|
Parvicursor
Parvicursor (meaning "small runner") is a genus of tiny maniraptoran dinosaur with long slender legs for fast running.[3] Discovery and namingThe holotype PIN no. 4487/25, mostly consisting of vertebrae, the pelvis and the right hindlimb, was discovered in 1992 and described in 1996.[4] It was discovered in Barun Goyot Formation of Khulsan, Mongolia, dated at approximately 72 million years old.[1] DescriptionAt only about 39 centimetres (15 in; 1.28 ft) from snout to end of tail, and 162 g (5.7 oz) in weight, it was initially seen as one of the smallest non-avian dinosaurs known from an adult specimen.[5] However, in 2022 its holotype was concluded to represent a juvenile individual.[1] 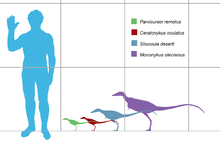 Like other members of the family Alvarezsauridae, the forelimbs of Parvicursor were short and stubby, with hands all but completely reduced to a single large claw, possibly useful for opening tough termite mounds or other types of digging. It is unlikely that the claw could have served much for defense, as it was short and not adapted for flexible movements — it is more likely it would do as the animal's name implies: cursor means runner. Close relatives include Shuvuuia and Mononykus, and together with these it is classified in the alvarezsaurid subfamily Parvicursorinae. TaxonomyThere may be a second, yet-unnamed, species of Parvicursor. Two specimens of tiny alvarezsaurids were described by Suzuki et al. in 2002. These authors considered the specimens to be juvenile Shuvuuia, which lived in the same formation.[6] However, a study by Nick Longrich and Phil Currie in 2009 suggested that several characters of the skeleton, including fused wrist and pelvic bones, indicated that these specimens were in fact adults of a tiny alvarezsaurid species. A phylogenetic analysis found that they grouped together with Parvicursor, and the authors provisionally referred them to Parvicursor sp. pending further study.[7] It has been suggested that Linhenykus and Ceratonykus may be junior synonyms of Parvicursor.[2][1] PhylogenyParvicursor in a cladogram after Fowler et al. (2020):[8] References
Information related to Parvicursor |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||