The Spirit of Law
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

If Death Ever Slept AuthorRex StoutCover artistBill EnglishCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishSeriesNero WolfeGenreDetective fictionPublisherViking PressPublication dateOctober 25, 1957Media typePrint (Hardcover)Pages186 pp. (first edition)OCLC1836728Preceded byThree for the Chair Followed byAnd Four to Go If Death Ever Slept is a Nero Wolfe detective novel by Rex Stout, published by the Viking Press in 1957 and collected in the omnibus volume Three Trumps (Viking …

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Jompet, nama asli Agustinus Kuswidananto adalah seorang seniman kelahiran Jogja, 16 Desember 1976 dari pasangan keluarga petani dan wiraswasta yang memiliki karakter sebagai penjelajah media. Ia merupakan lulusan Fakultas Ilmu Sosial dan Ilmu Politik Univ…

BadaiGenre Drama Roman Fantasi Remaja PembuatMD EntertainmentDitulis olehDono IndartoSkenarioDono IndartoSutradara Diki Redi Fidel Sukawidianto Pemeran Adly Fairuz Anggika Bölsterli Ikbal Fauzi Hengky Kurniawan Sonya Fatmala Adi Bing Slamet Penggubah lagu temaAdly FairuzLagu pembukaBadai Cinta oleh Adly FairuzLagu penutupBadai Cinta oleh Adly FairuzNegara asalIndonesiaBahasa asliBahasa IndonesiaJmlh. musim1Jmlh. episode40ProduksiProduser eksekutifRaam PunjabiProduser Manoj Punjabi Dhamoo Punjab…
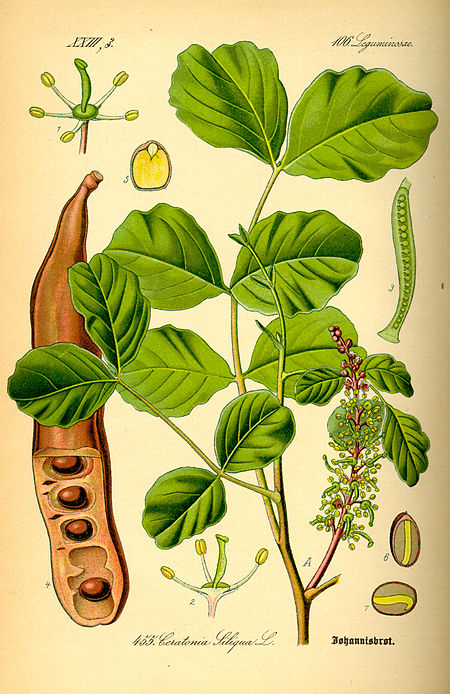
Ceratonia Ceratonia siliqua Klasifikasi ilmiah Domain: Eukaryota Kerajaan: Plantae Upakerajaan: Trachaeophyta Divisi: Magnoliophyta Kelas: Magnoliopsida Subkelas: Rosidae Ordo: Fabales Famili: Fabaceae Subfamili: Caesalpinioideae Tribus: Umtizieae Genus: CeratoniaL. (1753) Spesies[1] Ceratonia oreothauma Hillc., G.P.Lewis & Verdc. Ceratonia siliqua L. Ceratonia emarginata (punah) Sinonim[1] Ceratia Adans. (1763) Siliqua Duhamel (1755), nom. superfl. Acalis (nama usang) Cerato…

Часть серии статей о Холокосте Идеология и политика Расовая гигиена · Расовый антисемитизм · Нацистская расовая политика · Нюрнбергские расовые законы Шоа Лагеря смерти Белжец · Дахау · Майданек · Малый Тростенец · Маутхаузен · …

CBS/CW affiliate in Hattiesburg, Mississippi This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: WHLT – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) WHLTSemi-satellite of WJTV, Jackson, MississippiHattiesburg–Laurel, MississippiUnited StatesCityHa…

