Karnataka Sexual Minorities Forum v. State of Karnataka
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
Air terjun Bajuin adalah tempat wisata alam yang berada di desa Sungai Bakar, kecamatan Pelaihari, kabupaten Tanah Laut, Kalimantan Selatan. Air terjun Bajuin adalah termpat wisata populer di kurun waktu 1980 - 1995, namun meredup setelahnya.[1] Hingga di 2019, dimulailah penataan lokasi wisata air terjun Bajuin dan dibuka kembali untuk umum pada 1 Juli 2020 dan berhasil mendapatkan kunjungan wisata sebanyak 2000 pengunjung selama 2 minggu dan kawasan ini pun berubah menjadi Bajuin Park.…

Carolyn LawrenceLawrence pada tahun 2008Lahir13 Februari 1967 (umur 57)Baltimore, Maryland, A.S.PekerjaanAktris, Akrtis suaraTahun aktif1987–sekarang Carolyn Lawrence (lahir 13 Februari 1967) adalah orang Amerika aktris dan pengisi suara, yang dikenal karena peran suaranya yang sudah lama berjalan Sandy Cheeks di Acara TV Nickelodeon→ SpongeBob SquarePants.[1] Filmografi Televisi dan film Tahun Judul Peran Catatan 1987 Little Women Amy March Podcast[butuh rujukan] 1…

Pembentukan angin darat-laut. Gambar A menunjukkan perpindahan panas dari daratan ke lautan. Angin hanya terbentuk di malam hari. Angin darat (land breeze) adalah jenis angin yang bertiup dari daratan ke laut (angin lepas pantai) yang berkembang di wilayah pesisir pada malam hari.[1] Angin darat adalah sistem angin lokal yang ditandai dengan aliran dari darat ke laut pada larut malam. Daratan menyerap dan melepas energi panas lebih cepat daripada lautan.[2] Angin darat bergantian…

Vivien LeighLeigh pada tahun 1939LahirVivian Mary Hartley(1913-11-05)5 November 1913Meninggal7 Juli 1967(1967-07-07) (umur 53)London, InggrisPekerjaanAktrisTahun aktif1933–1967Suami/istriHerbert Leigh Holman (1932–1940) Laurence Olivier (1940–1960)PasanganJohn Merivale (1960–1967) Vivien Leigh, Lady Olivier (5 November 1913 – 7 Juli 1967) merupakan seorang aktris berkebangsaan Inggris yang memenangkan dua nominasi Academy Award sebagai aktris terbaik. Dia dilahi…

Часть серии статей о Холокосте Идеология и политика Расовая гигиена · Расовый антисемитизм · Нацистская расовая политика · Нюрнбергские расовые законы Шоа Лагеря смерти Белжец · Дахау · Майданек · Малый Тростенец · Маутхаузен · …

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Iveco SuperAV adalah kendaraan tempur lapis baja amfibi yang dikembangkan oleh IVECO. Dua baling-baling dipasang di belakang memungkinkan kendaraan berjalan pada kecepatan maksimum 10kmp di atas air. SUPERAV ini memiliki desain modular memungkinkan untuk…

TitanoboaRentang fosil: 60–58 jtyl PreЄ Є O S D C P T J K Pg N ↓ Paleosen Titanoboa cerrejonensis Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Subfilum: Vertebrata Kelas: Reptilia Ordo: Squamata Subordo: Serpentes Famili: Boidae Subfamili: Boinae Genus: TitanoboaHead, 2009 Species Titanoboa cerrejonensis Titanoboa (Boa Titan) adalah genus ular yang hidup sekitar 60 hingga 58 juta tahun yang lalu pada periode Paleosen.[1] Satu-satunya spesies dalam genus ini yang d…

United States historic placeSpaulding BridgeU.S. National Register of Historic Places Show map of VermontShow map of the United StatesLocationMill St., Cavendish, VermontCoordinates43°22′57″N 72°36′31″W / 43.38250°N 72.60861°W / 43.38250; -72.60861Arealess than one acreBuilt1905 (1905)Built byNorton, HenryArchitectural styleParker pony trussMPSMetal Truss, Masonry, and Concrete Bridges in Vermont MPSNRHP reference No.05001522[1]Adde…

Fareed ZakariaFareed Zakaria tahun 2013LahirFareed Rafiq Zakaria20 Januari 1964 (umur 60)Mumbai, Maharashtra, IndiaAlmamaterUniversitas Yale (B.A.)Universitas Harvard (Ph.D.)PekerjaanWartawan, penulisKarya terkenalTime, penyunting kontributor (2010–2014)Fareed Zakaria GPS, pembawa acara (2008–sekarang) Newsweek International, penyunting (2000–2010) Foreign Exchange, pembawa acara (2005–2007) Foreign Affairs, mantan penyunting pelaksanaGelarPemerintah India menganugerahi penghargaan …
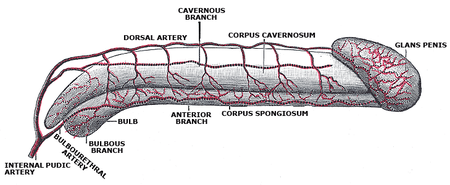
Penis manusiaPenis manusia dalam keadaan relaksasi.RincianPendahuluTuberkulum genital, Lipatan urogenitalSistemSistem genitourinariArteriArteri penis, arteri dorsal penis, arteri dalam penis, arteri bulbus uretraVenaVena dorsal penisSarafSaraf dorsal penisLimfaKelenjar getah bening inguinalis superfisialPengidentifikasiBahasa Latinpenis, pl. penesMeSHD010413TA98A09.4.01.001TA23662FMA9707Daftar istilah anatomi[sunting di Wikidata] Penis manusia adalah organ genital luar pria yang juga berfung…

