Joseph Galloway
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
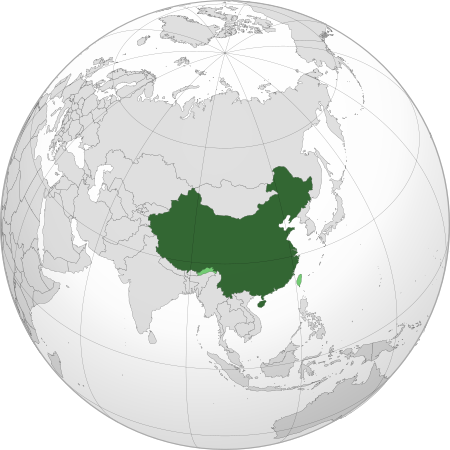
Country in East Asia People's Republic of China redirects here. For the present-day Republic of China, see Taiwan. PRC redirects here. For other uses, see PRC (disambiguation) and China (disambiguation). People's Republic of China中华人民共和国 (Chinese)Zhōnghuá Rénmín Gònghéguó (pinyin) Flag Emblem Anthem: 义勇军进行曲Yìyǒngjūn JìnxíngqǔMarch of the Volunteers Location of the People's Republic of China Territory claimed but not con…

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Zeppelin (disambigua). L'LZ 127 Graf Zeppelin, lo Zeppelin più famoso Lo Zeppelin è un tipo di dirigibile rigido sviluppato in Germania ai primi del Novecento. Prende il nome dal suo ideatore, il conte Ferdinand von Zeppelin e dalla ditta costruttrice fondata nel 1908 Luftschiffbau Zeppelin GmbH (Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung, in sigla GmbH, società a responsabilità limitata), che completò la costruzione di 119 dirigibili…

BelizeBelize (Latin) Bendera Lambang Semboyan: Sub Umbra Floreo(Latin: Di Bawah Bayangan Teduh Aku Berkembang)Lagu kebangsaan: Land of the Free (Indonesia: Tanah Merdeka) Lagu kerajaan: God Save the King (Indonesia: Tuhan Menjaga sang Raja) Perlihatkan BumiPerlihatkan peta BenderaIbu kotaBelmopan17°15′N 88°46′W / 17.250°N 88.767°W / 17.250; -88.767Kota terbesarBelize City 17°29′N 88°11′W / 17.483°N 88.183°W / 17.483…

2 Tesalonika 2Potongan surat 1 Tesalonika 5:8-10 pada Papirus 30, yang ditulis sekitar abad ke-3 M.KitabSurat 2 TesalonikaKategoriSurat-surat PaulusBagian Alkitab KristenPerjanjian BaruUrutan dalamKitab Kristen14← pasal 1 pasal 3 → 2 Tesalonika 2 (disingkat 2Tes 2) adalah bagian dari Surat Paulus yang Kedua kepada Jemaat di Tesalonika dalam Perjanjian Baru di Alkitab Kristen.[1][2] Digubah oleh rasul Paulus, Silwanus dan Timotius.[3] Teks Surat aslinya ditulis…

Tulang belakangKoluma verterba manusia dan bagian bagiannyaKoluma vertebra kambingRincianPengidentifikasiBahasa Latincolumna vertebralisDaftar istilah anatomi[sunting di Wikidata] Koluma vertebra, Turus ruas tulang belakang atau turus vertebra, juga dikenali sebagai tulang belakang atau spina, adalah bagian inti dari kerangka aksial pada hewan vertebrata. Tulng belakakng menjadi karakteristik ciri dari endoskeleton yang mana sebuah notokorda (sebuah tabung glikoprotein fleksibel yang tertutu…

