|
List of trans-Neptunian objects
This is a list of trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs), which are minor planets in the Solar System that orbit the Sun at a greater distance on average than Neptune, that is, their orbit has a semi-major axis greater than 30.1 astronomical units (AU). The Kuiper belt, scattered disk, and Oort cloud are three conventional divisions of this volume of space.[1][nb 1] As of April 2022[update], the catalog of minor planets contains 901 numbered TNOs. In addition, there are more than 3,000 unnumbered TNOs, which have been observed since 1993.[3][4][5] This list consists of all types of TNO subgroups: classical Kuiper belt objects, also known as "cubewanos", the resonant trans-Neptunian objects with their main and higher-order resonant subgroups, the scattered disc objects (SDOs), and the extreme trans-Neptunian objects including the ESDOs, EDDOs, and sednoids, which have a semi-major axis of at least 150 AU and a perihelion (closest approach to the Sun) greater than that of Neptune.[6] The list also contains several centaurs, if the object's orbit has a sufficiently large semi-major axis (a). Centaurs have unstable orbits in which the perihelion (q) is well inside of Neptune's orbit but the farthest point (aphelion, Q) is very distant. The first TNO to be discovered was Pluto in 1930. It became the namesake of a larger group of resonant objects called plutinos (another such resonant subgroups are the twotinos, threetinos, fourtinos, fivetinos, sixtinos, seventinos, eightinos, ninetinos, tentinos, and eleventinos). It took more than 60 years to discover a second TNO, Albion (provisionally known as 1992 QB1), in 1992. The largest known trans-Neptunian objects are Pluto and Eris, followed by Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Quaoar, Sedna, and Orcus, all of them being officially recognized as dwarf planets by the IAU except for Gonggong, Sedna, and Orcus. There are also many possible dwarf planets, such as Salacia, (307261) 2002 MS4, Varda, Ixion, and Varuna. Most TNOs have low albedos typically around 0.09. Their color varies from blue-grey to very red (classes BB, BR, IR and RR). The following list also gives an object's full designation, mean-diameter (D), and discovery circumstances (date, discoverer and discovery site), as well as its orbital inclination (i) and eccentricity (e). ListThis list includes all numbered trans-Neptunian objects with a semi-major axis greater than 30.1 astronomical units (AU), Neptune's average orbital distance from the Sun. The data is sourced from MPC's "List of Trans Neptunian Objects" and "List Of Centaurs and Scattered-Disk Objects", in addition to MPC's "List of Neptune Trojans", completed with remarks and information from Johnston's Archive (diameter, class, binary, albedo, spectral taxonomy and B–R color index).[3][4][5]
Unnumbered TNOsThere are more than 3,000 unnumbered trans-Neptunian objects, defined here as minor planets with a semi-major axis larger than 30.1 AU (Neptune's average orbital distance from the Sun). The data is sourced from MPC's "List of Trans Neptunian Objects" and "List Of Centaurs and Scattered-Disk Objects", completed with information from Johnston's Archive (diameter, class, binary status, etc.).[3][4][5] For the list of numbered TNOs, see § List. Trans-Neptunian satellitesA growing number of TNOs are revealed to be binary systems with a minor-planet moon orbiting its primary. There are also several multiple systems with more than one satellite. Diagram: orbital classes
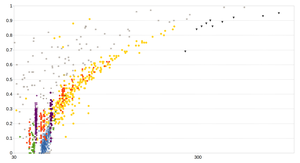
4140 TNOs (a > 30.1 AU) from Johnston's archive grouped by orbital subclasses.[5] Trans-Neptunian objects colorized by their orbital subclass and plotted in the orbital parameter space (eccentricity and inclination versus semi-major axis). The plot for the entire region contains 1418 objects including plutinos (#185), twotinos (#36), other resonant objects (#124), cubewanos (#420), inner (#40) and outer classical objects (#6), SDOs (#289), sednoids (#11), centaurs (#101) and other TNOs (#206).[5] Full region on a logarithmic scale from 30 to 1000 AU: inclination (left) and eccentricity (right) vs. a See also
Notes
References
External links
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||