Romania and weapons of mass destruction
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Ari Freyr Skúlason 2014 Austria - pertandingan sepak bola IslandiaInformasi pribadiNama lengkap Ari Freyr SkúlasonTanggal lahir 14 Mei 1987 (umur 36)Tempat lahir Reykjavík, IslandiaTinggi 170 cm (5 ft 7 in)Posisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini LokerenNomor 6Karier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2016 – Lokeren 49 (6)Tim nasional2009 – Islandia 58 (0) * Penampilan dan gol di klub senior hanya dihitung dari liga domestik Ari Freyr Skúlason (lahir 14 Mei 1987)…
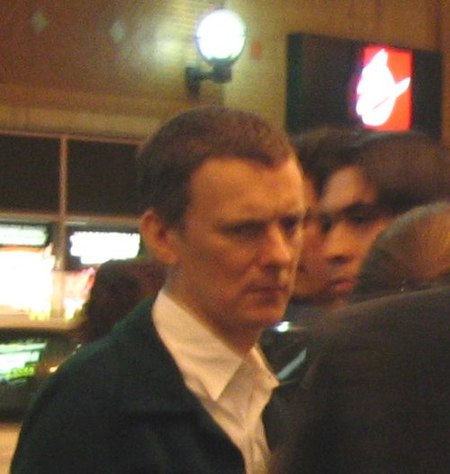

Michel GondryMichel Gondry, 2005.Lahir8 Mei 1963 (umur 60)Versailles, PrancisPekerjaansutradara, penulis naskah, sutradara video musik Michel Gondry, (lahir 8 Mei 1963) adalah seorang penulis naskah, sutradara film, iklan dan video musik yang pernah memenangkan Academy Award. Ia dikenal dengan gaya visual yang inovatif dan manipulasi atas mise en scène. Filmografi Master of Space and Time (2008) Be Kind Rewind (2007) The Science of Sleep (2006) Dave Chappelle's Block Party (2006) (dokument…

Boyko BorissovБойко Борисов Perdana Menteri BulgariaMasa jabatan4 Mei 2017 – 12 Mei 2021PresidenRumen RadevWakilTomislav DonchevValeri SimeonovKrasimir KarakachanovEkaterina Zakharieva PendahuluOgnyan Gerdzhikov (Pelaksana tugas)PenggantiStefan Yanev (Pelaksana tugas)Masa jabatan7 November 2014 – 27 Januari 2017PresidenRosen PlevnelievRumen RadevWakilRumyana BachvarovaTomislav DonchevMeglena KunevaIvaylo Kalfin PendahuluGeorgi Bliznashki (Pelaksana tugas)Penggan…

Wilayah Bani Qasi dan saingannya, Kerajaan Pamplona, pada abad ke-10, setelah mereka kehilangan sebagian besar wilayah di Andalusia. Bani Qasi, atau Bani Kasi, atau Bani Casi (dalam bahasa Arab: بني قسي atau بنو قسي), yang berarti putra atau pewaris Cassius atau Bani Musa) adalah Muwallad yang memerintah di daerah lembah Ebro pada abad ke-9, sebelum mereka pindah pada kuartal pertama abad ke-10. Daftar pustaka Ball, Warwick (2009). Out of Arabia: Phoenicians, Arabs, and the discovery…

Peta wilayah Kongo yang dibuat oleh Henry Morton Stanley. Kakongo adalah kerajaan kecil yang terletak di pesisir Samudra Atlantik di Afrika Tengah. Wilayah kerajaan ini kini merupakan bagian dari Republik Kongo serta Provinsi Cabinda di Angola. Kerajaan ini merupakan salah satu pusat perdagangan yang penting di kawasan tersebut pada abad ke-17 hingga abad ke-19 bersama dengan Kerajaan Ngoyo dan Loango. Rakyatnya menuturkan dialek bahasa Kikongo dan dapat dianggap sebagai bagian dari kelompok etn…
Letak Distrik Thaba-Tseka di Lesotho Distrik Thaba-Tseka merupakan sebuah distrik di Lesotho yang memiliki luas wilayah 4.270 km² dan populasi 170.000 jiwa (2004). Ibu kotanya ialah Thaba-Tseka. lbsDistrik di Lesotho Berea · Butha-Buthe · Leribe · Mafeteng · Maseru · Mohale's Hoek · Mokhotlong · Qacha's Nek · Quthing · Thaba-Tseka Artikel bertopik geografi atau tempat Lesotho ini adalah sebuah rintisan. Anda dapat membantu Wikipedia den…

artikel ini tidak memiliki pranala ke artikel lain. Tidak ada alasan yang diberikan. Bantu kami untuk mengembangkannya dengan memberikan pranala ke artikel lain secukupnya. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Air Terjun Si…

العلاقات الآيسلندية الهندية آيسلندا الهند آيسلندا الهند تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الآيسلندية الهندية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين آيسلندا والهند.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة آيس�…

