Smithsonian–Roosevelt African Expedition
| |||||||

Luca Siligardi Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Luca SiligardiTanggal lahir 26 Januari 1988 (umur 36)Tempat lahir Correggio, ItaliaTinggi 1,80 m (5 ft 11 in)Posisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini LivornoNomor 26Karier junior1994–2001 Campagnola2001–2002 Riese2002–2004 Dorando Pietri2004–2005 Parma2005–2006 Dorando Pietri2006–2007 InternazionaleKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2008–2011 Internazionale 0 (0)2008–2009 → Bari (pinjaman) 5 (0)2009 �…

Voce principale: Lost (serie televisiva). I sopravvissuti della sezione centrale del volo Oceanic Airlines 815 nella puntata Esodo, prima parte Questa voce contiene un elenco dei personaggi presenti nella serie televisiva Lost. Indice 1 Sopravvissuti della sezione centrale del volo Oceanic Airlines 815 1.1 Jack Shephard 1.2 Kate Austen 1.3 James Sawyer Ford 1.4 Charlie Pace 1.5 Claire Littleton 1.6 Aaron Littleton 1.7 Sayid Jarrah 1.8 Hugo Hurley Reyes 1.9 John Locke 1.10 Boone Carlyle 1.11 Shan…

Season of television series Star Trek: The Original SeriesSeason 2DVD and Blu-ray coverStarring William Shatner Leonard Nimoy DeForest Kelley Country of originUnited StatesNo. of episodes26ReleaseOriginal networkNBCOriginal releaseSeptember 15, 1967 (1967-09-15) –March 29, 1968 (1968-03-29)Season chronology← PreviousSeason 1 Next →Season 3 List of episodes The second season of the American science fiction television series Star Trek, premiered on NBC on September 1…
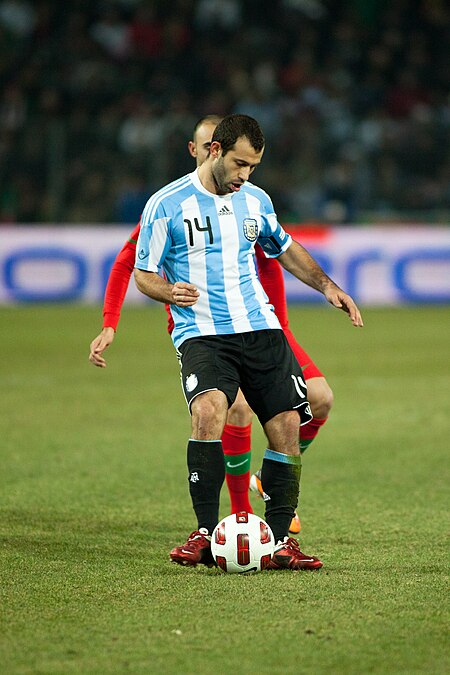

Javier Mascherano Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Javier Alejandro MascheranoTanggal lahir 8 Juni 1984 (umur 39)Tempat lahir San Lorenzo, Santa Fe, ArgentinaTinggi 1,74 m (5 ft 8+1⁄2 in)[1]Posisi bermain Gelandang BertahanBekKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2003–2005 River Plate 46 (1)2005–2006 Corinthians 26 (0)2006–2007 West Ham United 5 (0)2007–2010 Liverpool 94 (2)2010–2018 Barcelona 203 (1)2018–2019 Hebei China Fortune 53 (0)2019–2020 Estudia…

Clemens Walch Informasi pribadiTanggal lahir 10 Juli 1987 (umur 36)Tempat lahir Rum, AustriaTinggi 1,80 m (5 ft 11 in)Posisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini SV RiedKarier junior SU Inzing0000–2006 BNZ TirolKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2007–2008 FC Red Bull Salzburg II 19 (3)2008–2010 VfB Stuttgart II 49 (8)2009–2010 VfB Stuttgart 2 (0)2010–2012 1. FC Kaiserslautern 12 (0)2012 → Dynamo Dresden (pinjaman) 0 (0)2012– SV Ried 0 (0)Tim nasional‡…

Keuskupan WrexhamDioecesis GurecsamiensisEsgobaeth WrecsamDiocese of WrexhamKatolik Katedral Bunda Maria Berdukacita, WrexhamLokasiNegara Wales, Britania RayaWilayahAberconwy, Colwyn, Anglesey, Denbighshire, Flintshire, Gwynedd, Wrexham, dan MontgomeryProvinsi gerejawiCardiffDekanat6Kantor pusatWrexham, Wales Utara, Wales, Britania RayaStatistikLuas8.361 km2 (3.228 sq mi)Populasi- Total- Katolik(per 2017)745.50034,000 (4,6%)Paroki33Sekolah18Imam53 (23 imam…
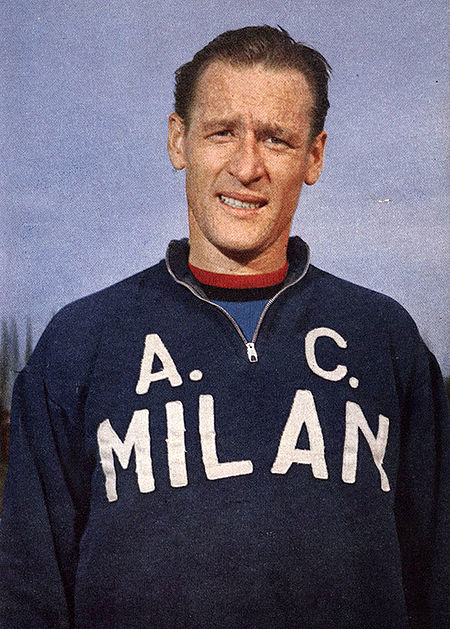

