Ranger 5
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Kai-┼īshima Stationńö▓µ¢ÉÕż¦Õ│Čķ¦ģJR Kai-┼īshima Station, March 2006Lokasi┼īshima, Minobu, Minamikoma, Yamanashi’╝łÕ▒▒µó©ń£īÕŹŚÕĘ©µæ®ķāĪĶ║½Õ╗Čńö║Õż¦Õ│Č’╝ēJapanKoordinat35┬░19ŌĆ▓41ŌĆ│N 138┬░27ŌĆ▓08ŌĆ│E / 35.3281┬░N 138.4523┬░E / 35.3281; 138.4523Operator JR CentralJalur Minobu LineLetak39.8 kilometers from FujiJumlah peron1 island platformInformasi lainStatusUnstaffedSejarahDibukaApril 8, 1919PenumpangFY20164 daily Lokasi pada petaKai-┼īshima StationLokasi di Prefekfur Yam…

Bangladeshi cuisine refers to the food and culinary traditions prevalent in Bangladesh. Dating far in the past, the cuisine emphasizes fish, vegetables and lentils served with rice. Because of differences in history and Bangladeshi geography, the cuisine is rich in regional variations. While having unique traits, Bangladeshi cuisine is closely related to that of surrounding Bengali and North-East Indian, with rice and fish as traditional favorites. Bangladesh also developed the only multi-course…

Mt. OphirMt. Ophir secara jelas tergambar pada peta dari tahun 1228, gunung ini digambarkan berlokasi di daerah selatan dari Gunung MarapiTitik tertinggiKoordinat0┬░4ŌĆ▓45ŌĆ│N 99┬░59ŌĆ▓0ŌĆ│E / 0.07917┬░N 99.98333┬░E / 0.07917; 99.98333 GeografiMt. OphirMount Ophir berlokasi di Sumatera Barat (bagian dari negara modern Indonesia)Tampilkan peta SumatraMt. OphirMt. Ophir (Indonesia)Tampilkan peta IndonesiaPegununganBukit Barisan Mount Ophir (/╦ło╩Ŗf╔Ör/, terj. 'Gunung …

filmografi Bae SuzySuzy pada 18 Juli 2017.Film4Seri Televisi10Acara Televisi5 Bae Suzy (Hangul: ļ░░ņłśņ¦Ć; lahir 10 Oktober 1994), lebih dikenal dengan mononim Suzy, adalah penyanyi dan aktris Korea Selatan. Dia adalah mantan anggota girl grup miss A di bawah label JYP Entertainment.[1] Film Tahun Judul Peran Ref. 2012 Architecture 101 Yang Seo-yeon (muda) [2] 2015 The Sound of a Flower Jin Chae-seon [3] 2017 Real Cameo - Seniman tato [4] 2019 Ashfall Choi Ji-youn…

Symbol V├żgskyltar anv├żnder ofta symboler. H├żr en symbol f├Čr avsmalnande v├żg. Betydelse ŌĆō ett m├żrke, ett tecken eller en geometrisk form som anv├żnds som en kulturell a) representation f├Čr eller b) association till eller c) metonymi av ett f├Črem├źl, en funktion, en process, en organisation eller grupp, eller n├źgot abstrakt, p├ź grund av medveten eller omedveten likhet eller enligt konvention.[1] Betydelse 2 ŌĆō ett f├Črem├źl eller en person som exemplifierar n├źgot annat, en metonym[2]…

Wilayah desa (bahasa Burma: ßĆĆßĆ╗ßĆ▒ßĆĖßĆøßĆĮßĆ¼ßĆĪßĆ»ßĆĢßĆ║ßĆģßĆ») adalah pembagian adminsitratif tingkat keempat dari kota-kota pedesaan Myanmar.[1] Pada April 2015, terdapat 13.602 wilayah desa di Myanmar yang terdiri dari 70.838 desa. Bentuk setara dari wilayah desa untuk kota-kota perkotaan adalah Distrik kota di Myanmar. Lihat pula Pembagian administratif Myanmar Referensi ^ Myanmar Administrative Structure (PDF). Myanmar Information Management Unit. August 2015. Diarsipkan da…

San Mart├ŁnIl San Mart├Łn in combattimento contro gli inglesiDescrizione generale Tipogaleone Varo1580 Nomi precedentiS├Żo Martinho Fuori servizio1588 Caratteristiche generaliDislocamento1.000 Lunghezza57,3 m Larghezza9,3 m Propulsione2 alberi a vele quadre, 1 albero a vele latine Equipaggio350 marinai e artiglieri, 300 soldati ArmamentoArmamento48 cannoni voci di navi e imbarcazioni a vela presenti su Wikipedia Il S├Żo Martinho, costruito come galeone portoghese, in seguito all'Unione…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. Ary Laksmana Widjaja Informasi pribadiLahir10 Januari 1965 (umur 59)Bandung, Jawa BaratAlma materSepa Milsuk ABRI, Perwira Beasiswa (1989)PekerjaanPolriKarier militerPihak IndonesiaDinas/cabang Kepolisian Negara Republik IndonesiaMasa dinas…

