Reapportionment Act of 1929
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
Kegubernuran Al Muthanna Ibu kota Samawah Kota terbesar Kepala pemerintah Luas (km²) 83.268 Populasi (jiwa) 1.035.000 Kepadatan (/km²) 6 Bahasa Arab Komposisi etnis Kegubernuran Al Muthanna (Arab: المثنى) merupakan sebuah kegubernuran di Irak. Kegubernuran ini terletak di bagian selatan di negara itu. Dekat perbatasan Arab Saudi. Kegubernuran ini memiliki luas wilayah 83.268 km² dengan memiliki jumlah penduduk 1.035.000jiwa (2015). Ibu kotanya ialah Samawah. Pada tahun 1976 merupak…

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2018年3月17日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:羅生門 (電影) — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 此�…

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (فبراير 2016) لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع الحكومة السورية (توضيح). حكومة سعد الله الجابري الأولىمعلومات عامةالبلد الجمهوري�…

Resolusi 1149Dewan Keamanan PBBIbukota Angola, LuandaTanggal27 Januari 1998Sidang no.3.850KodeS/RES/1149 (Dokumen)TopikSituasi di AngolaRingkasan hasil15 mendukungTidak ada menentangTidak ada abstainHasilDiadopsiKomposisi Dewan KeamananAnggota tetap Tiongkok Prancis Rusia Britania Raya Amerika SerikatAnggota tidak tetap Bahrain Brasil Kosta Rika Gabon Gambia Jepang Kenya Portugal Slovenia Swedia Resolusi 1149 De…

English singer-songwriter Sarah CracknellSarah Cracknell performing in December 2012Background informationBirth nameSarah Jane CracknellBorn (1965-04-12) 12 April 1965 (age 58)[citation needed]Chelmsford, Essex, England[1]GenresHousealternative dancesynthpopindie popalternative rockOccupation(s)Singer-songwriterYears active1987–presentLabelsHeavenlyGutInstinctCherry RedVirginWebsiteSaint Etienne websiteMusical artist Sarah Jane Cracknell[2] (born 12 April 1965) is …

Megalithic enclosure on Bodmin Moor, Cornwall, England For the building in Tintagel, see King Arthur's Hall, Tintagel. King Arthur's HallShown within CornwallLocationBodmin Moor, CornwallCoordinates50°34′06″N 4°38′33″W / 50.56833°N 4.64250°W / 50.56833; -4.64250TypeMegalithic enclosureHistoryPeriodsNeolithic / Bronze Age King Arthur's Hall is a megalithic enclosure on Bodmin Moor in Cornwall, England. It is thought to be a late Neolithic or early Bronze Age ce…

HanomanLukisan Hanoman di buat oleh Raja Ravi Varma.Dewa MemperlihatkanEjaan Dewanagariहनुमान्Ejaan IASTHanumānNama lainAnoman; Hanumat;Anjaneya; Marutsutha;Bayusutha; IriGolonganWanaraSenjataGadaMantraOm Sri Hanumante Namahlbs Hanoman (Sanskerta: हनुमान्; Hanumān) atau Hanumat (Sanskerta: हनुमत्; Hanumat), juga disebut sebagai Anoman, adalah salah satu dewa dalam kepercayaan agama Hindu, sekaligus tokoh protagonis dalam wiracarita Ramayana yang paling t…

High bandwidth channel access method Part of a series onAntennas Common types Dipole Fractal Loop Monopole Satellite dish Television Whip Components Balun Block upconverter Coaxial cable Counterpoise (ground system) Feed Feed line Low-noise block downconverter Passive radiator Receiver Rotator Stub Transmitter Tuner Twin-lead Systems Antenna farm Amateur radio Cellular network Hotspot Municipal wireless network Radio Radio masts and towers Wi-Fi Wireless Safety and regulation Wireless device rad…

1970–1979 bicameral legislature of Rhodesia Parliament of RhodesiaTypeTypeBicameral HousesSenateHouse of AssemblyHistoryFounded1970Disbanded1979Preceded byLegislative AssemblySucceeded byParliament of ZimbabweElectionsLast House of Assembly electionAugust 1977Meeting placeParliament building, Salisbury Politics of Rhodesia Political history— Overview1890–1923 BSA Company rule1923–1980 Southern Rhodesia1953–1963 Rhodesia–Nyasaland Federation1965–1979…

Zamfara merupakan sebuah negara bagian di Nigeria. Letaknya di bagian baratlaut. Ibu kotanya ialah Gusau. Didirikan pada tahun 1996. Negara bagian ini memiliki luas wilayah 39.762 km². Dengan memiliki jumlah penduduk sebanyak 3.602.356 jiwa (2005). Pembagian administrasi Anka Bakura Birnin-Magaji/Kiyaw Bukkuyum Bungudu Gummi Gusau Kaura-Namoda Maradun Maru Shinkafi Talata-Mafara Tsafe Zurmi lbsNegara bagian di Nigeria Abia · Wilayah Ibu Kota Federal Abuja · Adamawa · Akwa…

