Multnomah people
|
Read other articles:

Ar-Rabi'PermukimanAr-Rabi'Location in the Kingdom of Saudi ArabiaKoordinat: 24°38′N 46°43′E / 24.633°N 46.717°E / 24.633; 46.717Koordinat: 24°38′N 46°43′E / 24.633°N 46.717°E / 24.633; 46.717Negara Arab SaudiPemerintahan • Gubernur Pangeran RiyadhFaisal bin Bandar Al Saud • Wali kotaIbraheem Mohammed Al-SultanKetinggian612 m (2,008 ft)Zona waktuUTC+3 (AST) • Musim panas (DST…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. BIKO 3 Publikasi-GenreStalkerKarakteristik teknisPlatformWindows Format kode Daftar 30 Informasi tambahanSitus webillusion.jp… (Jepang) MobyGamesbiko-3 Portal permainan videoSunting di Wikidata • L • B • PWBantuan penggunaan te…

Часть серии статей о Холокосте Идеология и политика Расовая гигиена · Расовый антисемитизм · Нацистская расовая политика · Нюрнбергские расовые законы Шоа Лагеря смерти Белжец · Дахау · Майданек · Малый Тростенец · Маутхаузен · …

God Save the KingPublikasi versi awal dalam The Gentleman's Magazine, 15 Oktober 1745. Judul di halaman Daftar Isi adalah God save our lord the king: A new song set for two voices.Lagu kebangsaan Britania RayaAliasGod Save the Queen(ketika penguasa monarki adalah wanita)Penulis lirikHenry Carey, 1790KomponisTidak diketahuiPenggunaan1745Sampel audioGod Save the King (instrumental)berkasbantuan Sampel audioGod Save the Kingberkasbantuan God Save the King (Tuhan Jagalah sang Raja) atau secara…

Keseluruhan atau sebagian dari artikel ini membutuhkan perhatian dari ahli subyek terkait. Jika Anda adalah ahli yang dapat membantu, silakan membantu perbaiki kualitas artikel ini. Artikel atau sebagian dari artikel ini mungkin diterjemahkan dari Antropologi biologis di en.wikipedia.org. Isinya masih belum akurat, karena bagian yang diterjemahkan masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Jika Anda menguasai bahasa aslinya, harap pertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menyempurnakan ter…

Star Wars Episode III:Revenge of the SithSutradaraGeorge LucasProduserRick McCallumDitulis olehGeorge LucasPemeranEwan McGregorHayden ChristensenNatalie PortmanIan McDiarmidFrank OzSamuel L. JacksonChristopher LeePenata musikJohn WilliamsSinematograferDavid TattersallPenyuntingRoger BartonBen BurttDistributor20th Century FoxLucasfilmTanggal rilis19 Mei 2005Durasi146 menitNegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaInggrisAnggaran$113 jutaPendapatankotorWorldwide:$848,998,815PrekuelStar Wars Episode II: Att…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Chiffre (homonymie). Les dix chiffres des chiffres arabes, par ordre de valeur. Un chiffre est un signe d'écriture utilisé seul ou en combinaison pour représenter des nombres entiers. Dans un système de numération positionnel comme le système décimal, un petit nombre de chiffres suffit pour exprimer n'importe quelle valeur. Le nombre de chiffres du système est la base. Le système décimal, le plus courant des systèmes de numération, comporte dix chiff…

Study of the role of time in communication This article's tone or style may not reflect the encyclopedic tone used on Wikipedia. See Wikipedia's guide to writing better articles for suggestions. (October 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Chronemics – news ·…

2,392 1 13 1 1 71 1 564 121 This is Muboshgu's talk page, where you can send him messages and comments. Put new text under old text. Click here to start a new topic. New to Wikipedia? Welcome! Learn to edit; get help. Assume good faith Be polite and avoid personal attacks Be welcoming to newcomers Seek dispute resolution if needed Archives: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39…

Statue by Henry Kirke Brown Statue of Richard StocktonYear1888 (1888)MediumMarble sculptureSubjectRichard StocktonLocationWashington, D.C., United States Richard Stockton is a marble sculpture depicting the American lawyer, jurist, legislator of the same name by Henry Kirke Brown (completed by Henry Kirke Bush-Brown), installed in the United States Capitol's crypt, in Washington, D.C., as part of the National Statuary Hall Collection. The statue was donated by the U.S. state of New Jersey i…