Ne pas confondre avec la chanson Après toi interprétée par Christophe Willem. Après toi Chanson de Vicky Leandrosau Concours Eurovision de la chanson 1972 Sortie 1972 Langue Français Genre Chanson française Auteur-compositeur Yves Dessca ; Mario Panas (en), Klaus Munro Label Philips Chansons représentant le Luxembourg au Concours Eurovision de la chanson Pomme, pomme, pomme(1971) Tu te reconnaîtras(1973) Chansons ayant remporté le Concours Eurovision de la chanson Un banc…

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع الكلاسيكو (توضيح). هذه المقالة عن منافسات كرة سلة. لمنافسات كرة القدم، طالع الكلاسيكو. الكلاسيكو (كرة السلة) El Clásicoأسماء أخرىبرشلونة وريال مدريدالمنطقةالفرقبرشلونةريال مدريدأول مواجهةريال مدريد 35–30 برشلونة 29 أبريل 1945 [1]أحدث مواجهةبرشلون…

Sony Dwi KuncoroInformasi pribadiKebangsaan IndonesiaLahir7 Juli 1984 (umur 39)Surabaya, Jawa Timur, IndonesiaTinggi174 cm (5 ft 9 in)PeganganKananPelatihJoko SupriyantoTunggal PutraPeringkat tertinggi3 (7 Oktober 2004)Peringkat saat ini236 (3 Mei 2022)Sony Dwi Kuncoro (lahir 7 Juli 1984) adalah pemain bulu tangkis dari Indonesia. Pada Olimpiade Athena 2004, putra pasangan Mochammad Sumadji dan Asmiati ini merebut medali perunggu di bagian tunggal putra setelah…

City in Maharashtra, IndiaVirarCityPanoramic view of the cityVirarCoordinates: 19°28′N 72°48′E / 19.47°N 72.8°E / 19.47; 72.8CountryIndiaStateMaharashtraDistrictPalgharDivisionKonkanGovernment • TypeMunicipal Corporation • BodyVasai-Virar Municipal Corporation • Member of Legislative Assembly of Maharashtra.Kshitij ThakurElevation10 m (30 ft)Population (2011) • Total1,221,234Languages • Off…

Reproduksi sebuah lembaran yang mengiklankan budak di Charleston, Carolina Selatan, pada 1769. Perbudakan Perbudakan kontemporer Pekerja anak Konskripsi Ijon Kawin paksa Beli pasangan pengantin Penjualan istri Prostitusi Perdagangan manusia Pekerja sewa Buruh hukuman Perbudakan seks Sejarah perbudakan Perbudakan antiquity Perbudakan di Romawi kuno Hukum Babylonia Perbudakan di Yunani kuno Topik dan praktik Perbudakan Atlantik Middle Passage Perbudakan Arab Ghilman Mamluk Saqaliba Perbudakan Azte…

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang karya buatan Rabbi Yosef Karo. Untuk karya buatan Rabbi Schneur Zalman dari Liadi, lihat Shulchan Aruch HaRav. Untuk karya buatan rabbi dan posek Lithuania Yechiel Michel Epstein, lihat Aruch HaShulchan. Shulchan Aruch PengarangJoseph KaroNegaraTanah IsraelBahasaIbraniSubjekHukum YudaisTanggal terbit1565, Venesia Shulchan Aruch (Ibrani: שֻׁלְחָן עָרוּך [ʃulˈħan ʕaˈʁuχ]),[1] terkadang disebut sebagai Kode Hukum Yahudi, adalah ko…

F-Zero GXDéveloppeur Amusement VisionÉditeur NintendoRéalisateur Shigeru Miyamoto (producteur), Toshihiro Nagoshi (producteur), Takaya Imamura (directeur)Compositeur Hidenori Shoji (en), Daiki Kasho (en)Producteur Toshihiro Nagoshi, Shigeru MiyamotoDate de sortie JAP : 25 juillet 2003AN : 25 août 2003EUR : 31 octobre 2003 Genre De 1 à 4 joueursMode de jeu Solo, multijoueurPlate-forme GameCubeÉvaluation PEGI 3 (d)Site web www.f-zero.comF-ZeroF-Zero: Maximum VelocityF-Zero AXm…

