Thrombospondin 1
|
Read other articles:

Culinary traditions of Nepal This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Nepalese cuisine – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Nepali dal-bhat-tarkari 84 byanjan food with rice on a leaf platter Nepali-style momo with chili Nepali-styl…

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut). …

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Arthur Green (disambiguasi). Arthur (Art) Green Arthur Green (Ibrani: אברהם יצחק גרין, lahir 21 Maret 1941) adalah seorang cendekiawan mistisisme Yahudi dan teolog Neo-Hasidik asal Amerika Serikat. Ia adalah dekan pendiri program rabbinikal non-denominasional di Hebrew College, Boston, dimana ia masih mengajar. Karya yang diterbitkan Green, Arthur (2014). Judaism's ten best ideas. Jewish Lights. ISBN 978-1580238038. Green, Arthur (2015). The Hea…

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع ساحل العاج (توضيح). يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (مارس 2016) ساحل العاج في الألعاب الأولمبية علم ساحل العاج رمز ل.أ.د.&#…

Wakil Bupati PurbalinggaPrasetyaning nayaka amangun praja (Jawa) Segenap masyarakat dan pemerintah setia untuk membangun daerahPetahanaH. Sudono, S.T., M.T.sejak 26 Februari 2021Masa jabatan5 tahunDibentuk2000Pejabat pertamaDrs. Sotarto RahmadSitus webwww.purbalinggakab.go.id Berikut ini adalah daftar Wakil Bupati Purbalingga dari masa ke masa. No Wakil Bupati Mulai Jabatan Akhir Jabatan Prd. Ket. Bupati 1 Drs.Sotarto Rahmad 2000 2005 1 Drs.Triyono Budi SasongkoM.Si. 2 Drs. H.Heru Su…

CBS affiliate in New Orleans WWL-TVNew Orleans, LouisianaUnited StatesChannelsDigital: 27 (UHF)Virtual: 4BrandingWWL LouisianaProgrammingAffiliations4.1: CBSfor others, see § SubchannelsOwnershipOwnerTegna Inc.(WWL-TV, Inc.)Sister stationsWUPLHistoryFirst air dateSeptember 7, 1957(66 years ago) (1957-09-07)Former channel number(s)Analog: 4 (VHF, 1957–2009)Digital: 36 (UHF, until 2020)Former affiliationsNTA Film Network (secondary, 1957–1961)Call sign meaningWorld Wide LoyolaT…

1952 film LoveDirected byGustaf MolanderWritten byKaj Munk (play) Rune Lindström Gustaf MolanderProduced byAllan EkelundStarringSven Lindberg Doris Svedlund Victor SjöströmCinematographyÅke DahlqvistEdited byGösta LewinMusic byLars-Erik LarssonProductioncompanySvensk FilmindustriDistributed bySvensk FilmindustriRelease date22 December 1952Running time106 minutesCountrySwedenLanguageSwedish Love (Swedish: Kärlek) is a 1952 Swedish drama film directed by Gustaf Molander and starring Sven Lin…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada November 2022. Habemus PapamPoster ItaliaSutradaraNanni MorettiProduserNanni MorettiDomenico ProcacciDitulis olehNanni MorettiFrancesco PiccoloFederica PontremoliPemeranMichel PiccoliNanni MorettiPenata musikFranco PiersantiSinematograferAlessandro PesciPenyuntin…

Team sport Beach volleyballThe blocker (left) attempts to stop the opposing team's attack over the net.Highest governing bodyFIVBFirst played1915, Waikiki, Hawaii, United StatesCharacteristicsContactNoTeam members2 or more per sideMixed-sexSingle and mixedTypeOutdoor, team sport, net sportEquipmentBeach volleyballGlossaryVolleyball jargonPresenceCountry or regionWorldwideOlympicSince 1996World Games1993 Beach volleyball is a team sport played by two teams of two players each on a sand …

This template was considered for deletion on 2019 August 13. The result of the discussion was no consensus. Israel Template‑class Israel portalThis template is within the scope of WikiProject Israel, a collaborative effort to improve the coverage of Israel on Wikipedia. If you would like to participate, please visit the project page, where you can join the discussion and see a list of open tasks.IsraelWikipedia:WikiProject IsraelTemplate:WikiProject IsraelIsrael-related articlesTemplateThis te…