Beautiful ChristmasSingel oleh Red Velvet dan aespaBahasaKoreaInggrisDirilis14 Desember 2022 (2022-12-14)StudioSMGenreMusik NatalDurasi3:29Label SM Dreamus Pencipta Kim Jae Won (Jam Factory) Komponis musik Justin Reinstein ALYSA JJean (@NUMBER K) Kronologi singel Red Velvet dan aespa Birthday (2022) Beautiful Christmas (2022) Chill Kill (2023) Video musikBeautiful Christmas di YouTube Beautiful Christmas (bahasa Indonesia: Natal yang Indah) adalah sebuah lagu dan singel yang direkam dan din…

Isabella del BalzoRitratto di Isabella del Balzo, Museo Filangieri, NapoliRegina consorte di NapoliStemma In carica7 ottobre 1496 ŌĆō1┬║ agosto 1501 PredecessoreGiovanna d'Aragona SuccessoreAnna di Bretagna NascitaMinervino Murge, 24 giugno 1465 MorteFerrara, 22 maggio 1533 Luogo di sepolturaMonastero di Santa Caterina Martire DinastiaDel Balzo PadrePirro del Balzo, IV duca di Andria MadreMaria Donata Orsini Consorte diFederico I di Napoli FigliFerdinandoGiuliaIsabellaAlfonsoCesare Re…

Jean de Murat de Cros Jean de Murat du Cros merupakan seorang kardinal Gereja Katolik asal Prancis. Ia menjadi Uskup Limoges (1347ŌĆō1371). Ia merupakan pemimpin dalam Skisma Besar pada Gereja Barat. Ia lahir pada tanggal yang tidak diketahui di Istana Calimafort, di Provinsi Limousin,[1] sebagai putra dari Aymar de Murat de Cros, seorang bangsawan Auvergnat, dan Marie de Montclar.[2] Saudaranya yang bernama Pierre de Murat de Cros menjadi seorang biarawan dan kemudian Uskup Agun…

Resolutevillaggio (hamlet)Qausuittuq - ߢāßÉģßō▒ßÉāßæ”ßæÉߢģ Resolute ŌĆō Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Canada Territorio Nunavut Divisione censuariaRegione di Qikiqtaaluk AmministrazioneSindacoTabitha Mullin TerritorioCoordinate74┬░41ŌĆ▓51ŌĆ│N 94┬░49ŌĆ▓56ŌĆ│W / 74.6975┬░N 94.832222┬░W74.6975; -94.832222’╗┐ (Resolute)Coordinate: 74┬░41ŌĆ▓51ŌĆ│N 94┬░49ŌĆ▓56ŌĆ│W / 74.6975┬░N 94.832222┬░W74.6975; -94.832222’╗┐ (Resolute) Altitudine66 m s.l.m. Superfic…
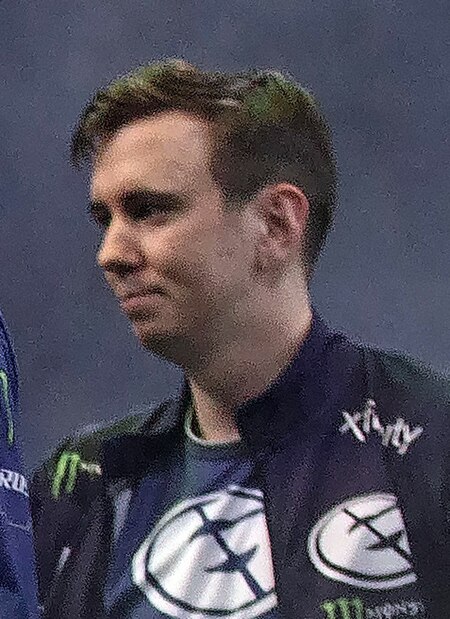

Gustav MagnussonMagnusson, 2018StatusAktifTanggal lahir1 April 1992 (umur 31)Tempat tinggalStockholm, SwediaKebangsaan SwediaTim saat iniAlliancePermainanDota 2Riwayat karir2013ŌĆō2014Alliance2014ŌĆō2015Team Secret2015Alliance2016ŌĆō2018OG2018ŌĆō2019Evil Geniuses2020ŌĆōkiniAlliance Pencapaian dan penghargaan Pemenang The International (2013) Pemenang 2├Ś Dota Major (Boston, Kiev) Gustav Magnusson (lahir 1 April 1992), lebih dikenal dengan nama s4, adalah seorang pemain profesional Dota…

Banjar Margo KecamatanNegara IndonesiaProvinsiLampungKabupatenTulang BawangPemerintahan ŌĆó Camat-Populasi (2020)[1] ŌĆó Total40.138 jiwa ŌĆó Kepadatan301/km2 (780/sq mi)Kode pos34684Kode Kemendagri18.05.20 Kode BPS1808031 Luas132,95 km┬▓Desa/kelurahan12 kampungSitus webbanjarmargo.tulangbawangkab.go.id Banjar Margo (aksara Lampung: )adalah sebuah kecamatan di Kabupaten Tulang Bawang, Lampung, Indonesia. Awalnya, kecamatan ini merupakan daerah…