Austronesian language spoken in Vanuatu MwotlapMotlavM̄otlapPronunciation[ŋ͡mʷɔtˈlap]Native toVanuatuRegionMota Lava island, Banks IslandsNative speakers2,100 (2012)[1]Language familyAustronesian Malayo-PolynesianOceanicSouthern OceanicNorth-Central VanuatuNorth VanuatuTorres-BanksMwotlapDialects Volow (or a separate language) Language codesISO 639-3mlvGlottologmotl1237ELPMotlavMwotlap is not endangered according to the classification system of the UNESCO Atlas of the Wor…

Peta pembagian administratif tingkat pertama Spanyol Pembagian administratif Spanyol terdiri atas 17 komunitas otonom pada tingkat pertama dan 50 provinsi pada tingkat kedua. lbsPembagian administratif EropaNegaraberdaulat Albania Andorra Armenia1 Austria Azerbaijan1 Belanda Belarus Belgia Bosnia dan Herzegovina Britania Raya Inggris Irlandia Utara Skotlandia Wales Bulgaria Ceko Denmark Estonia Finlandia Georgia1 Hungaria Republik Irlandia Islandia Italia Jerman Kazakhstan2 Kroasia Latvia Liecht…

Robert Golob Pemimpin Partai Gerakan KebebasanPetahanaMulai menjabat 26 Januari 2022WakilUrška Klakočar Zupančič PendahuluJure LebenPenggantiPetahanaAnggota Dewan Kota Nova GoricaPetahanaMulai menjabat 2002 Informasi pribadiLahir23 Januari 1967 (umur 57)Šempeter pri Gorici, RS Slovenia, RFS YugoslaviaPartai politikPS (2011–2013)SAB (2013–2022)GS (sejak 2022)Alma materUniversitas LjubljanaSunting kotak info • L • B Robert Golob (lahir 23 Januari 1967)[1]…

Much Hoole is a civil parish in the South Ribble district of Lancashire, England. It contains eight buildings that are recorded in the National Heritage List for England as designated listed buildings. Of these, one is listed at Grade II*, the middle grade, and the others are at Grade II, the lowest grade. The parish contains the village of Much Hoole, and is otherwise rural. Most of the listed buildings are houses or farmhouses, the others being a church and a milestone. Key Map all c…

UK Parliament constituency in England since 1885 BurtonCounty constituencyfor the House of CommonsBoundary of Burton in StaffordshireLocation of Staffordshire within EnglandCountyStaffordshirePopulation102,731 (2011 census)[1]Electorate75,302 (December 2010)[2]Major settlementsBurton upon Trent and UttoxeterCurrent constituencyCreated1885Member of ParliamentKate Kniveton (Conservative)SeatsOneCreated fromEast Staffordshire and North Staffordshire Burton is a constituency represen…

Voce principale: Marina Militare (Italia). Corpo delle capitanerie di portoGuardia costieraEmblema della Guardia costiera italiana Descrizione generaleAttiva20 luglio 1865 - oggi Nazione Italia Italia Servizio Regia Marina Marina Militare TipoGuardia costiera RuoloRicerca e soccorsoPolizia marittimaPolizia giudiziariaPolizia militareAntiterrorismoPolizia tecnico-amministrativa marittimaPolizia ambientalePolizia di frontieraSicurezza della navigazioneProtezione Civile Dimensione…

Italian singer Damiano DavidDavid in February 2024Background informationBorn (1999-01-08) 8 January 1999 (age 25)Rome, ItalyGenres Pop[1][2] pop rock alternative rock glam rock funk rock Occupation(s) Singer songwriter Instrument(s)VoiceYears active2016–present[3]Member ofMåneskinMusical artist Damiano David (Italian pronunciation: [daˈmjaːno ˈdaːvid]; born 8 January 1999)[4] is an Italian singer and songwriter. He is the frontman of the rock b…