Nils Liedholm Informasi pribadiTanggal lahir (1922-10-08)8 Oktober 1922Tempat lahir Valdemarsvik, SwediaTanggal meninggal 5 November 2007(2007-11-05) (umur 85)Tempat meninggal Cuccaro Monferrato, ItaliaTinggi 1,83 m (6 ft 0 in)Posisi bermain Gelandang serangKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1938–1943 Valdemarsviks IF 1943–1946 IK Sleipner 60 (24)1946–1949 IFK Norrköping 48 (22)1949–1961 AC Milan 359 (81)Tim nasional1947–1958 Swedia 23 (12)Kepelatihan1961–1963 A…

Alison SweeneySweeney pada tahun 2009LahirAlison Ann Sweeney[1]19 September 1976 (umur 47)Los Angeles, California, Amerika SerikatPekerjaanAktrisSutradaraTahun aktif1981–sekarangSuami/istriDavid Sanov (m. 2000)Anak2 Alison Ann Sweeney (lahir 19 September 1976)[2] adalah seorang aktris drama, pembawa acara realitas, sutradara dan penulis asal Amerika Serikat. Sweeney terkenal karena perannya sebagai Samantha Sami Brady pada opera sabun NB…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Khao[pranala nonaktif permanen] Chang Phueak Gunung Khao Chang Phueak adalah sebuah gunung di Taman Nasional Thong Pha Phum Thailand.[1][2] lebih tepatnya berada di Kecamatan Pilok, Distrik Thong Pha Phum, Provinsi Kanchanaburi. gu…

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang kardinal Inggris. Untuk uskup Amerika-Bohemia, lihat Yohanes Neumann. SantoJohn Henry NewmanC.O.Kardinal-Diakon San Giorgio in VelabroPotret Newman karya John Everett Millais, 1881Penunjukan12 Mei 1879Masa jabatan berakhir11 Agustus 1890PendahuluTommaso MartinelliPenerusFrancis Aidan GasquetJabatan lainFellow Oriel College, Oxford; Provost Birmingham OratoryImamatTahbisan imam13 Juni 1824 (diakon; Gereja Inggris)29 Mei 1825 (imam; Gereja Inggris)30 Mei 1847 (im…

Endank SoekamtiAsalYogyakarta, IndonesiaGenreRock alternatifpop punkskate-punkindie rockTahun aktif2001–sekarangLabelProton Record (2003-2004)Warner (2005-2007)Nagaswara (2010-2011)Euforia Record (2012-Sekarang)Situs websoekamti.comAnggotaErix SoekamtiDory SoekamtiTony SoekamtiMantan anggotaUlogFendyAri Hamzah Endank Soekamti adalah grup musik rock Indonesia yang dibentuk pada tahun 2001 di Yogyakarta. Sejarah Awal Terbentuk (2001) Berdiri pada malam tahun baru, 1 Januari 2001, dengan personil…

In association football, or soccer, scoring a goal is the only method of scoring. In National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division I soccer, where a player's career is at most four seasons long, it is considered a notable achievement to reach the 60-goal threshold. In even rarer instances, players have reached the 80 and 100-goal plateaus. The top 30 highest goal-scorers in NCAA Division I men's soccer history are listed below. The NCAA did not split into its current divisions format …

Lambang Kota Erdenet Pemandangan Kota Erdenet Erdenet (Mongol: Эрдэнэт) merupakan sebuah kota di Mongolia. Kota ini letaknya di bagian utara. Tepatnya di Provinsi Orkhon, 150 km dari ibu kota negara Ulan Bator. Pada tahun 2008, kota ini memiliki jumlah penduduk sebesar 86.866 jiwa dan memiliki luas wilayah 208 km². Kota ini memiliki angka kepadatan penduduk sebesar 418 jiwa/km². Pranala luar Wikitravel's Erdenet travel guide Artikel bertopik geografi atau tempat Mongolia ini a…

