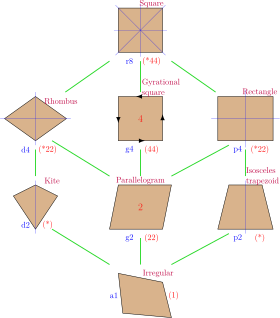
Rectangle
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

1946 incident Lengkong incidentPart of the Indonesian National RevolutionDate25 January 1946LocationLengkong, Tangerang, BantenResult Japanese victoryBelligerents Indonesia JapanCommanders and leaders Major Daan Mogot †Strength Cadets and officers Local garrisonCasualties and losses 36 killed Unknown vteIndonesian National Revolution1945 Bersiap Kotabaru Semarang Medan Ambarawa Surabaya Kolaka Cumbok Borneo West Kalimantan Kumai 1946 Lengkong East Sumatra Bandung 3 July Ma…

AgordatUna fotografia dell'AgordatDescrizione generale Tipoincrociatore torpediniere (1900-1914)esploratore (1914-1921)cannoniera (1921-1923) ClasseAgordat Proprietà Regia Marina CostruttoriRegio Arsenale, Castellammare di Stabia Impostazione18 febbraio 1897 Varo11 ottobre 1899 Entrata in servizio26 settembre 1900 Radiazione4 gennaio 1923 Destino finaledemolito Caratteristiche generaliDislocamentocarico normale 1340 tpieno carico 1530 t Lunghezza91,6 m Larghezza9,3 m Pescaggio4,3&…

George Bancroft(1846) Nama dalam bahasa asli(en) George Bancroft BiografiKelahiran3 Oktober 1800 Worcester Kematian17 Januari 1891 (90 tahun)Washington, D.C. Tempat pemakamanRural Cemetery (en) Dewan Direksi Institusi Smithsonian11 Desember 1874 – Maret 1878 United States Secretary of the Navy (en) 11 Maret 1845 – 9 September 1846 ← John Y. Mason (en) – John Y. Mason (en) → Duta besar Daftar dut…

Iffat binti Muhammad ats-TsunayanRatu mengunjungi Sekolah Dar Al HannanKelahiran1916Istanbul, Kesultanan UtsmaniyahKematian17 Februari 2000 (umur 84)Riyadh, Arab SaudiWangsaWangsa SaudNama lengkapIffat binti Muhammad bin Abdullah bin Abdullah bin ThunayanAyahMuhammad bin Abdullah ats-TsunayanIbuAsia HanımPasanganFaisal dari Arab Saudi (m. 1932; meninggal 1975)Anak Daftar Putri SaraPangeran Mohammad Putri Latifa Pangeran Saud Pangeran Abdul Rah…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. artikel ini perlu dirapikan agar memenuhi standar Wikipedia. Tidak ada alasan yang diberikan. Silakan kembangkan artikel ini semampu Anda. Merapikan artikel dapat dilakukan dengan wikifikasi atau membagi artikel ke paragraf-paragraf. Jika sudah dirapikan,…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada November 2022. Dalam artikel ini, nama keluarganya adalah de Bruyn. Erik de BruynLahir27 Oktober 1962 (umur 61)Terneuzen, Zeeland, BelandaPekerjaanSutradara, pemeranTahun aktif1990-kini Erik de Bruyn (lahir 27 Oktober 1962) adalah seorang sutradara dan pemera…

Chronologie de la France ◄◄ 1771 1772 1773 1774 1775 1776 1777 1778 1779 ►► Chronologies Louis XVI en costume de sacre, Joseph-Siffrein Duplessis, 1775.Données clés 1772 1773 1774 1775 1776 1777 1778Décennies :1740 1750 1760 1770 1780 1790 1800Siècles :XVIe XVIIe XVIIIe XIXe XXeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies thématiques Art Architecture, Arts plastiques (Dessin, Gravure, Peinture et Sculpture), Littérature…

Wells Fargo Center Informasi stadionNama lamaCoreStates Center (1996–1998)[1]First Union Center (1998–2003)[1]Wachovia Center (2003–2010)[2]PemilikComcast SpectacorLokasiLokasiPhiladelphia, PennsylvaniaKoordinat39°54′4″N 75°10′19″W / 39.90111°N 75.17194°W / 39.90111; -75.17194Koordinat: 39°54′4″N 75°10′19″W / 39.90111°N 75.17194°W / 39.90111; -75.17194Transportasi umum NRG station: Galat Lua: ex…

Mountain in Canada and USA This article is about the mountain in Canada and the United States. For the mountain in New Zealand, see Mount Vancouver (New Zealand). Mount VancouverWest aspectHighest pointElevation4,812 m (15,787 ft)[1]Prominence2,692 m (8,832 ft)[1]ListingNorth America highest peaks 15thNorth America prominent peak 26thCanada highest major peaks 7thCanada most prominent peaks 9thCoordinates60°21′32″N 139°41′53″W / …

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Nakankoyo, California – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2021) Nakankoyo (also, Naku) is a former Maidu village in Plumas County, California.[1] It was located at Big Spring, but its precise location is unknown.[1] Refer…

Italian artist, architect and poet (1475–1564) For other uses, see Michelangelo (disambiguation). MichelangeloPortrait by Daniele da Volterra, c. 1545BornMichelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni6 March 1475Caprese, Republic of FlorenceDied18 February 1564(1564-02-18) (aged 88)Rome, Papal StatesKnown for Sculpture painting architecture poetry Notable workPietà (1498–1499)David (1501–1504)Sistine Chapel ceiling (1508–1512)Moses (1513–1515)The Last Judgment (1536–1541…