ديفيد هيلبرت (بالألمانية: David Hilbert) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 23 يناير 1862 [1][2][3][4][5][6] زنامينسك، وكالينينغراد الوفاة 14 فبراير 1943 (81 سنة) [7][1][2][3][4][6][8] غوتينغن[9][8] الإقامة ألمانيا مواطنة مملكة …

American politician Senator Mead redirects here. For other uses, see Senator Mead (disambiguation). James Michael MeadMead in 1937United States Senatorfrom New YorkIn officeDecember 3, 1938 – January 3, 1947Preceded byRoyal S. CopelandSucceeded byIrving M. IvesChair of the Federal Trade CommissionIn officeMay 24, 1950 – March 31, 1953Preceded byLowell MasonSucceeded byEdward F. HowreyMember of the Federal Trade CommissionIn officeNovember 15, 1949 – September 25,…

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Птиц�…

Questa voce o sezione deve essere rivista e aggiornata appena possibile. Sembra infatti che questa voce contenga informazioni superate e/o obsolete. Se puoi, contribuisci ad aggiornarla. Voce principale: Virtus Entella. Virtus EntellaStagione 2021-2022Sport calcio Squadra Entella Allenatore Gennaro Volpe All. in seconda Massimiliano Bongiorni Presidente Antonio Gozzi Serie C4º posto Playoff Serie COttavi di finale Coppa Italia Serie CSecondo turno Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Magrassi (37)…

Line of PowerPC-based server computers by Apple Computer, Inc This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Apple Network Server – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Apple Network ServerDeveloperApple ComputerTypeServerRelease dateFebr…

Election in Kansas Main article: 1920 United States presidential election 1920 United States presidential election in Kansas ← 1916 November 2, 1920 1924 → Nominee Warren G. Harding James M. Cox Party Republican Democratic Home state Ohio Ohio Running mate Calvin Coolidge Franklin D. Roosevelt Electoral vote 10 0 Popular vote 369,268 185,464 Percentage 64.75% 32.52% County Results Harding 50-60% 60-70% 70-80% …

Northern Irish association football player For people with a similar name, see Steve Davis (disambiguation). Steven DavisMBE Davis with Northern Ireland in 2019Personal informationFull name Steven Davis[1]Date of birth (1985-01-01) 1 January 1985 (age 39)Place of birth Ballymena, Northern IrelandHeight 5 ft 8 in (1.73 m)[2]Position(s) MidfielderYouth career St Andrews Boys Club2002–2004 Aston VillaSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2004–2007 Aston Villa 91…
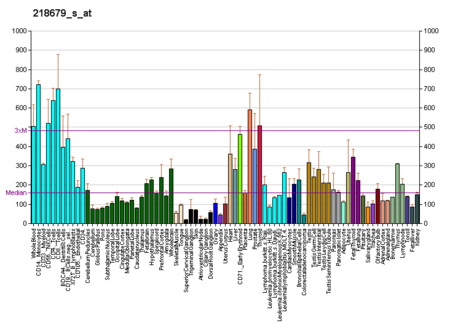
VPS28 المعرفات الأسماء المستعارة VPS28, ESCRT-I subunit, subunit of ESCRT-I معرفات خارجية الوراثة المندلية البشرية عبر الإنترنت 611952 MGI: MGI:1914164 HomoloGene: 69205 GeneCards: 51160 علم الوجود الجيني الوظيفة الجزيئية • GO:0032403 protein-containing complex binding• ubiquitin binding• GO:0001948، GO:0016582 ربط بروتيني المكونات الخلوية • سيتوبلا…

Town in Brandenburg, GermanyKönigs Wusterhausen TownKönigs Wusterhausen Castle Coat of armsLocation of Königs Wusterhausen within Dahme-Spreewald district Königs Wusterhausen Show map of GermanyKönigs Wusterhausen Show map of BrandenburgCoordinates: 52°17′30″N 13°37′30″E / 52.29167°N 13.62500°E / 52.29167; 13.62500CountryGermanyStateBrandenburgDistrictDahme-Spreewald Subdivisions7 OrtsteileGovernment • Mayor (2021–29) Michaela Wiezorek&#…

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁地�…