Exoprosopa pandora Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Arthropoda Kelas: Insecta Ordo: Diptera Famili: Bombyliidae Genus: Exoprosopa Spesies: Exoprosopa pandora Exoprosopa pandora adalah spesies lalat yang berasal dari genus Exoprosopa dan famili Bombyliidae. Lalat ini juga merupakan bagian dari ordo Diptera, kelas Insecta, filum Arthropoda, dan kingdom Animalia. Lalat ini biasanya memakan nektar dan polen yang ada dalam bunga. Referensi Bisby F.A., Roskov Y.R., Orrell T.M., Nicolson D.…
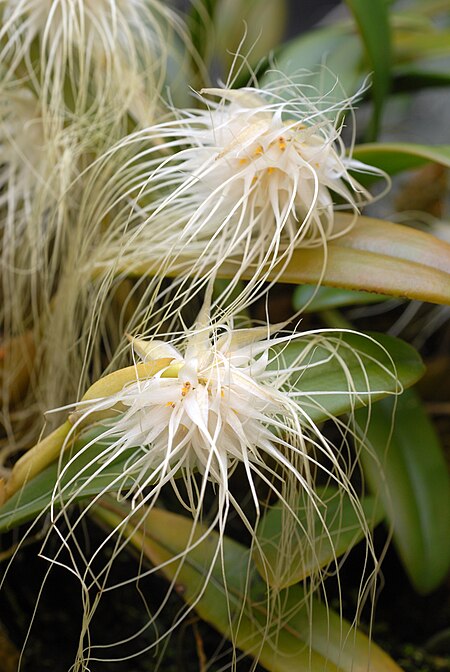

Bulbophyllum medusae Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae (tanpa takson): Angiospermae (tanpa takson): Monocots Ordo: Asparagales Famili: Orchidaceae Genus: Bulbophyllum Spesies: Bulbophyllum medusae Nama binomial Bulbophyllum medusae(Lindl.) Rchb.f. in W.G.Walpers 1861 Bulbophyllum medusae adalah spesies tumbuhan yang tergolong ke dalam famili Orchidaceae. Spesies ini juga merupakan bagian dari ordo Asparagales. Spesies Bulbophyllum medusae sendiri merupakan bagian dari genus Bulbophyllum.[…

Katedral SpoletoKatedral Santa Maria Diangkat ke SurgaItalia: Cattedrale di S. Maria Assuntacode: it is deprecated Katedral SpoletoLokasiSpoletoNegaraItaliaDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaArsitekturStatusKatedralStatus fungsionalAktifAdministrasiKeuskupanKeuskupan Agung Spoleto-Norcia Katedral Spoleto (Italia: Cattedrale di Santa Maria Assuntacode: it is deprecated ; Duomo di Spoleto) adalah sebuah gereja katedral Katolik yang terletak di Spoleto, Umbria, Italia. Katedral ini didedikasikan untuk Ma…
Peta Lokasi Kabupaten Bener Meriah di Aceh Berikut ini adalah daftar kecamatan dan kampung di kabupaten Bener Meriah.Kabupaten Bener Meriah memiliki 10 kecamatan dan 232 kampung dengan kode pos 24553-24582 (dari total 289 kecamatan dan 6.497 gampong/desa/kute/kampong di seluruh Aceh). Pada tahun 2010, jumlah penduduk di wilayah ini adalah 121.870 jiwa (dari penduduk seluruh provinsi Aceh yang berjumlah 4.486.570 jiwa) yang terdiri atas 61.871 pria dan 59.999 wanita (rasio 103,12). Dengan luas da…

Falsepilysta Falsepilysta roseolata Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Arthropoda Kelas: Insecta Ordo: Coleoptera Famili: Cerambycidae Genus: Falsepilysta Falsepilysta adalah genus kumbang tanduk panjang yang tergolong famili Cerambycidae. Genus ini juga merupakan bagian dari ordo Coleoptera, kelas Insecta, filum Arthropoda, dan kingdom Animalia. Larva kumbang dalam genus ini biasanya mengebor ke dalam kayu dan dapat menyebabkan kerusakan pada batang kayu hidup atau kayu yang telah dit…

Diskografi CravityAlbum studio2Video musik8Extended play5Singel7Singel promosi1 Diskografi Cravity ini terdiri dari dua album studio, lima album mini, delapan musik video, tujuh singel, dan satu singel promosi. Album studio Daftar album studio, dengan detail pilihan, posisi tangga lagu, dan penjualan Judul Detail Posisi grafik puncak Penjualan KOR[1] JPN[2] The Awakening: Written in the Stars Released: August 19, 2021 Label: Starship Entertainment Formats: CD, digital download 3 …

Lao ArmyNama lengkapLao Army Football ClubLigaLiga Lao2023ke-4 Lao Army adalah tim sepak bola asal Laos. Tim ini bermain di Liga Lao, liga sepak bola tertinggi di Laos. Sponsor Periode Pakaian olahraga Sponsor 2014- FBT Penghargaan Liga Lao: Pemenang 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1996, 1997, 2008 Piala Perdana Menteri Pemenang (1): 2013 Pemain Catatan: Bendera menunjukkan tim nasional sesuai dengan peraturan FIFA. Pemain dapat memiliki lebih dari satu kewarganegaraan non-FIFA. No. Pos. Negara Pe…

