|
Styloglossus
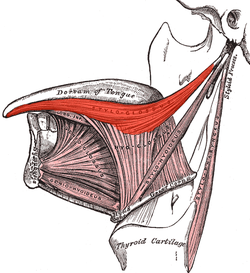
The styloglossus muscle is a bilaterally paired muscle of the tongue. It originates at the styloid process of the temporal bone. It inserts onto the side of the tongue. It acts to elevate and retract the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII).[1] AnatomyThe styloglossus muscle is the shortest and smallest of the three styloid muscles.[citation needed] OriginIt arises from (the anterior and lateral surfaces of) the styloid process of the temporal bone near its apex, and from the stylomandibular ligament.[citation needed] Course and relationsIt passes anterioinferiorly from its origin to its insertion between the internal carotid artery and the external carotid artery,[citation needed] and between the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle and the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle.[1] InsertionIt divides upon the side of the tongue near the dorsal surface of the tongue, blending with the fibers of the longitudinalis inferior muscle anterior to the hyoglossus muscle.[citation needed] InnervationThe styloglossus is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) (like all muscles of the tongue except palatoglossus which is innervated by the pharyngeal plexus of vagus nerve (CN X)).[citation needed] FunctionThe styloglossus draws up the sides of the tongue to create a trough for swallowing. Acting bilaterally (both styloglossus muscles contracting simultaneously) they also aid in retracting the tongue.[citation needed] Additional images
References
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||