Vahid Hashemian Vahid Hashemian KorbekandiInformasi pribadiNama lengkap Vahid Hashemian KorbekandiTanggal lahir 21 Juli 1976 (umur 47)Tempat lahir Tehran, IranTinggi 1,82 m (6 ft 0 in)Posisi bermain PenyerangKarier junior1994–1996 Fath TehranKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1996–1997 Fath Tehran 25 (8)1997–1999 Pas 26 (9)1999–2001 Hamburger SV 12 (0)2001–2004 VfL Bochum 87 (34)2004–2005 Bayern Munich 9 (0)2005–2008 Hannover 96 80 (9)2008–2010 VfL Bochum 41 …
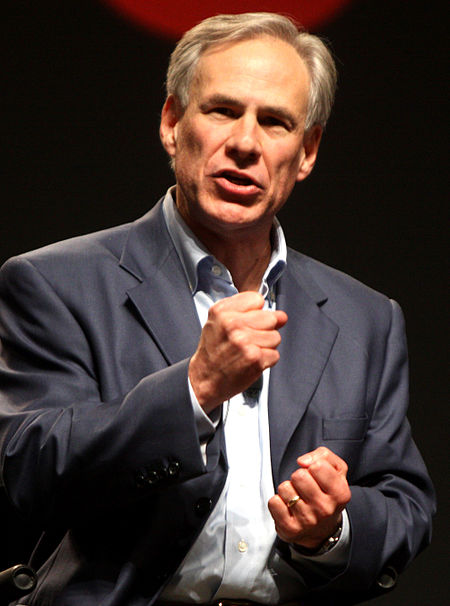

Voce principale: Texas. Governatore del Texas Greg Abbott 48º governatore del Texas Nome originaleGovernor of Texas Stato Stati Uniti Stato federato Texas In caricaGreg Abbott (R) da20 gennaio 2015 Istituito19 febbraio 1846 Durata mandato4 anni, nessun limite di durata SedePalazzo del Governatore del Texas, Downtown Austin - Austin Indirizzo1010 Colorado St. Sito webwww.governor.state.tx.us/ Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Stendardo del Governatore Il Governatore del Texas (…

Yesaya 49Gulungan Besar Kitab Yesaya, yang memuat lengkap seluruh Kitab Yesaya, dibuat pada abad ke-2 SM, diketemukan di gua 1, Qumran, pada tahun 1947.KitabKitab YesayaKategoriNevi'imBagian Alkitab KristenPerjanjian LamaUrutan dalamKitab Kristen23← pasal 48 pasal 50 → Yesaya 49 (disingkat Yes 49) adalah bagian dari Kitab Yesaya dalam Alkitab Ibrani dan Perjanjian Lama di Alkitab Kristen.[1] Memuat Firman Allah yang disampaikan oleh nabi Yesaya bin Amos terutama berkenaan ten…

Bangkok Love StorySutradaraPoj ArnonDitulis olehPoj ArnonPemeranRattaballung TohssawatChaiwat TongsangPenata musikGiantwaveSinematograferTiwa MoeithaisongPenyuntingTiwa MoeithaisongDistributorSahamongkol Film InternationalTanggal rilis13 September 2007Negara ThailandBahasaThai Bangkok Love Story (Thai: เพื่อน ... กู รัก มึง ว่ะ atau pêuan ... goo rak wa meung, harfiah Teman ... Aku cinta padamu) adalah sebuah film Thailand 2007 yang ditulis dan disutradar…

Team LiquidOlahragaApex LegendsArtifactClash RoyaleFortniteCounter-Strike: Global OffensiveDota 2HearthstoneHeroes of the StormLeague of LegendsPUBGStarCraft IIStreet FighterSuper Smash Bros.Tom Clancy's Rainbow Six SiegeTekken 7LokasiUtrecht, BelandaAmerika Serikat (Tim LoL, Tim CS:GO)Didirikan2000; 24 tahun lalu (2000)ManajerVictor Goossens (co-CEO)Steve Arhancet (co-CEO)SponsorAlienwareHondaHyperXJersey Mike's SubsMarvel EntertainmentMonster EnergySecretlabSAP SETwitchEarningsUS$33.70 mi…
Questa voce o sezione sugli argomenti tecnologia e economia ha un'ottica geograficamente limitata. Contribuisci ad ampliarla o proponi le modifiche in discussione. Se la voce è approfondita, valuta se sia preferibile renderla una voce secondaria, dipendente da una più generale. Segui i suggerimenti dei progetti di riferimento 1, 2. Questa voce o sezione sugli argomenti processi industriali e economia non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare q…

Mirza Teletović (lahir di Mostar, 18 September, 1985) adalah seorang pemain bola basket profesional berkebangsaan Bosnia & Herzegovina yang terakhir kali membela Milwaukee Bucks di kompetisi bolabasket National Basketball Association (NBA). Ia juga mewakili dan merupakan seorang kapten bola basket team nasional Bosnia Herzegovina. Bertinggi badan 206 cm, Mirza melakukan debut NBA pada 5 November 2012, berposisi sebagai Power forward dan Small forward.[1] Mirza TeletovićNo. 33,35,35…