För fastigheten i Göteborg, se Gibraltar (landeri). För andra betydelser, se Gibraltar (olika betydelser). Gibraltar Flagga Statsvapen Valspråk: Nulli Expugnabilis Hosti Conquerable by no enemy Nationalsång: Gibraltar Anthem Kunglig hymn: God Save the King läge HuvudstadGibraltar Största stad Westside (största distrikt) Officiellt språk Engelska (officiellt) Spanska (inofficiellt) Llanito (dagligt tal) Statsskick - Monark Charles III - Guvernö…

South African TV series or program Takalani SesameTakalani Sesame logoCreated byJoan Ganz CooneyJim HensonBased onSesame Streetby Joan Ganz Cooney Lloyd MorrisettDeveloped bySesame WorkshopSABC EducationSanlamCountry of originSouth AfricaProductionExecutive producerSeipati Bulane-HopaProducerPulane BoesakRunning time30 minutes per episodeProduction companiesSesame WorkshopSABC EducationSanlamOriginal releaseNetworkSABC 2Release7 August 2000 (2000-08-07) –presen…

Indian missionary Arhat Nāgasena by Guanxiu. King Milinda and Nāgasena. Nāgasena was a Sarvāstivādan Buddhist sage who lived around 150 BC. His answers to questions about Buddhism posed by Menander I (Pali: Milinda), the Indo-Greek king of northwestern India, are recorded in the Milindapañhā and the Sanskrit Nāgasenabhiksusūtra.[1] According to Pali accounts, he was born into a Hindu family in the Himalayas and was well-versed in the Vedas at an early age. However, he later conv…

Russian footballer (born 1989) In this name that follows Eastern Slavic naming customs, the patronymic is Yuryevich and the family name is Yerokhin. Aleksandr Yerokhin Yerokhin with Russia at the 2018 World CupPersonal informationFull name Aleksandr Yuryevich YerokhinDate of birth (1989-10-13) 13 October 1989 (age 34)Place of birth Barnaul, Russian SFSR, Soviet UnionHeight 1.95 m (6 ft 5 in)[1]Position(s) MidfielderTeam informationCurrent team Zenit St. Petersburg…

Земская почтаУезды Алатырский Александрийский Ананьевский Ардатовский Арзамасский Аткарский Ахтырский Балашовский Бахмутский Бежецкий Белебеевский Белозерский Бердянский Бобровский Богородский Богучарский Борисоглебский Боровичский Бронницкий Бугульминский Бугу…

The neutrality of this article is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met. (September 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) 2012–2014 Romanian protests against shale gasPart of 2012–2015 unrest in RomaniaBârladVasluiPungeștiBucharestVama VecheSânmartinCluj-NapocaTimișoaraSibiuCurticiIașiPiatra NeamțAlba IuliaAradOradeaBrașovCodleaBuzăuCălărașiMangaliaCostineștiConstanțaGalațiTâ…

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Yoo Yong-sung. Dalam nama Korean ini, nama keluarganya adalah Yoo. Yoo Yeon-seongYoo Yeon-seong, 2013Informasi pribadiKebangsaanSouth KoreaLahir19 Agustus 1986 (umur 37)Jeongeup, Jeonbuk, Korea SelatanTinggi180 m (590 ft 7 in)Berat68 kg (150 pon)PeganganRightGanda putra dan ganda campuranPeringkat tertinggi1 (MD dengan Lee Yong-dae 14 Agustus 2014)[1]11 (XD) Rekam medali Putra bulu tangkis Mewakili Korea Selatan World Champio…
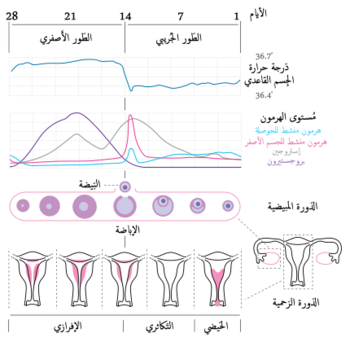
الدورة الشهرية الطور الجُريبي Follicular Phase المرحلة الجرابية (أوالطور التكاثري) في البشر والقردة العليا وهو طور من اطوار الدورة الشهرية خلاله تنضج بصيلات المبيض ويبدأ هذا الطور بالحيض (أول يوم في الدورة الشهرية) وينتهي بإفراز هرمون الإباضة. وينتهي مع هذا الطور ببداية التبويض (با…

Chapaev Film biografi, atau biopic (/ˈbaɪoʊpɪk/; singkatan dari biographical motion picture), adalah sebuah film yang mendramatisasikan kehidupan orang atau tokoh dalam kehidupan nyata. Film-film semacam itu menampilkan kehidupan dari seorang tokoh sejarah dan menggunakan nama asli dari karakter utama.[1] Dalam sejumlah kasus, yang terkadang disebut auto biopics, subyek dari film tersebut memerankan dirinya sendiri: Jackie Robinson dalam The Jackie Robinson Story; Muhammad Ali dalam …

Sub-tradition of Digambara Jainism For other uses, see Terapanth. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Digambara Terapanth – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Part of a series onJainism Jains History Timeline Index Philosophy Anekanta…
