Principle of minimum energy
|
Read other articles:

Ruud Brood Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Ruud BroodTanggal lahir 19 Oktober 1962 (umur 61)Tempat lahir Gorinchem, BelandaPosisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini RKC Waalwijk (Manajer)Karier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1983–1985 Feyenoord Rotterdam ? (?)1985–1987 RKC Waalwijk ? (?)1987–1989 FC Den Bosch ? (?)1989–1990 Willem II Tilburg ? (?)1990–1998 NAC Breda ? (?)Kepelatihan1997–2004 NAC Breda (pelatih junior)2004–2006 Helmond Sport2006–2007 Heracles Almelo2008…

Brazilian military unit who fought with the Allies in the Mediterranean Theatre of WWII Brazilian Expeditionary ForceForça Expedicionária BrasileiraBrazilian Expeditionary Force shoulder sleeve insignia (Army component) with a smoking snakeActive1942–1945Country BrazilAllegianceUnited NationsBranchBrazilian ArmyBrazilian Air ForceTypeExpeditionary ForceRoleAerial warfareCombined armsExpeditionary warfareSize25,900Engagements World War II Italian campaign Gothic Line offensive Battle of Monte…

Cet article est une ébauche concernant le chemin de fer et le Japon. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. La traduction de cet article ou de cette section doit être revue (octobre 2023). Le contenu est difficilement compréhensible vu les erreurs de traduction, qui sont peut-être dues à l'utilisation d'un logiciel de trad…

Private, historically Black women's college in Atlanta, Georgia, US Spelman CollegeFormer namesAtlanta Baptist Female Seminary (1881–1884) Spelman Baptist Seminary (1884–1924)MottoOur Whole School for ChristTypePrivate historically Black[1] women's liberal arts collegeEstablishedApril 11, 1881; 142 years ago (1881-04-11)[2][3]Academic affiliationsACSSpace-grantEndowment$459.5 million (2022)[4]Budget$133.8 million (2023)[5]PresidentHel…

Об экономическом термине см. Первородный грех (экономика). ХристианствоБиблия Ветхий Завет Новый Завет Евангелие Десять заповедей Нагорная проповедь Апокрифы Бог, Троица Бог Отец Иисус Христос Святой Дух История христианства Апостолы Хронология христианства Ранне…

The Michigan State University Vietnam Advisory Group (commonly known as the Michigan State University Group and abbreviated MSUG) was a program of technical assistance provided to the government of South Vietnam as an effort in state-building by the US Department of State.[1] From 1955 to 1962, under contract to the International Cooperation Administration in Washington and the Vietnamese government in Saigon, faculty and staff from Michigan State University consulted for agencies of the…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Saint-Maurice. Saint-Maurice-l'Exil Hôtel de ville de Saint-Maurice-l'Exil. Administration Pays France Région Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Département Isère Arrondissement Vienne Intercommunalité Communauté de communes Entre Bièvre et Rhône(siège) Maire Mandat Philippe Genty 2020-2026 Code postal 38550 Code commune 38425 Démographie Gentilé Samauritain, Samauritaine Populationmunicipale 6 555 hab. (2021 ) Densité 511 hab./km2 Géographie Coor…

Kepolisian Daerah JambiSingkatanPolda JambiYurisdiksi hukumProvinsi JambiMarkas besarJalan Jenderal Sudirman no. 45, Tambak Sari, Jambi Selatan, Kota JambiPejabat eksekutifIrjen Pol. Rusdi Hartono, KepalaBrigjen Pol.Edi Mardianto, Wakil KepalaSitus webjambi.polri.go.id Kepolisian Daerah Jambi atau Polda Jambi (dulu bernama Komando Daerah Kepolisian (Komdak atau Kodak) V/Jambi) adalah pelaksana tugas Kepolisian RI di wilayah Provinsi Jambi. Polda Jambi tergolong polda tipe A karena itu dipimpin o…

Political party in Poland Yes! For PolandLocal Governments for Poland Tak! Dla PolskiSamorządy dla PolskiAbbreviationT!DPLLeaderJacek Karnowski [pl]Founded31 August 2020 (2020-08-31)Registered6 October 2020 (2020-10-06)Headquartersul. Kartuska 81/680-136 GdańskMembership (2021)500[1]IdeologyRegionalismLocalismDecentralizationPro-EuropeanismProgressivismPolitical positionCentre-left[nb 1]National affiliationSenate Pact 2023 (fo…

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori brasiliani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Renato Renato con la maglia del Siviglia nel 2010 Nazionalità Brasile Altezza 177 cm Peso 71 kg Calcio Ruolo Centrocampista Termine carriera 3 dicembre 2018 Carriera Giovanili -1997 Guarani Squadre di club1 1998-1999 Guarani37 (5)2000-2004 Santos127 (12)2004-2011 Siviglia204 (26)2011-…

Occupied Palestinian territory in the Middle East For other uses, see Palestinian territories (disambiguation). Palestinian territoriesالأراضي الفلسطينيةal-Arāḍī al-FilasṭīniyyaPalestinian territories according to a Green Line based definitionLargest citiesGazaHebronNablusKhan YunisEast Jerusalem[note 1]LanguagesArabicHebrewEnglishEthnic groups PalestiniansJewsSamaritansDemonym(s)PalestiniansIsraeli/Jewish settlersArea • Total6,220 km2 (2,400…