Kanika MannMann pada Januari 2023Lahir7 Oktober 1993 (umur 30)[1]Panipat, Haryana, IndiaAlmamaterPanjab University, ChandigarhPekerjaanAktrismodelTahun aktif2015–sekarangDikenal atasGuddan Tumse Na Ho PayegaKhatron Ke Khiladi 12 Kanika Mann (lahir 7 Oktober 1993) adalah seorang aktris televisi India yang dikenal karena perannya sebagai Guddan Jindal dan Guddan Birla di Guddan Tumse Na Ho Payega. Dia juga menjadi finalis dalam Khatron Ke Khiladi 12. Kehidupan awal Mann lahir p…

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Stasiun Kuala Bingai, Stasiun Kuala Begumit, Stasiun Kuala Tanjung, atau Stasiun Kualanamu. Stasiun Kuala Kuala Bekas Stasiun Kuala, yang kini menjadi rumah warga.LokasiPekan Kuala, Kuala, Langkat, Sumatera UtaraIndonesiaKoordinat3°31′36″N 98°23′24″E / 3.526665°N 98.390029°E / 3.526665; 98.390029Koordinat: 3°31′36″N 98°23′24″E / 3.526665°N 98.390029°E / 3.526665; 98.390029Operator Kereta Api Indone…

Tai Ji Dian beralih ke halaman ini. Untuk Hall in the Forbidden City, lihat Hall of the Supreme Principle. Artikel ini kekurangan informasi tentang krisis chip global. Tolong kembangkan artikel untuk meliputi informasi tersebut. Rincian lebih lanjut mungkin tersedia di halaman pembicaraan. (April 2021) Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company LimitedNama dagangTSMCNama asli臺灣積體電路製造股份有限公司JenisPublikKode emitenTWSE: 2330NYSE: TSMISINUS8740391003IndustriSemikonduktorDi…

Kolkata Municipal Corporation in West Bengal, IndiaWard No. 1Kolkata Municipal CorporationInteractive Map Outlining Ward No. 1Ward No. 1Location in KolkataCoordinates: 22°37′04″N 88°22′14″E / 22.617889°N 88.370556°E / 22.617889; 88.370556Country IndiaStateWest BengalCityKolkataNeighbourhood coveredCossiporeReservationOpenParliamentary constituencyKolkata UttarAssembly constituencyKashipur-BelgachhiaBurough1Elevation36 ft (11 m)Population (2…

ToubkalTubkal / ⵜⵓⴱⴽⴰⵍ توبقال / توبكالTizi'n'Toubkal dari puncak bukitTitik tertinggiKetinggian4.165 m (13.665 ft)[1]Puncak3.755 m (12.320 ft)[1]Urutan 36GeografiToubkalMarokoPegununganPegunungan AtlasPeta topografiToubkal Massif Map and Guide [2] Jbel Toubkal atau Tubkal (Berber: ⵜⵓⴱⴽⴰⵍ, Tubkal, atau ⵜⵓⴱⵇⴰⵍ, Tubqal; Arab: توبقال) adalah puncak gunung di barat daya Maroko, 63 km sebelah selatan kota…

Roman Catholic archdiocese in the Philippines This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Nueva Segovia – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Archdiocese of Nueva SegoviaArchidioecesis Novae SegobiaeArk…

TumlongtownTumlongLokasi di Sikkim, IndiaTampilkan peta SikkimTumlongTumlong (India)Tampilkan peta IndiaKoordinat: 27°25′N 88°35′E / 27.42°N 88.58°E / 27.42; 88.58Koordinat: 27°25′N 88°35′E / 27.42°N 88.58°E / 27.42; 88.58Negara IndiaNegara bagianSikkimDistrikDistrik Sikkim UtaraKetinggian1.473 m (4,833 ft)Bahasa • ResmiNepali, Bhutia, Lepcha, Limbu, Newari, Rai, Gurung, Mangar, Sherpa, Tamang and SunwarZo…
Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Sayram. Sayram bahasa Kazakh: СайрамNegara KazakhstanProvinsiKazakhstan SelatanPemerintahan • Akim (wali kota)Husan Muzafarhanovich AkhmadhanovLuas • Kota10 km2 (4,2 sq mi)Ketinggian600 m (1.970 ft)Populasi (2009) • Kota32,757 • MetropolitanShymkentZona waktuUTC+6 (ALMT)Kode pos160812Kode area telepon+7 72531IklimCsa Sayram (bahasa Kazakh: Сайрам, Sayram, سايرام…


