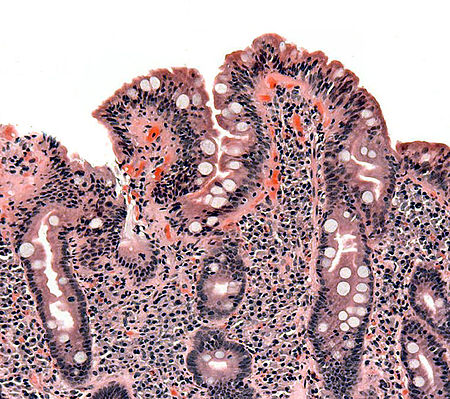
سوء الامتصاص للعناصر الغذائية سوء الامتصاص معلومات عامة الاختصاص طب الجهاز الهضمي من أنواع أمراض الجهاز الهضمي الأسباب الأسباب داء بطني؛ التهاب المعدة الضموري؛ داء كرون؛ داء ويبل؛ عدم تحمل اللاكتوز؛ فرط النمو البكتيري؛ أضطرابات وراثية؛ أمراض الجهاز الهضمي المزمنة الأ…

يعتبر زيت النخيل -المنتج من نخيل الزيت- مصدر دخل أساسيًا للعديد من المزارعين في جنوب شرق آسيا ووسط وغرب أفريقيا وأمريكا الوسطى. يُستخدم محليًا كزيت للطبخ ويُصدّر للاستخدام في الكثير من منتجات الأغذية والعناية الشخصية ويُحول إلى وقود حيوي ينتج ما يصل إلى 10 أضعاف كمية الزيت لك…

90 mm Gun Motor Carriage M36 Jenis Penghancur tank Negara asal Amerika Serikat Sejarah produksi Perancang U.S. Army Ordnance Department Tahun 1943 Produsen General Motors Massey-Harris American Locomotive Company Montreal Locomotive Works Biaya produksi $51.290 (M36) Diproduksi April–Agustus 1944 Oktober–Desember 1944 Mei 1945 Jumlah produksi 2.324 (semua model) Varian Lihat Varian Spesifikasi (90 mm Gun Motor Carriage M36[1]) Berat 63.000 lb (28,6 metric tons) Panjang…

Pajtim Kasami Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Pajtim KasamiTanggal lahir 2 Juni 1992 (umur 31)Tempat lahir Winterthur, Swiss[1]Tinggi 1,87 m (6 ft 1+1⁄2 in)[1]Posisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini OlympiacosNomor 11Karier junior2003–2006 Winterthur2006–2009 Grasshopper2008 → Liverpool (pinjaman)2009 LazioKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2010 Bellinzona 13 (4)2010–2011 Palermo 14 (0)2011–2014 Fulham 38 (3)2012–2013 → Luzern (p…

Rewriting system and type of formal grammar This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: L-system – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2013…