Benediktus Tambonop Bupati Boven Digoel ke-3Masa jabatan29 April 2016 – 13 Januari 2020PresidenJoko WidodoGubernurLukas EnembeWakilChaerul AnwarPendahuluYesaya MerasiPenggantiChaerul Anwar Informasi pribadiLahir(1975-05-27)27 Mei 1975[1]Merauke, Papua, IndonesiaMeninggal13 Januari 2020(2020-01-13) (umur 44)[2]Jakarta, IndonesiaPartai politikPDI PerjuanganSuami/istriJuliana Tangke AlloAnak5Alma materSTPDN JatinangorSunting kotak info • L • B Bened…

Södermanland County Södermanlands länDaerah di Swedia CountrySwediaIbu kotaNyköpingPemerintahan • GubernurBo Könberg • DewanLandstinget SörmlandLuas • Total6.061 km2 (2,340 sq mi)Populasi (March 31 2011)[1] • Total270.981 • Kepadatan45/km2 (120/sq mi)Zona waktuUTC+1 (CET) • Musim panas (DST)UTC+2 (CEST)GDP/ NominalSEK 52,235 million (2004)GDP per capitaSEK 202,000NUTS RegionSE122 …

British TV series or programme Lord Peter WimseyOpening titlescreenGenre Mystery Period drama Based onStories by Dorothy L. SayersWritten by Anthony Steven John Bowen Bill Craig Starring Ian Carmichael Glyn Houston Mark Eden ComposerHerbert ChappellCountry of originUnited KingdomOriginal languageEnglishNo. of episodes21ProductionProducers Richard Beynon Bill Sellars Camera setupMulti-cameraRunning time44-60 minutesOriginal releaseNetworkBBC1Release5 April 1972 (1972-04-05) –13 August…

丹尼爾·奧蒂嘉José Daniel Ortega Saavedra尼加拉瓜總統现任就任日期2007年1月10日前任恩里克·博拉尼奥斯任期1985年1月10日—1990年4月25日前任自己(國家重建軍政府协调员)继任比奥莱塔·查莫罗國家重建軍政府协调员任期1979年7月18日—1985年1月10日前任安纳斯塔西奥·索摩查·德瓦伊莱继任改任總統 个人资料出生 (1945-11-11) 1945年11月11日(78歲) 尼加拉瓜瓊塔萊斯省[1]政党�…

「俄亥俄」重定向至此。关于其他用法,请见「俄亥俄 (消歧义)」。 俄亥俄州 美國联邦州State of Ohio 州旗州徽綽號:七葉果之州地图中高亮部分为俄亥俄州坐标:38°27'N-41°58'N, 80°32'W-84°49'W国家 美國加入聯邦1803年3月1日,在1953年8月7日追溯頒定(第17个加入联邦)首府哥倫布(及最大城市)政府 • 州长(英语:List of Governors of {{{Name}}}]]) • …

「俄亥俄」重定向至此。关于其他用法,请见「俄亥俄 (消歧义)」。 俄亥俄州 美國联邦州State of Ohio 州旗州徽綽號:七葉果之州地图中高亮部分为俄亥俄州坐标:38°27'N-41°58'N, 80°32'W-84°49'W国家 美國加入聯邦1803年3月1日,在1953年8月7日追溯頒定(第17个加入联邦)首府哥倫布(及最大城市)政府 • 州长(英语:List of Governors of {{{Name}}}]]) • …

Village in Estonia Village in Saare County, EstoniaSutuVillageCountry EstoniaCountySaare CountyParishSaaremaa ParishTime zoneUTC+2 (EET) • Summer (DST)UTC+3 (EEST) Sutu is a village in Saaremaa Parish, Saare County, on the island of Saaremaa, Estonia.[1] Before the administrative reform in 2017, the village was in Pihtla Parish.[2] References ^ Lisa. Asustusüksuste nimistu (PDF). haldusreform.fin.ee (in Estonian). Rahandusministeerium. Retrieved 5 December 2017.…

土库曼斯坦总统土库曼斯坦国徽土库曼斯坦总统旗現任谢尔达尔·别尔德穆哈梅多夫自2022年3月19日官邸阿什哈巴德总统府(Oguzkhan Presidential Palace)機關所在地阿什哈巴德任命者直接选举任期7年,可连选连任首任萨帕尔穆拉特·尼亚佐夫设立1991年10月27日 土库曼斯坦土库曼斯坦政府与政治 国家政府 土库曼斯坦宪法 国旗 国徽 国歌 立法機關(英语:National Council of Turkmenistan) 土�…

Travis FimmelFimmel di San Diego Comic-Con International 2015Lahir15 Juli 1979 (umur 44)Echuca, Victoria, AustraliaPekerjaanPemeran, mantan modelTahun aktif2002–sekarangInformasi modelingTinggi182 cm (6 ft 0 in) Travis Fimmel (lahir 15 Juli 1979) adalah seorang pemeran dan mantan model asal Australia. Ia dikenal karena memerankan Ragnar Lothbrok dalam seri televisi History Channel Vikings.[1][2] Referensi ^ Prudom, Laura Vikings On History: Travis Fimme…