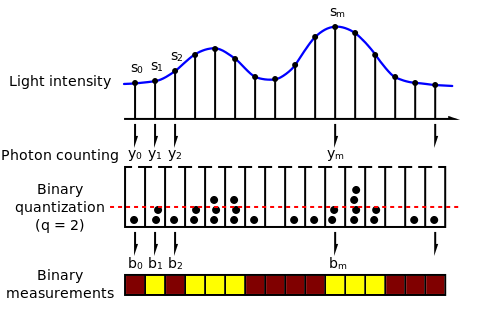
Oversampled binary image sensor
|
Read other articles:

Caravan PicturesJenisAnak perusahaanIndustriHiburanNasibDitutupPenerusSpyglass EntertainmentDidirikan17 November 1992; 31 tahun lalu (1992-11-17)PendiriRoger BirnbaumJoe RothDitutup1999; Galat: first parameter cannot be parsed as a date or time. (1999)KantorpusatSanta Monica, California, Amerika SerikatTokohkunciRoger Birnbaum (pimpinan, CEO)Jonathan Glickman (presiden)ProdukFilmKaryawan7 (1997)IndukThe Walt Disney StudiosCatatan kaki / referensi[1][2][3&#…

Sporting event delegationMalaysia at the1964 Summer OlympicsIOC codeMAS(MAL used at these Games)NOCOlympic Council of MalaysiaWebsitewww.olympic.org.my (in English)in TokyoCompetitors62 in 10 sportsFlag bearer Kuda Ditta[1]Medals Gold 0 Silver 0 Bronze 0 Total 0 Summer Olympics appearances (overview)195619601964196819721976198019841988199219962000200420082012201620202024Other related appearances North Borneo (1956) Malaysia competed at the 1964 Summer Olympics in Tokyo, Ja…

Spar extending forward from a sailing vessel's prow Bowsprit held down by a bobstay Bowsprit with forestays and bobstays The bowsprit of a sailing vessel is a spar extending forward from the vessel's prow. The bowsprit is typically held down by a bobstay that counteracts the forces from the forestays. The word bowsprit is thought to originate from the Middle Low German word bōchsprēt – bōch meaning bow and sprēt meaning pole.[1] It is sometimes used to hold up the figurehead. Refer…

Drug formerly in development MardepodectClinical dataOther namesPDF-2545920ATC codeNoneLegal statusLegal status Investigational Identifiers IUPAC name 2-(4-(1-Methyl-4-pyridin-4-yl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenoxymethyl)quinoline CAS Number898562-94-2 NPubChem CID11581936DrugBankDB08387 NChemSpider9756702 NUNIIR9Y8EY0G42KEGGD11171ChEMBLChEMBL1642569 NChemical and physical dataFormulaC25H20N4OMolar mass392.462 g·mol−13D model (JSmol)Interactive image SMILES n3c1ccccc1ccc3COc5cc…

Jembatan Phu MyKoordinat10°44′42″N 106°44′40″E / 10.744992°N 106.744456°E / 10.744992; 106.744456Moda transportasiKendaraan bermotor, sepeda, pejalan kakiMelintasiSungai SaigonLokalHo Chi Minh City, VietnamNama resmiCầu Phú MỹPengelolaPhu My Bridge Corporation (PMC)KarakteristikDesainjembatan kabel-tetapBahan bakuBetonPanjang total705 meter (2.313 ft)Lebar27 meter (89 ft)Tinggi140 meter (460 ft)Bentang terpanjang380 meter (1.250 ft)Jum…

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento attori tedeschi non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Questa voce sull'argomento attori tedeschi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. August Diehl al Festival di…

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Птиц�…

Species of lichen Lecidea lapicida Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Fungi Division: Ascomycota Class: Lecanoromycetes Order: Lecideales Family: Lecideaceae Genus: Lecidea Species: L. lapicida Binomial name Lecidea lapicida(Ach.) Ach. (1803) Synonyms[1] List Lecidea austrogeorgica Müll.Arg. Lecidea confluens var. ochromela Ach. Lecidea contenebricans Nyl. Lecidea contigua var. declinans (Nyl.) Boistel Lecidea contigua var. declinascens (Nyl.) Boistel Lecidea cont…
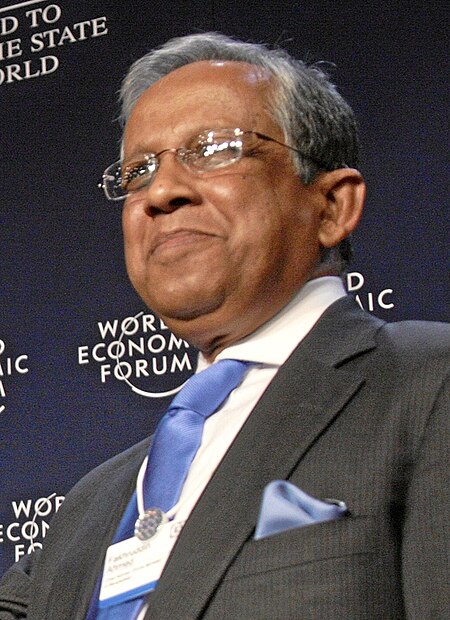

Fakhruddin Ahmed Fakhruddin Ahmed adalah seorang ekonom terkemuka Bangladesh. Ia pernah menjabat sebagai gubernur Bank Bangladesh. Pada 12 Januari 2007 ia diangkat menjadi kepala pemerintahan sementara di tengah-tengah kekacauan yang melanda politik negara itu. Profil Dr. Fakhruddin Ahmed dilahirkan di Munshiganj. Ia menjadi lulusan terbaik dari kelasnya untuk memperoleh gelar BA (Hons) dan MA dari Departmen Ekonomi di Universitas Dhaka pada 1960 dan 1961. Ia memperoleh gelar master lainnya dala…