Edgar SengierLahirEdgar Edouard Bernard Sengier(1879-10-09)9 Oktober 1879Kortrijk, West Flanders, BelgiaMeninggal26 Juli 1963(1963-07-26) (umur 83)Cannes, Alpes-Maritimes, PrancisKebangsaanBelgiaAlmamaterUniversitas LeuvenPekerjaanTeknik pertambangan, direkturTempat kerjaUnion Mini├©re du Haut KatangaDikenal atasPemasokan uranium untuk Proyek ManhattanPenghargaan Commander of the Order of the Belgian Crown (1945) Grand Officer of the Royal Order of the Lion (1945) E…
Cari artikel bahasa Cari berdasarkan kode ISO 639 (Uji coba) Kolom pencarian ini hanya didukung oleh beberapa antarmuka Halaman bahasa acak Bahasa Gagauz Gagauz dili, ąōą░ą│ą░čāąĘ ą┤ąĖą╗ąĖ Dituturkan diMoldova, Ukraina, RusiaWilayahGagauziaPenutur162.200[1] Rincian data penutur Jumlah penutur beserta (jika ada) metode pengambilan, jenis, tanggal, dan tempat.[2][3] 115.000 (Moldova, 2014)148.720 (2014) Rumpun bahasaAltaik[4] (kontroversial) TurkikO…

Beverage containing stimulants This article contains weasel words: vague phrasing that often accompanies biased or unverifiable information. Such statements should be clarified or removed. (September 2018) Energy drinkA variety of energy drinks in a German supermarket shelfTypeFunctional beverageCountry of origin JapanIntroduced20th centuryColorVariousFlavorVariousIngredientsUsually caffeine, various others An energy drink is a type of drink containing stimulant compounds, usually caffeine,…

Contoh gawit penggeser dengan nilai 0 hingga 9, saat ini disetel ke 3 Bilah geser atau bilah lacak adalah elemen kontrol grafis yang dengannya pengguna dapat menetapkan nilai dengan menggerakkan indikator, biasanya secara horizontal. Dalam beberapa kasus, pengguna juga dapat mengklik titik pada penggeser untuk mengubah pengaturan. Berbeda dengan bilah gulir karena tidak berkesinambungan tetapi digunakan untuk mengatur nilai tanpa mengubah format tampilan atau informasi lain di layar. Penggunaann…

Enny Anggraeny Anwar Wakil Gubernur Sulawesi Barat ke-3Masa jabatan12 Mei 2017 ŌĆō 12 Mei 2022PresidenJoko WidodoGubernurAli Baal Masdar PendahuluAladin S. MenggaPenggantiPetahanaAnggota DPR-RIDapil Sulawesi BaratFraksi Partai Golongan KaryaMasa jabatan1 Oktober 2014 (2014-10-01) ŌĆō 10 Januari 2016 (2016-1-10)PresidenSusilo Bambang Yudhoyono Joko Widodo PenggantiIbnu MunzirMayoritas58.518 (2014) Informasi pribadiLahir9 April 1956 (umur 67)Parepare, Sulawesi,…

ąĀąŠą║čüą░ąĮą░ ąĀąŠą║čüą░ąĮą░ą░ąĮą│ą╗. Roxanne Roxanne ą¢ą░ąĮčĆčŗ ą▒ąĖąŠą│čĆą░čäąĖčÅ, ą┤čĆą░ą╝ą░, ą╝čāąĘčŗą║ą░ ąĀąĄąČąĖčüčüčæčĆ ą£ą░ą╣ą║ą╗ ąøą░čĆąĮąĄą╗ ą¤čĆąŠą┤čÄčüąĄčĆčŗ ąØąĖąĮą░ ą»ąĮą│ ąæąŠąĮą┤ąČąŠą▓ąĖ,ą£ąĖą╝ąĖ ąÆą░ą╗ą┤ąĄčü,ążąŠčĆąĄčüčé ąŻąĖčéą░ą║ąĄčĆ,ążą░čĆčĆąĄą╗ą╗ ąŻąĖą╗čīčÅą╝čü ąÉą▓č鹊čĆčüčåąĄąĮą░čĆąĖčÅ ą£ą░ą╣ą║ą╗ ąøą░čĆąĮąĄą╗ ąÆ ą│ą╗ą░ą▓ąĮčŗčģčĆąŠą╗čÅčģ ą©ą░ąĮč鹥 ąÉą┤ą░ą╝čü,ą£ą░čģąĄčĆčłą░ą╗ą░ ąÉą╗ąĖ,ąØąĖą░ ąøąŠąĮą│,ąŁą╗ą▓ąĖčü ąØąŠą╗ą░čüą║ąŠ,ąÜąĄą▓ąĖąĮ ążąĖą╗ą╗ąĖą┐čü,ą©ąĄąĮąĄą╗ą…