L'infermiere pediatrico è un professionista sanitario responsabile dell'assistenza infermieristica pediatrica, in possesso della Laurea in Infermieristica Pediatrica e dell'iscrizione all'ordine professionale. Indice 1 Storia 2 Nel mondo 2.1 Italia 2.1.1 Formazione 2.1.2 Competenze e funzioni 2.1.3 Cartella infermieristica 3 Note 4 Bibliografia 5 Voci correlate 6 Collegamenti esterni Storia L'infermieristica pediatrica esisteva come professione con caratteristiche proprie già nell'XIX seco…

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、蘭&…

American racing driver NASCAR driver James Roy Jim Paschal, Jr.Born(1926-12-05)December 5, 1926High Point, North Carolina, United StatesDiedJuly 5, 2004(2004-07-05) (aged 77)Atlanta, GeorgiaCause of deathCancerAchievements1964, 1967 World 600 WinnerNASCAR Cup Series career421 races run over 23 yearsBest finish5th (1956)First race1949 Race No. 1 (Charlotte)Last race1972 World 600 (Charlotte)First win1953 Race #36 (Martinsville)Last win1967 Race #27 (Montgomery) Wins Top tens Poles 25 230 12 …

American track and field athlete For other people with the same name, see Ed Moses (disambiguation). Edwin MosesMoses in 2008Personal informationFull nameEdwin Corley Moses[1]Born (1955-08-31) August 31, 1955 (age 68)[1]Dayton, Ohio, U.S.[2]Height6 ft 2 in (188 cm)[2]Weight180 lb (82 kg)[2]SportSportTrack and FieldEventHurdlesClubMorehouse CollegeTeam adidasAchievements and titlesPersonal best(s)110 mH – 13.64 (1978)400…

1971 EuropeanAthletics ChampionshipsTrack events100 mmenwomen200 mmenwomen400 mmenwomen800 mmenwomen1500 mmenwomen5000 mmen10,000 mmen100 m hurdleswomen110 m hurdlesmen400 m hurdlesmen3000 msteeplechasemen4×100 m relaymenwomen4×400 m relaymenwomenRoad eventsMarathonmen20 km walkmen50 km walkmenField eventsHigh jumpmenwomenPole vaultmenLong jumpmenwomenTriple jumpmenShot putmenwomenDiscus throwmenwomenHammer throwmenJavelin throwmenwomenCombined eventsPentathlonwomenDecathlonmenvte The women's …

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Simplicius et Simplice. Simplice Portrait imaginaire. Basilique Saint-Paul-hors-les-Murs (mosaïque du milieu du XIXe siècle). Biographie Nom de naissance Simplicius Naissance Vers 420Tivoli Décès 10 mars 483 Rome Pape de l'Église catholique Élection au pontificat 3 mars 468 Fin du pontificat 10 mars 483 Hilaire Félix III (en) Notice sur www.catholic-hierarchy.org modifier Simplice (en latin : Simplicius), né à Tivoli et mort à Rome le 1…

Chronologies Données clés 1279 1280 1281 1282 1283 1284 1285Décennies :1250 1260 1270 1280 1290 1300 1310Siècles :XIe XIIe XIIIe XIVe XVeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies thématiques Religion (,) et * Croisades Science () et Santé et médecine Terrorisme Calendriers Romain Chinois Grégorien Julien Hébraïque Hindou Hégirien Persan Républicain modifier Années de la santé et de la médecine : 1…

إبراهيم قصيعة معلومات شخصية الميلاد 7 ديسمبر 1991 [1] غزة الوفاة 14 نوفمبر 2023 (31 سنة) مخيم جباليا سبب الوفاة ضربة جوية قتله القوات الجوية الإسرائيلية الطول 187 سنتيمتر[1] الجنسية دولة فلسطين المدرسة الأم جامعة الأقصى الحياة العملية المهنة لاعب…
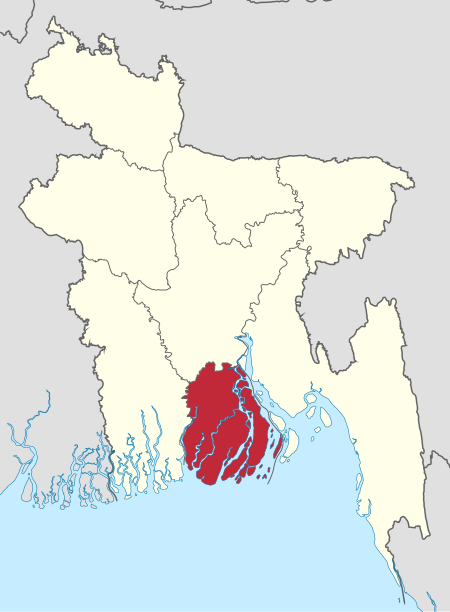
Lalmohan redirects here. For other uses, see Lalmohan (disambiguation). Upazila in Barisal Division, BangladeshLalmohan লালমোহনUpazilaCoordinates: 22°19.3′N 90°44.8′E / 22.3217°N 90.7467°E / 22.3217; 90.7467Country BangladeshDivisionBarisal DivisionDistrictBhola DistrictArea • Total396.24 km2 (152.99 sq mi)Population (2011) • Total283,889 • Density720/km2 (1,900/sq mi)Time zoneUTC+6 (B…



