Nonprofit organization in Washington D.C., United States This article is about the Washington, D.C., think tank. For other uses, see Third Way (disambiguation). This article contains content that is written like an advertisement. Please help improve it by removing promotional content and inappropriate external links, and by adding encyclopedic content written from a neutral point of view. (December 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Third WayFounded2005; 19 y…

Academic disciplines that study society and culture This article is about the academic discipline. For the magazine, see Humanities (magazine). Not to be confused with Humanity. The philosopher Plato – Roman copy of a work by Silanion for the Academia in Athens (c. 370 BC) Humanities are academic disciplines that study aspects of human society and culture, including certain fundamental questions asked by humans. During the Renaissance, the term 'humanities' referred to the s…

.ie البلد جمهورية أيرلندا الموقع الموقع الرسمي تعديل مصدري - تعديل ie. هو امتداد خاص بالعناوين الإلكترونية (نطاق) domain للمواقع التي تنتمي إلى ايرلندا .[1][2] مراجع ^ النطاق الأعلى في ترميز الدولة (بالإنجليزية). ORSN [الإنجليزية]. Archived from the original on 2019-05-07. Retrieved 2017-08-07. ^ ا�…

Amount of twist in a particular DNA strand This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: DNA supercoil – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Supercoiled structure of circular DNA molecules with low writhe. The helical nature of the D…

American breed of chicken Jersey GiantAt the County Fair in Ontario County, New YorkConservation statusLivestock Conservancy: Watch[1]Country of originUnited StatesTraitsWeightMale: Standard: 13 lb (5.9 kg)[2]Bantam: 38 oz (1.1 kg)Female: Standard: 10 lb (4.5 kg)Bantam: 34 oz (0.96 kg)Skin coloryellowEgg colorbrownComb typesingleClassificationAPAAmerican[3]ABAsingle comb, clean leggedPCGBrare soft feather: heavy[4]ChickenGal…

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) A major contributor to this article appears to have a close connection with its subject. It may require cleanup to comply with Wikipedia's content policies, particularly neutral point of view. Please discuss further on the talk page. (March 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) This article may rely excessively on sources t…

Vikariat Apostolik BruneiVicariatus Apostolicus BruneiensisKerasulan Vikariat Brunei (Melayu)Katolik Logo Vikariat Apostolik BruneiLokasiNegara Brunei DarussalamProvinsi gerejawiTunduk langsung pada Takhta SuciKantor pusat49 Jalan Lorong 1 Barat, Seria, Belait KB3533StatistikLuas5.765 km2 (2.226 sq mi)Populasi- Total- Katolik(per 2017)459.00016,770 (3,7%)Paroki3Sekolah3Imam3InformasiDenominasiKatolik RomaGereja sui iurisGereja LatinRitusRitus RomaPendirian…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2022. SDN Palmeriam 02Sekolah Dasar Negeri Palmeriam 02InformasiJenisNegeriNomor Statistik Sekolah101016401053Nomor Pokok Sekolah Nasional20108303Jumlah siswa276 2010StatusAktifAlamatLokasiJln Kayumanis I Lama, Jakarta Timur, DKI Jakarta, IndonesiaSitus&#…

Town in England This article is about the town in England. For the city in Ohio, see Kettering, Ohio. For other uses, see Kettering (disambiguation). Human settlement in EnglandKetteringClockwise from top left: St Peter and St Paul's Church, Bust of Sir Alfred East, Kettering Cenotaph, Town Centre and MuralKetteringLocation within NorthamptonshirePopulation56,676 (Parish, 2021)63,150 (Built up area, 2021)[1]OS grid referenceSP8778• London67 miles (108 km)Civil paris…

Republican political strategist and lobbyist (born 1962) For the American football player, see Michael Caputo (American football). For the West Virginia politician, see Mike Caputo. Michael CaputoAssistant Secretary of Health and Human Services for Public AffairsIn officeApril 16, 2020 – January 20, 2021PresidentDonald TrumpPreceded byRyan Murphy (acting)Succeeded byMark Weber (acting) Personal detailsBornMichael Raymon Caputo (1962-03-24) March 24, 1962 (age 62)Buffalo, New York…

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Чайки (значения). Чайки Доминиканская чайкаЗападная чайкаКалифорнийская чайкаМорская чайка Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:Вторичн�…

Mexican footballer (born 1995) Deneva Cagigas Cagigas in 2018Personal informationFull name Deneva Cagigas GabilondoDate of birth (1995-04-01) 1 April 1995 (age 29)Place of birth Mexico City, MexicoHeight 1.61 m (5 ft 3 in)[1]Position(s) DefenderSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2017–2023 UNAM 132 (5) *Club domestic league appearances and goals, correct as of 12 February 2020 Deneva Cagigas Gabilondo (born 1 April 1995) is a former Mexican professional football defe…