العلاقات الزامبية الكوبية زامبيا كوبا زامبيا كوبا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الزامبية الكوبية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين زامبيا وكوبا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة زامبيا كوبا ال�…

Los Angeles TimesTipesurat kabar harianFormatkoranPemilikTribune CompanyPenerbitEddy Hartenstein[1]RedaksiRuss StantonDidirikan4 Desember 1881PusatLos Angeles, CaliforniaAmerika SerikatSirkulasi surat kabar773.884 edisi harian 1.101.981 edisi Minggu[2]ISSN0458-3035Situs webwww.latimes.com Los Angeles Times (populer sebagai LA Times) adalah surat kabar harian yang terbit di Los Angeles, California, dan beredar di seluruh wilayah Amerika Serikat Barat. Dalam total oplah, surat kaba…

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Птиц�…
Translation app by Apple This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Translate Apple – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) TranslateScreenshot of the Translate app in iOS 16Developer(s)Apple Inc.Initial releaseSeptember 16, 2…

Untuk kasino di Britania Raya, lihat Star City, Birmingham. Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan cara menambahkan rujukan ke sumber tepercaya. Pernyataan tak bersumber bisa saja dipertentangkan dan dihapus.Cari sumber: The Star, Sydney – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR (Februari 2007) The Star, SydneyThe Star, Sydney, selama Vivid Sydney, 2015.Inform…

Calendaring and mail server Microsoft Exchange ServerExchange Server 2019 logoDeveloper(s)MicrosoftInitial releaseApril 2, 1996; 28 years ago (1996-04-02)[1]Stable release2019 CU14 Mar24SU (15.02.1544.009)[2] (March 12, 2024; 45 days ago (2024-03-12)) [±] Operating systemWindows ServerPlatformx64TypeCollaborative softwareLicenseProprietary commercial softwareWebsitewww.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/exchange/email Microsof…

Gli spiriti dell'isolaColin Farrell e Brendan Gleeson in una scena del filmTitolo originaleThe Banshees of Inisherin Lingua originaleinglese Paese di produzioneStati Uniti d'America, Regno Unito, Irlanda Anno2022 Durata114 min Rapporto2,39:1 Generedrammatico, commedia, grottesco RegiaMartin McDonagh SceneggiaturaMartin McDonagh ProduttoreMartin McDonagh, Graham Broadbent, Peter Czernin Produttore esecutivoDaniel Battsek, Ben Knight, Ollie Madden, Diarmuid McKeown Casa di produzio…

Whispering SmithDa sinistra, Guy Mitchell e Audie Murphy.PaeseStati Uniti d'America Anno1961 Formatoserie TV Generewestern Stagioni1 Episodi26 Durata30 min Lingua originaleinglese Dati tecniciB/N1,33 : 1 CreditiInterpreti e personaggi Audie Murphy: Tom 'Whispering' Smith Guy Mitchell: George Romack MusicheRichard Shores ProduttoreJoseph Hoffman, Herbert Coleman, Willard Willingham Casa di produzioneWhispering Co., NBC Prima visioneDall'8 maggio 1961 Al30 ottobre 1961 Rete televisivaNBC Oper…

Vietnamese Buddhist monk Thích Trí QuangThích Trí Quang in 1966Born(1923-12-21)21 December 1923Diêm Điền village, Quảng Bình, French IndochinaDied8 November 2019(2019-11-08) (aged 95)Huế, Thừa Thiên-Huế, Vietnam Thích Trí Quang (chữ Hán: 釋智光) (21 December 1923 – 8 November 2019) was a Vietnamese Mahayana Buddhist monk best known for his role in leading South Vietnam's Buddhist population during the Buddhist crisis in 1963, and in later Buddhist protests agains…

Buckley-class destroyer escort USS Bunch (DE-694), running trials in Lake Huron on 25 July 1943 History United States NameBunch NamesakeKenneth Cecil Bunch Ordered9 October 1942 BuilderDefoe Shipbuilding Company, Bay City, Michigan Laid down23 February 1943 Launched29 May 1943 Commissioned21 August 1943 Decommissioned31 May 1946 ReclassifiedAPD-79, 31 July 1944 Stricken1 April 1964 Honors andawards2 battle stars (World War II) FateSold for scrapping, 11 May 1965 General characteristics Class and…