Major League Baseball team season 1994 Chicago CubsLeagueNational LeagueDivisionCentralBallparkWrigley FieldCityChicagoOwnersTribune CompanyGeneral managersLarry HimesManagersTom TrebelhornTelevisionWGN-TV/Superstation WGN(Harry Caray, Steve Stone, Thom Brennaman, Wayne Larrivee)RadioWGN(Thom Brennaman, Ron Santo, Harry Caray)StatsESPN.comBB-reference ← 1993 Seasons 1995 → A ticket for the Cubs' 1994 Opening Day game against the New York Mets. The 1994 Chicago Cubs sea…

Californian bandit Tiburcio VásquezBorn(1835-04-11)April 11, 1835Monterey, Alta California, First Mexican Republic(today California, U.S.)DiedMarch 19, 1875(1875-03-19) (aged 39)San Jose, California, U.S.Criminal statusExecutedConviction(s)MurderCriminal penaltyDeath by hanging Tiburcio Vásquez (April 11, 1835 – March 19, 1875) was a Californio bandido who was active in California from 1854 to 1874. The Vasquez Rocks, 40 miles (64 km) north of Los Angeles, were one of his many hide…

American economist (born 1944) James HeckmanBornJames Joseph Heckman (1944-04-19) April 19, 1944 (age 80)Chicago, Illinois, USAcademic careerInstitutionUniversity of ChicagoUniversity of Southern CaliforniaColumbia UniversityFieldMicroeconomicsSchool ortraditionChicago School of EconomicsAlma materColorado College (BA)Princeton University (PhD)DoctoraladvisorHarry H. KelejianStanley Warren BlackDoctoralstudentsCarolyn HeinrichGeorge BorjasPetra ToddStephen CameronMark RosenzweigRu…

L'ultimo dei TemplariBehmen (Nicolas Cage) e Felson (Ron Perlman) in una scena del filmTitolo originaleSeason of the Witch Lingua originaleinglese Paese di produzioneStati Uniti d'America Anno2011 Durata95 min Rapporto1,85:1 Genereorrore, avventura, epico, fantastico RegiaDominic Sena SceneggiaturaBragi F. Schut ProduttoreAlex Gartner, Charles Roven Produttore esecutivoAlan Glazer, Ryan Kavanaugh, Steve Alexander, Tom Karnowski, Tucker Tooley Casa di produzioneAtlas Entertainment, Re…

För filmerna, se Under falsk flagg. Del av en artikelserie om Desinformation ochfelaktig information Typer Alternativa fakta · Argumentationsfel · Deepfake · Ekokammare · Faktaresistens · Faktoid · Falsk anklagelse · Falsk flagg · Fejknyheter · Felslut · Filterbubbla · Förtal · Gaslighting · Politisk historierevisionism · Hoax · Klickbete · Konfabulation · Lurendrejeri · Lögn&…

1963 film by Francis Ford Coppola This article is about the 1963 film. For the remake, see Dementia 13 (2017 film). Dementia 13Theatrical release posterDirected byFrancis CoppolaWritten byFrancis CoppolaProduced byRoger CormanStarring William Campbell Luana Anders Bart Patton Mary Mitchell Patrick Magee Eithne Dunne CinematographyCharles HannawaltEdited byStuart O'Brien[1]Music byRonald SteinProductioncompaniesThe FilmgroupGarrick Ltd.[1]Distributed byAmerican International Pictu…

1976 studio album by the Gary Burton QuintetDreams So RealStudio album by the Gary Burton QuintetReleasedJune 1976[1]RecordedDecember 1975StudioStudio BauerLudwigsburg, W. GermanyGenreJazzLength38:31LabelECMECM 1072 STProducerManfred EicherGary Burton chronology Matchbook(1975) Dreams So Real(1976) Passengers(1977) Dreams So Real: Music of Carla Bley is an album by the Gary Burton Quintet, featuring compositions by Carla Bley, recorded in December 1975 and released on ECM the fol…

Railway line in India Pagidipalli–Guntur sectionRoute map of Guntur Division showingPagidipalli–Nallapadu sectionOverviewStatusOperationalOwnerIndian RailwaysLocaleTelangana Andhra PradeshTerminiGunturPagidipalliWebsitescr.indianrailways.gov.inServiceOperator(s)South Central Railway zoneHistoryOpened1930; 94 years ago (1930)TechnicalLine length238.49 km (148 mi)Track length130 km (81 mi)Number of tracks1 (doubling approved in year 2023)Track gauge5 …

提示:此条目页的主题不是中華人民共和國最高領導人。 中华人民共和国 中华人民共和国政府与政治系列条目 执政党 中国共产党 党章、党旗党徽 主要负责人、领导核心 领导集体、民主集中制 意识形态、组织 以习近平同志为核心的党中央 两个维护、两个确立 全国代表大会 (二十大) 中央委员会 (二十届) 总书记:习近平 中央政治局 常务委员会 中央书记处 中�…

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6] 得…

Railway route in India Bhopal–Nagpur sectionBhopal Junction an Important railway station at Bhopal–Nagpur sectionOverviewStatusOperationalOwnerIndian RailwaysTerminiBhopalNagpurServiceOperator(s)West Central Railway, Central RailwayDepot(s)ItarsiRolling stockWDM-2, WDM-3A, WDM-3D, WDS-6 and WDP-4 diesel locos. WAM-4, WAP-4, WAP-7 and WAG-5 electric locos.HistoryOpened1924TechnicalTrack length390 km (242 mi)Number of tracks2/3Track gauge5 ft 6 in (1,676 mm) broad…