American baseball player (born 1981) Baseball player Casey JanssenJanssen with the Washington NationalsPitcherBorn: (1981-09-17) September 17, 1981 (age 42)Orange, California, U.S.Batted: RightThrew: RightMLB debutApril 27, 2006, for the Toronto Blue JaysLast MLB appearanceOctober 3, 2015, for the Washington NationalsMLB statisticsWin–loss record31–29Earned run average3.63Strikeouts395Saves90 Teams Toronto Blue Jays (2006–2007, 2009–2014) Washington Nat…
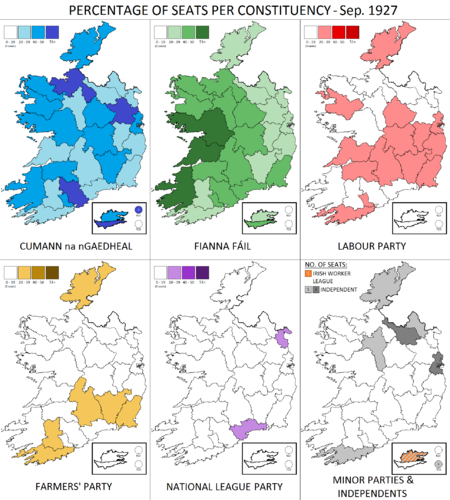
Election to the 6th Dáil September 1927 Irish general election ← Jun 1927 15 September 1927 1932 → ← outgoing memberselected members →153 seats in Dáil Éireann[a]77 seats needed for a majorityTurnout69.0% 0.9pp First party Second party Third party Leader W. T. Cosgrave Éamon de Valera Thomas Johnson Party Cumann na nGaedheal Fianna Fáil Labour Leader since April 1923 26 March 1926 1922 Leader's seat Cork Boroug…

Elio Binda Nazionalità Italia Calcio Ruolo Difensore CarrieraSquadre di club1 1947-1949 Parabiago31+ (2+)1949-1952 Juventus0 (0)1952-1953 Piombino32 (4)1953-1955 L.R. Vicenza35 (1)1955-1956 Mestrina20 (0)1956-1959 Treviso71 (0)1959-1960 Varese0 (0) 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le sole partite di campionato.Il simbolo → indica un trasferimento in prestito. Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Elio Binda (Cellina…

La Lancia D23 è un'automobile da competizione realizzata dalla casa torinese Lancia nel 1953. Le due spider D23 al debutto, a Monza, il 29 giugno 1953 Indice 1 Il contesto 2 Storia e caratteristiche 3 Caratteristiche tecniche 4 L'attività sportiva 5 Altri progetti Il contesto Ormai decisa a scendere ufficialmente in campo nelle competizioni della categoria “sport” (e poi, come vedremo, anche nella “Formula Uno”), la Lancia, dopo l'esordio piuttosto soddisfacente della berlinetta D20 da…

Thunderbird Classic 1978 Sport Tennis Data 2 ottobre - 8 ottobre Edizione 8ª Superficie Cemento Campioni Singolare Martina Navrátilová Doppio Tracy Austin / Betty Stöve 1977 1979 Il Thunderbird Classic 1978 è stato un torneo di tennis giocato sul cemento. È stata l'8ª edizione del torneo, che fa parte del WTA Tour 1978. Si è giocato a Phoenix negli USA, dal 2 all'8 ottobre 1978. Indice 1 Campionesse 1.1 Singolare 1.2 Doppio 2 Collegamenti esterni Campionesse Singolare Lo stesso argomento…

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento partiti politici non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Partito Nazionale(ES) Partido Nacional LeaderLuis Alberto Lacalle Pou PresidentePablo Iturralde Stato Uruguay SedeMontevideo Fondazione10 agosto 1836 IdeologiaConservatorismo nazionaleConservat…
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)[2…

烏克蘭總理Прем'єр-міністр України烏克蘭國徽現任杰尼斯·什米加尔自2020年3月4日任命者烏克蘭總統任期總統任命首任維托爾德·福金设立1991年11月后继职位無网站www.kmu.gov.ua/control/en/(英文) 乌克兰 乌克兰政府与政治系列条目 宪法 政府 总统 弗拉基米尔·泽连斯基 總統辦公室 国家安全与国防事务委员会 总统代表(英语:Representatives of the President of Ukraine) 总理…

Tiger Woods Tiger Woods nel maggio del 2019 Nazionalità Stati Uniti Altezza 185 cm Peso 80 kg Golf Specialità Golf Ranking 744°[1] Best ranking 1°[2] Palmarès Oro The Masters 1997, 2001, 2002, 2005, 2019 Oro PGA Championship 1999, 2000, 2006, 2007 Oro U.S. Open 2000, 2002, 2008 Oro British Open 2000, 2005, 2006 Statistiche aggiornate al 4 febbraio 2022 Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Eldrick Tont Woods, meglio conosciuto come Tiger Woods (Cypress, 30 dice…

Professor of Cell Biology Anne RidleyFRS FRSB FMedSci FRMSAnne Ridley at the Royal Society admissions day in London, July 2017BornAnne Jacqueline Ridley1963 (age 60–61)[4]Alma materUniversity of Cambridge (BA)University of London (PhD)Awards EMBO Member (2002)[1] Liliane Bettencourt Prize (2004)[2] Scientific careerFields Cancer Metastasis Cell biology Cell migration Cell signalling Rho GTPases Institutions University of Bristol King's College …